![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Price elasticity of demand |
Measures how much the quantity demanded of a good changes when its price changes Measures a goods sensitivity to price changes |
|
|
Higher demand price elasticity |
Luxury goods Available substitute goods Longer time period |
|
|
Calculating Demand Elasticity |

|
|
|
Rules in calculating price elasticity |
1. All elasticities are positive 2. Percent changes NOT absolute changes *changes in unity does not affect elasticity 3. Use of averaging for base price |
|
|
Formula for demand elasticity |

|
|
|
Elastic demand |
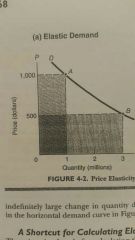
E>1 |
|
|
Unit elastic demand |
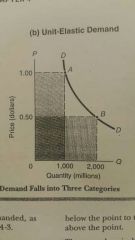
E = 1 |
|
|
Inelastic demand |
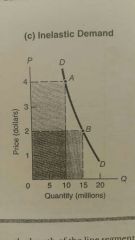
E < 1 |
|
|
Perfectly elastic demand |

E = infinite |
|
|
Perfectly inelastic demand |
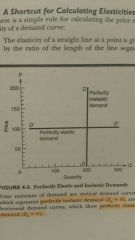
E = 0 |
|
|
Elasticity at a point on a line |
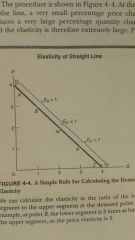
Ratio of the length of the straight line segment below the point to the line segment aove
* for curved lines, get tangent |
|
|
Total Revenue |
Price X Quantity |
|
|
Price inelastic demand (revenue) |
Price decrease reduces revenue |
|
|
Price elastic demand (revenue) |
Price decrease increases total revenue |
|
|
Unit elastic demand (revenue) |
Price decrease leads to mo change in revenue |
|
|
Supply Elasticity |

Responsiveness of qty supplied of a good to its market price |
|
|
Supply elasticity tends to be high |
1. Availability of inputs 2. Longer time frames |
|
|
Tax incidence |
Impact of a tax on the incomes of producers and consumers |
|
|
Burden of taxes |
Cosumers if demand is inelastic relative to supply Producers if supply is inelastic relative to demand |
|
|
Subsidy |
Negative tax Causes a shift down in the supply curve |

