![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the national debt? |
The sum of all the annual deficits accumulated since 1776 |
Sum... |
|
|
How much is the national debt? |
Over 17 trillion dollars |
|
|
|
What is budget surplus? |
When the government takes in more money then it can spend. |
|
|
|
What is budget deficit? |
Any single year the government spends more then it borrows. (i.e., revenue) from taxes, fees, and tariffs |
|
|
|
What is trade deficit? |
When the county value of goods and services imported is greater than the value of goods and services exported. |
|
|
|
What causes the national debt? |
Paying for wars, increased government spending during recessions, tax decreases not accompanied by decrease government spending |
|
|
|
What is inflation? |
The steady rising of prices |
|
|
|
Causes of inflation |
Demand pull, cost-push, and wage price spiral. Demand pull (too much consumer buying to meet supply, resulting in shortages), Cost-push (cost of resources goes up), Wage-price spiral (workers wants more wages and this drives up wages and it just keeps going up and up) |
|
|
|
Who are the winners of inflation? |
The borrowers. (also debtors and gov). The money they borrow now will be paid back with money worth less than when it was borrowed. |
|
|
|
Who are the losers of inflation? |
The savers (also the fixed-income receivers, savers, and creditors). The money out in the bank will not be worth less later when they with drawal it. |
|
|
|
What are kinds of unemployment? |
Frictional, structural, and seasonal
Frictional is when people are between jobs Structural is when jobs are no longer needed. Seasonal is when jobs may be available only at certain times |
|
|
|
What would be an acceptable unemployment rate? |
5% |
|
|
|
The goal of the Fed with regards to production |
They can influence what we think. Wants there to be money out there and productive capability |
|
|
|
The criteria that taxers must meet |
Equal, simple, and efficient |
|
|
|
Basic principles of taxation |
Benefit Principle- The more you benefit from something, the more you should pay. Taxes on gasoline. Ability to Pay- The more you make the more you should pay. |
|
|
|
Proportional Tax |
Regardless of income, the same tax rate is imposed upon everyone. Another term for a proportional tax is a flat tax. STRAIGHT LINE!!!!! |
|
|
|
Progressive Tax |
People with higher incomes pay a higher % in taxes. Federal and State income tax are progressive taxes. LINE GOING UP!!!!!! |
|
|
|
Regression Taxes |
The lower the income the higher the %age paid in taxes. Example- Sales tax. LINE GOING DOWN!!!!!!! |
|
|
|
Tax Freedom Day |
The day you will have earned enough money to pay for all of your federal, state, and local taxes. Ussally takes 4 months. |
|
|
|
What is fiscal policy? |
Changes in federal government spending or tax revenues designed to promote full employment, price stability, and reasonable rates of economic growth. |
|
|
|
What is Expansionary Fiscal Policy? |
And increase in government spending and/or a decrease in taxes designed to increase aggregate demand. The goal is to increase the GDP and decrease unemployment. |
|
|
|
What is Contractionary Fiscal Policy? |
A decrease in government spending and/or an increase in taxes designed aggregate demand in the economy. The intent is to control inflation. |
|
|
|
What are Multiplier effects? |
The idea that spending by consumers, businesses, or government becomes income for someone else, leading to increase production in the economy. |
|
|
|
Supply side economics |
-Stability and growth achieved increasing the supply of goods and services. Aggregate (total) supply -When Aggregate (total) supply increases -Mor workers hired -Lower unemployment rate -Workers spend more money |
|
|
|
Demand side economics |
-Have the government focus on increasing aggregate demand -Believed that the market forces alone could not increase aggregate demand during bad times -Active government involvement needed!!!!! |
|
|
|
John Maynard Keynes |
the "father" of demand side economics |
|
|
|
Tools of Fiscal Policy |
-Tax rates=increase or decrease -Tax incentives=tax break for businesses, increase or decrease -Government spending and borrowing, increase or decrease -Public transfer payments= increase safety nets |
|
|
|
Fiscal policy during recessions |
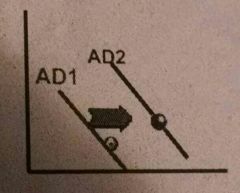
Expansion Fiscal Policy= G⬆(up) and T⬇(down) |
|
|
|
Fiscal Policy During Inflationis |
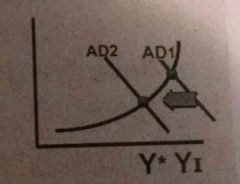
Contractionary Fiscal Policy= G⬇(down) and T⬆(up) |
|
|
|
Problems with fiscal policy |
-Wealthy benefit from tax cuts -Government spending cuts hurts the people who depend on social programs and services -Unpredictable behavior |
|
|
|
What is monetary policy? |
It is one of the ways that the U.S. government attempts to control the economy. If the money supply grows too fast, the rate of inflation will increase; if the growth of the money supply is slowed too much, then economic growth may also slow |
|

