![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
American Stock Exchange (AMEX) |
Third largest stock exchange, located in New York City. Handles 10% of priorities traded in the US. |
|
|
Securities Exchange Commission (S.E.C.) |
U.S. Government agency that oversees transactions of financial professionals to prevent fraud and deception. |
|
|
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE "Big Board") |
Oldest stock exchange in the United States (located on Wall Street). |
|
|
Dow-Jones Industrial Average |
Price-weighted average of 30 significant stocks on the NYSE and NASDAQ. |
|
|
Bull Market |
Financial market that is rising or expected to rise. |
|
|
Bear Market |
Market in which prices are falling. (Selling) |
|
|
Conglomerate |
Corporation made up of different businesses. |
|
|
Public Corporation |
Company whose shares are traded freely on a stock exchange. |
|
|
Portfolio |
A range of investments held by a person or organization. |
|
|
Society's Economic Goals |
employment, stability, economic growth, efficiency, equity |
|
|
4 Factors of Production |
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship |
|
|
Fundamental Economic "Problem" |
Economy's limited resources are not enough to satisfy all human wants and needs |
|
|
Basic Economic Questions |
What to produce?; How to produce?; For whom to produce? |
|
|
Invisible Hand |
Unobservable market force that helps the demand and supply of goods in a free market to reach equilibrium. |
|
|
Adam Smith |
Considered the "father of economics," came up with the ideas of the "invisible hand" and "capitalism" |
|
|
Karl Marx |
"Label theory of value." = Value of a good or service is dependent on the labor required in production |
|
|
Traditional Economy |
Original economic system in which traditions, customs, and beliefs shape the goods and services produced |
|
|
Market Economy |
Production and distribution determined by supply and demand |
|
|
Command Economy (socialism) |
Production and distribution determined centrally by a government |
|
|
Mixed Economy |
System combining private and public enterprise
|
|
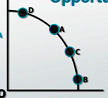
What type of graph is this? |
Guns and butter graph (demonstrates the idea of opportunity cost) |
|
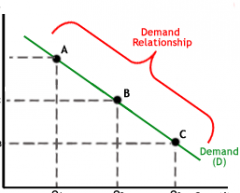
What type of graph is this? |
Demand curve graph (demonstrates "lower the quantity, lower the price and vice versa") |
|
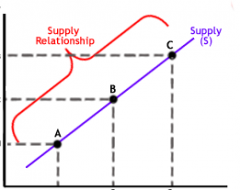
What type of graph is this? |
Supply curve graph (demonstrates "higher production, higher price") |
|
|
Entrepreneur |
Person who operates a business, taking great financial risks |
|
|
Capital |
Wealth in the form of money or other assets owned by a person or organization for a purpose |
|
|
Land |
Naturally occurring resources with fixed supply |
|
|
Labor |
Human exertion in production of wealth and services |
|
|
Opportunity Cost |
Loss of potential gain from other options when a decision is made. |
|
|
Scarcity |
Short supply; shortage. |
|
|
Incentive |
A benefit or reward that motivates an economic action |
|
|
Competition |
Rivalry among sellers to achieve economic goals |
|
|
Capitalism |
Economic system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners, rather than by the state (Adam Smith) |
|
|
Communism |
All means of production are owned by the government (Karl Marx) |
|
|
Economic Equity |
Concept of fairness in economics (taxation and welfare) |
|
|
Economic Efficiency |
Economic state in which every resource is allocated to serve each individual in the best way, minimizing inefficiency |
|
|
Economic Freedom |
Ability of members in a society to take economic actions |
|
|
Economic Growth |
Increase in the amount of good and services produced per head of the population |

