![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A demand curve is elastic when |
an increase in price reduces the quantity demanded a lot |
|
|
When the same increase in price reduces quantity demanded just a little, thenthe demand curve is |
Inelastic |
|
|
Price elasticity of demand |
the ratio of the percent change in the quantity demanded to the percent change in the price as we move along the demand curve (dropping the minus sign) |
|
|
% change in quantity demanded = |

|
|
|
% change in price = |
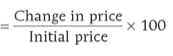
|
|
|
Price elasticity of demand = |
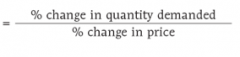
|
|
|
Midpoint method |
technique for calculating the percent change. In this approach, we calculate changes in avariable compared with the average, or midpoint, of the starting and finalvalues |
|
|
Midpoint method formula |
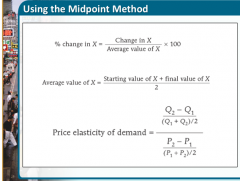
|
|
|
Perfectly inelastic |
when the quantity demanded does not respond at all to changes in the price.When demand is perfectly inelastic, the demand curve is a vertical line |
|
|
Perfectly elastic |
when any price increase will cause the quantity demanded to drop to zero. When demand is perfectly elastic, the demand curve is a horizontal line |
|
|
Demand is elastic if |
the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1 |
|
|
Demand is inelastic if |
the price elasticity of demand is less than 1 |
|
|
Demand is unit-elastic if |
the price elasticity of demand is exactly 1 |
|
|
Total revenue = |
Price x Quantity Sold |
|
|
A price effect: |
after a price increase, each unit sold sells at a higher price, which tends to raiserevenue |
|
|
A quantity effect: |
after a price increase, fewer units are sold, which tends to lower revenue |
|
|
What factors determine the price elasticity of demand? |
- the availability of close substitutes - whether the good is a necessity or luxury - share of income - time elapsed since the price change |
|
|
Cross-price elasticity of demand |
between two goods measures the effect of the change in one good’s price on the quantity demanded of the other good |
|
|
TheCross-Price Elasticity of Demand between Goods A and B = |
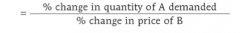
|
|
|
Goods are substitutes when |
the cross-price elasticity of demand is positive |
|
|
Goods are complements when |
the cross-price elasticity of demand is negative |
|
|
The income elasticity of demand |
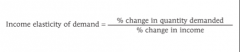
the percent change in the quantity of a good demanded when a consumer’s income changes divided by the percent change in the consumer’s income |
|
|
When the income elasticity of demand is positive, the good is a |
normal good (the quantity demanded at any given price increases as income increases) |
|
|
When the income elasticity of demand is negative, the good is an |
inferior good (the quantity demanded at any given price decreases as income increases) |
|
|
The price elasticity of supply |
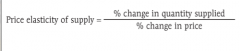
a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity of a good supplied to the priceof that good |

