![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is IR in relation to saving and borrowing? |
Interest rate is both the return to saving and the cost of borrowing |
|
|
S=I+NCO |
Each dollar saved=a dollar that can be used to finance purchase of a domestic capital or the purchase of an asset abroad |
|
|
Where does the supply of Loanable funds come from |
savings |
|
|
where does the demand of loanable funds come from |
investments + net capital outflow |
|
|
What is the impact of interest rates on SI? |
high interest rate encourages savings and discourages investments lower interest rate encourages investment and discourages investments |
|
|
What happens to NX when foreigners are buying more goods and services than Americans? |
NX>0 (surplus) |
|
|
What happens to NX when foreigners are spending more on foreign goods than they are earning from selling abroad? |
NX<0 (deficit) |
|
|
What happens to Exports and imports when US Real interest rate increases? |
US goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, imports increase and exports decrease, therefore net exports decreases as well. |
|
|
Graph for Foreign currency market |
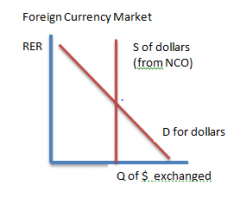
|
|
|
What does a higher exchange value of a dollar do to the price of foreign goods and assets? |
a higher exchange value of a dollar makes the price of foreign goods and assets less expensive |
|
|
What is the variable that links the market for loanable funds and the the market for foreign currency exchange? |
Net capital outflow |
|
|
Market for loanable funds graph |
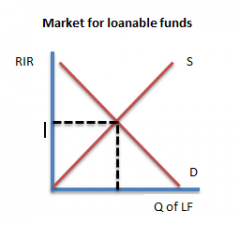
|
|
|
What determines real interest rate? |
Supply and demand in the market for loanable funds |
|
|
What determines net capital outflow? |
real interest rate |
|
|
what determines the supply of money for foreign currency? |
net capital outflow |
|
|
Net capital outflow graph |
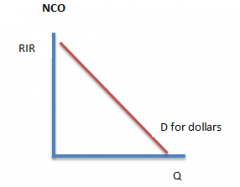
|
|
|
Simultaneous Markets graphs |
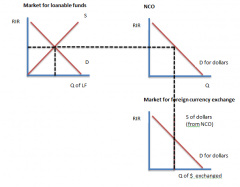
|
|
|
trade policy |
a government policy that directly influences the quantity of goods and services a country imports/exports |
|
|
tarrif |
a tax on imported goods |
|
|
import quota |
limit on the quantity of goods produced abroad that can be sold domestically |
|
|
What is the impact of an import quota on MLF, NCO, NX, MFE, trade balance, and SI? |
MLF: nothing NCO: nothing NX: increases D for $ in MFE: increase trade balance: nothing SI: nothing |
|
|
capital flight |
a large and sudden reduction in the demand for assets located in a country |
|
|
open capital flows |
no restrictions on where your citizens can invest/citizens from other countries investing in you |
|
|
independent monetary policy |
country's central bank can control its currency in such a way as to benefit their country |
|
|
exchange rate stability |
no fluctuations in exchange rate |
|
|
the great trilemma |
a country can only have 2 of the following: 1. open capital flows 2. independent monetary policy 3. exchange rate stability |

