![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Financial system |
a group of institutions that help to match one person's savings with another person's investments |
|
|
financial markets |
financial institutions through which savers can directly provide funds to borrowers |
|
|
Bond |
a certificate of indebtedness that specifies the obligations of the borrower to the holder of the bond |
|
|
why do businesses/the government provide bonds to the public |
bonds are businesses and the government's ways of borrowing directly from the public |
|
|
what is the relationship between bonds and interest rates |
value of bond moves in the opposite direction of interest rates |
|
|
date of maturity |
the time at which the loan will be repaid |
|
|
principal |
promise of interest and eventual repayment of the amount borrowed |
|
|
which bond is riskier, long term or short term? |
long term bonds are riskier than short term bonds, so they have higher interest rates |
|
|
debt finance |
sale of a bond |
|
|
stock |
a claim to partial ownership in a firm |
|
|
equity finance |
sale of a stock |
|
|
when do stockholders experience the most benefit from their investment |
when the business they invested in is successful |
|
|
what are stock prices a clean example of |
supply and demand |
|
|
financial intermediaries |
financial institutions through which savers can indirectly provide funds to borrowers |
|
|
characteristics of a saver |
high interest safety liquidity |
|
|
Characteristics of a borrower |
little interest time risk |
|
|
what is the primary job of a bank |
to take deposits from people who want to save and lend them out to people who want to borrow |
|
|
What are 3 cool things that banks do for borrowers and savers |
facilitate purchases of goods and services create a medium of exchange store of value |
|
|
mutual funds |
an institution that sells shares to the public and uses the proceeds to buy a portfolio of stocks and bonds |
|
|
GDP equation |
Y=C+I+G+NX |
|
|
Investment equation |
I=Y-C-G |
|
|
S=I |
savings = investment |
|
|
T= |
taxes |
|
|
Savings (in total) equals |
S=(Y-T-C) + (T-G)
Private saving minus public saving |
|
|
Private saving |
the income that households have leftover after paying for taxes and consumption |
|
|
public saving |
tax revenue that the government has leftover after paying for its spending |
|
|
budget surplus |
if T (taxes) exceeds G (government spending) there is a budget surplus |
|
|
budget defecit |
shortfall of tax revenue from government spending. G exceeds T. |
|
|
investment |
purchase of new capital (equipment, buildings) |
|
|
Market for loanable funds |
the market in which those who want to save supply funds and those who want to borrow demand funds |
|
|
Where does supply come from in the MLF |
people with extra income |
|
|
where does demand come from in MLF |
people who want to borrow |
|
|
Example of MLF graph |
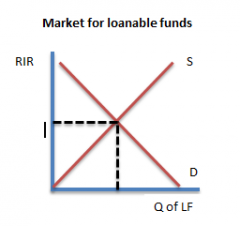
|
|
|
The IR is the |
price of the loan |
|
|
higher interest rates encourage |
savings |
|
|
Higher interest rate discourages |
borrowing |
|
|
nominal interest rate |
the interest rate as usually reported, monetary return of saving to borrowing |
|
|
Real interest rate |
nominal interest rate corrected for inflation
Real interest rate=Nominal IR - inflation |
|
|
what are some incentives to save? |
finance future production finance future consumption
|
|
|
crowding out |
fall in investment that results from government borrowing |

