![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
statutory incidence |
indicates who is legally responsible for a tax |
|
|
economic incidence |
change in distribution of real income caused by a tax; the actual burden of a tax |
|
|
tax shifting |
difference between statutory and economic incidence |
|
|
functional distribution of income |
how income is distributed among people who are classified according to inputs they supply to the production process |
|
|
size distribution of income |
the way total income is distributed across income classes |
|
|
lump sum tax |
tax whose value is independent of the individual's behavior |
|
|
proportional |
tax system under which average tax rate is same at each level of income |
|
|
average tax rate |
ratio of taxes paid to income (where income is taxable income or AGI?) |
|
|
progressive |
tax system under which an individual's average tax rate increases with income |
|
|
regressive |
tax system under which an individual's average tax rate decreases with income |
|
|
marginal tax rate |
proportion of the last dollar of income taxed by the government |
|
|
partial equilibrium models |
models that only study one market and ignore possible spillover effects in other markets |
|
|
unit tax |
tax levied as a fixed amount per unit of commodity purchased |
|
|
tax wedge |
tax-induced difference between price paid by consumers and price received by producers |
|
|
tax salience |
extent to which a tax rate is made prominent to a taxpayer |
|
|
ad valorem tax |
tax computed as a percentage of purchase value e.g. payroll tax on wages |
|
|
economic profit |
return to owners of a firm above opportunity costs of all factors used in production |
|
|
capitalization |
process by which a stream of tax liabilities becomes incorporated into the price of an asset |
|
|
general equilibrium analysis |
study of how various markets are interrelated |
|
|
partial factor tax |
tax levied on an input in only some of its uses |
|
|
elasticity of substitution |
ease with which one factor of production can be substituted for another |
|
|
capital intensive |
industry in which ratio of capital to labor is relatively high |
|
|
tax-interaction effect |
increase in excess burden in labor markets due to reduced wages from Pigouvian taxes |
|
|
excess burden |
loss of welfare above and beyond taxes collected; deadweight loss |
|
|
equivalent variation |
change in income that has same effect on utility as a change in the price of a commodity |
|
|
lump sum tax |
tax whose value is independent of an individual's behavior |
|
|
income effect |
effect of price change on quantity demanded due exclusively to the fact that the consumer's income has changed |
|
|
substitution effect |
tendency of an individual to consume more of one good and less of another because of a decrease in the price of one good relative to the other |
|
|
compensated demand curve |
demand curve that shows how quantity demanded varies with price, holding utility constant |
|
|
theory of the second best |
in the presence of existing distortions, policies that in isolation would decrease efficiency can increase it and vice versa |
|
|
double-dividend effect |
using proceeds from a Pigouvian tax to reduce inefficient tax rates |
|
|
AGI |
adjusted gross income total income from all taxable sources less certain expenses incurred in earning that income |
|
|
taxable income |
amount of income subject to tax |
|
|
exemption |
when calculating taxable income, the amount per family member that can be subtracted from AGI |
|
|
deductions |
certain expenses that may be subtracted from AGI in the computation of taxable income |
|
|
rate schedule |
shows the tax liability associated with each level of taxable income |
|
|
Haig-Simons definition of income |
money value of a net increase in an individual's power/potential to consume during a period saving must included |
|
|
capital gain |
increase in the value of an asset |
|
|
realized capital gain |
capital gain resulting from the sale of an asset |
|
|
unrealized capital gain |
capital gain on an asset not yet sold |
|
|
lock-in effect |
disincentive to change portfolios because an individual incurs a tax on realized capital gains but not unrealized gains |
|
|
IRA |
individual retirement account $5500 per year limit savings account in which the contributions are tax deductible and savings accrue tax free until withdrawal at retirement, at which point both contributions and accrued interest are subject to tax |
|
|
Roth IRA |
$5500 per year limit contributions are not tax deductible, but interest accrues tax free tax-preferred savings vehicle |
|
|
401(k) plan |
savings plan under which an employee can earmark a portion ($17,000 in 2012) of income each year, with no income tax liability incurred on that portion |
|
|
Keogh Plan |
savings plan that allows self-employed individuals to exclude a 20% of their net business income (up to $50,000) from taxation if money is deposited into a qualified account |
|
|
Education Savings Account |
tax-preferred savings vehicle contributions aren't tax deductible but they accumulate tax fee; funds can only be used for higher education expenses of a child |
|
|
itemized deduction |
specific type of expenditure that can be subtracted from AGI in computation of taxable income |
|
|
standard deduction |
fixed amount subtracted from AGI that doesn't require documentation |
|
|
tax credit |
subtraction from TAX LIABILITY (not taxable income) favors those with lower marginal tax rates (compared to deductions/exemptions, which affect taxable income) |
|
|
tax expenditure |
loss of tax revenue due to an item being excluded for tax base or receiving other preferential treatment |
|
|
tax indexing |
automatically adjusting tax schedule to compensate for inflation so that an individual's real tax burden is independent of inflation |
|
|
bracket creep |
increase in individual's nominal income pushes the individual into a higher tax bracket despite unchanged real income |
|
|
real income |
measure of income that accounts for changes in general price level |
|
|
nominal income |
income measured in terms of current prices |
|
|
nominal interest rate |
interest rate observed in the market |
|
|
AMT |
alternative minimum tax tax liability calculated by an alternative set of rules designed to force individuals with substantial preference income to incur at least some tax liability tends to be poor policy b/c it taxes away preferences of greatest importance to middle-income taxpayers also, why not just take away certain deductions/preferences instead minimum rate under AMT is 26%, which is really high pay the difference between tentative AMT and income tax usually kicks in at 150k-400k income |
|
|
marriage neutral |
individuals' tax liabilities are independent of marital status |
|
|
income splitting |
using half of family income to determine each family member's taxable income, regardless of whose income it is |
|
|
global system |
system under which an individual is taxed on income, whether it is earned in the home country or abroad |
|
|
territorial system |
system under which an individual earning income in a foreign country owes taxes only to host government |
|
|
tax inversion |
overseas relocation of a company's legal domicile to a lower tax-nation to escape taxes |
|
|
How does Apple avoid taxes? |
Foreign revenues (60% of Apple's revenue) flow through subsidiaries in Ireland, where Apple's companies claim non-residency b/c they are managed elsewhere; thus, Apple's foreign revenues are exempt from corporate tax. These revenues are ultimately re-routed to the Cayman islands, which are essentially a tax haven. US revenues are used to fund the use of patents, so net income is zero in US. |
|
|
Check-the-box rule |
Allows taxpayers to decide to treat a foreign corporation as if it doesn't exist for US law |
|
|
repatriation |
process of returning money back to US |
|
|
problems with corporate tax |
-high corporate tax rates -tax inversion -loss of tax revenue -revenue tied up in other countries -disincentives to invest in US -inability to reinvest profits without paying additional high marginal tax rate -replacing global system is a better fix than lowering corporate tax rates b/c there will always be countries w/ really lower corporate tax rates -little correlation between statutory rate and inversions |
|
|
earnings stripping |
method of avoiding taxes by paying excessive amount of interest to parent company |
|
|
transfer pricing |
shifting profits out of US to lower-tax countries via cross-border, non-market-based payments |
|
|
Why don't we abolish the corporate income tax? |
-would result in tax haven for the wealthy -represents a significant portion of federal gov't revenue |
|
|
balanced-budget incidence |
incidence of a tax that accounts for how revenue earned from tax is spent |
|
|
formula for tax incidence? |
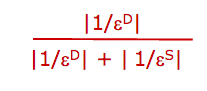
|
|
|
formula for excess burden? |
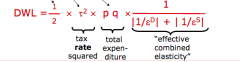
|
|
|
absolute tax incidence |
examines the effects of a tax when there is no change in either other taxes or government expenditures |
|
|
differential tax incidence |
examines how incidence differs when one tax is replaced with another, holding the government budget/revenue constant |

