![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
During recessions a. workers are laid off. b. factories are idle. c. firms may find they are unable to sell all they produce. d. All of the above are correct. |
D |
|
|
Business cycles a. are easily predicted by competent economists.b. have never occurred very close together. c. can only be seen as changes in real GDP. d. None of the above is correct. |
D |
|
|
3. Suppose a stock market crash makes people feel poorer. This decrease in wealth would induce people to a. decrease consumption, which shifts aggregate supply left. b. decrease consumption, which shifts aggregate demand left. c. increase consumption, which shifts aggregate supply right. d. increase consumption, which shifts aggregate demand right. |
B |
|
|
When taxes decrease, consumption a. increases, so aggregate demand shifts right. b. increases, so aggregate supply shifts right. c. decreases, so aggregate demand shifts left. d. decreases, so aggregate supply shifts left. |
A |
|
|
Which of the following does not determine the long-run level of real GDP? a. the price level b. the supply of labor c. available natural resources d. available technology |
A |
|
|
The misperceptions theory of the short-run aggregate supply curve says that if the price level increases more than people expect, firms believe that the relative price of what they produce has a. decreased, so they increase production. b. decreased, so they decrease production. c. increased, so they increase production. d. increased, so they decrease production. |
C |
|
|
The sticky wage theory of the short-run aggregate supply curve says that when the price level rises more than expected, the real wage a. rises, so employment rises. b. rises, so employment falls. c. falls, so employment rises. d. falls, so employment falls. |
C |
|
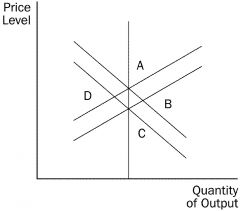
Which of the following would cause prices and real GDP to rise in the short run? a. Short-run aggregate supply shifts right. b. Short-run aggregate supply shifts left. c. Aggregate demand shifts right. d. Aggregate demand shifts left. |
C |
|
|
Refer to the figure. An increase in the money supply would move the economy from C to a. B in the short run and the long run. b. D in the short run and the long run. c. B in the short run and A in the long run. d. D in the short run and C in the long run. |
C |
|
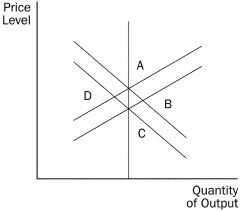
Refer to the figure. If the economy is at A and there is a fall in aggregate demand, in the short run the economy a. stays at A. b. moves to B. c. moves to C. d. moves to D. |
D |
|
|
Suppose a shift in aggregate demand creates an economic contraction. If policymakers can respond with sufficient speed and precision, they can offset the initial shift by shifting a. aggregate supply right. b. aggregate supply left. c. aggregate demand right. d. aggregate demand left. |
C |
|
|
Which of the following has been suggested as a cause of the Great Depression? a. a decline in the money supply b. a decrease in stock prices c. the collapse of the banking system d. All of the above are correct. |
D |

