![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Market failure |
Supply and demand do not result in the efficient allocation of resources |
|
|
|
6 reasons for market failure |
1) Immobility of labour 2) public goods 3) externalities 4) price instability in commodity markets 5) asymmetric information 6) government failure |
|
|
|
Social Marginal Cost |
addition to total cost of producing an extra unit of output |
|
|
|
Social Marginal Benefit |
addition to total benefits of consuming an extra unit |
|
|
|
Why is it necessary for social marginal benefits and social marginal costs to be equal? |
For resources to be allocated efficiently |
|
|
|
2 types of immobility of labour? |
1) geographical immobility of labour 2) occupational immobility of labour |
|
|
|
What is the difference between Geographical immobility of labour and Occupational immobility of labour? |
GIM limits the movement of workers from one country to another whereas OIL limits from occupations |
|
|
|
3 causes of the OIL |
1) lack of relevant skills and qualifications 2) no relevant experience 3) wage rate - worker might move if low WR |
|
|
|
Measures to increase OIL |
1) training programmes 2) increase higher education provisions 3) information about opportunities in other occupations |
|
|
|
3 causes of the OIL |
1) lack of relevant and qualifications 2) no relevant experience 3) wage rate - worker might move if low WR |
|
|
|
Measures to increase OML |
1) training programmes 2) increase higher education provisions 3) information about opportunities in other occupations |
|
|
|
Public good |
Goods which have 2 key characteristics: 1 - non-rivalrous, 2 - non- excludable |
|
|
|
Non-rivalrous |
Amount doesn't fall after one persons consumption |
|
|
|
What is the free rider problem? |
Once a good is provided it is impossible to prevent people from using it and therefore impossible to charge for it |
|
|
|
Why are free riders a problem? |
Not profitable for businesses |
|
|
|
Policy of government to correct free rider problem? |
Taxation |
|
|
|
Disadvantage of taxation to solve free riding |
Determined amount of resources allocated without reference to the electorate |
|
|
|
Why are externalities a form of market failure and what are the two types? |
Inefficient allocation of resources, positive and negative externalities |
|
|
|
External costs |
Costs in excess of private costs which affect 3rd parties who aren't part of the transaction |
|
|
|
3 difference types of external costs |
1) air pollution 2) noise pollution 3) pollution from deforestation |
Pollution |
|
|
The direct cost to producers and consumers for producing and consuming a product... |
Private costs |
|
|
|
The sum of private costs and external costs... (Private costs + external costs) |
Social costs |
|
|
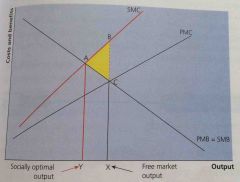
1)PMB indicates... |
1)private benefits to the consumer decrease as consumption increases
|
|
|
|
2 Disadvantages for indirect taxation? |
1)Ineffective in reducing pollution if demand is price inelastic 2) difficult to set tax because it's difficult to quantify the external cost |
|
|
|
Rights to sell and buy actual or potential pollution in artificially created markets |
Tradable permits |
|
|
|
2 Advantages of tradable permits? |
1) incentive for firms to reduce pollution 2) cost of administrating scheme is relatively low |
|
|
|
2 disadvantages of tradable permits? |
1) pollution will continue despite being lower 2) large firms might buy up the permits and continue to pollute |
|
|
|
Property rights |
Exclusive authority to determine how a resource used whether that resource is owned by the government, collective bodies or individuals |
|
|
|
3 advantages of property rights |
1) incentive to firms to take into account private and external costs 2) firms compensate 3) costs of administrating scheme relatively low
|
|
|
|
3 disadvantages of property rights? |
1) assigning property rights 2) breach of property rights, who should be compensated? 3) difficult agree on the monetary value of the external cost |
|
|
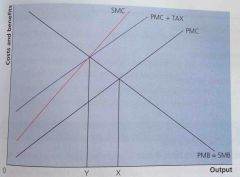
What will a leftward shift in the supply curve do? |
Cause consumption and output to fall to 0Y the socially optimal level |
|
|
|
what is the issue with legal restrictions? |
May require expense of enforcements e.g. inspectors |
|
|
|
1)PMB indicates... |
1)private benefits to the consumer decrease as consumption increases
|
|
|
|
External benefits |
Benefits in excess of private benefits which affects third parties who are not part of the transaction |
|
|
|
Example of external benefits? |
Commercially owned bees pollinating fruit trees of local farmers |
|
|
|
Direct benefits to producers and consumers in a transaction |
Private benefits |
|
|
|
Private benefit to a producer? |
Revenue |
|
|
|
Private Benefit to the consumer? |
Utility of product/service |
|
|
|
Social benefits |
Sum of private benefits and external benefits (Private benefits + external benefits) |
|
|
|
External benefits = |
Social benefits - private benefits |
|
|
|
When will PMB be the same as SMB? |
When it's assumed there's no marginal benefits |
|
|
|
PMC curve indicates private cost if borrowing the product rises as... |
Output rises |
|
|
|
Socially optimal level of output is determined from the equilibrium point at which... |
SMC=SMB (0Y) |
|
|
|
What does the triangle represent and why is it present? |
Welfare triangle, Over production and over consumption of XY |
|
|
|
Give an example of an external cost of consumption |
Smoking and health risks |
|
|
|
External costs and sustainability- environmental damage in the use of nonrenewable resources, however... |
There is an increase in renewable resources in production |
|
|
|
What are the three policies to correct market failure? |
1) indirect taxation 2) tradable permits 3extension of property rights |
|
|
|
What will a leftward shift in the supply curve do? |
Cause consumption and output to fall to 0Y the socially optimal level |
|
|
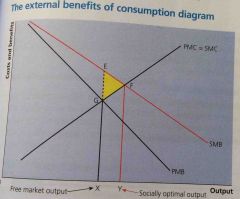
Front (Term) 1) PMB indicates... |
1) private benefits to consumer decrease as consumption increases |
|
|
|
When the social marginal benefit is greater than the social marginal cost... |
Welfare gain |
|
|
|
When a social optimum is produced there will be a... |
Welfare gain |
|
|
|
External benefits: 3 policies to correct market failure |
1) provision of the state (funded by taxes e.g. NHS) 2) subsidies (to reach optimal level) 3) encouraging changes in consumer behaviour (adverts) |
|
|
|
Example of a benefit of production |
Bees produce honey but also pollinate fruit trees of local farmers |
|
|
|
Main cause of commodity price instability? |
Price inelasticity of supply and demand |
|
|
|
Supply inelastic for soft commodities e.g. agriculture... |
because a long growing period is needed while for hard commodities e.g. diamonds time is required for developing new mines |
|
|
|
Demand price in elastic for commodities because… |
Price inelastic and required for production of other goods |
|
|
|
2 more examples of price volatility |
1) weather 2) speculators betting on future price changes |
|
|
|
What would any shift in the supply curve cause? |
Sharp change in price |
|
|
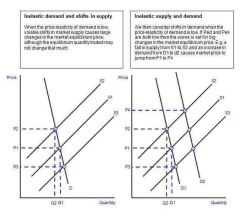
3 reasons demand may have increased? |
1.increasing world population 2.increase in real incomes 3.increasing demand for grain to be used for fuel
|
|
|
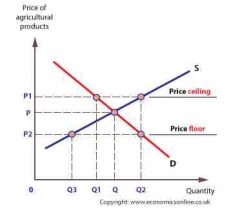
Buffer stock scheme |
Designed to reduce price fluctuations involving setting the ceiling and the floor price and buying and selling stocks to maintain price within these limits |
|
|
|
4 criticisms of buffer stock schemes |
1) floor price too high surpluses each year 2) ceiling price to low insufficient stocks available in years of shortage 3) costs to society, such as building costs 4) depends of all major producers agreeing to the scheme and not cheating e.g. selling to consumers at reduced price
|
|
|
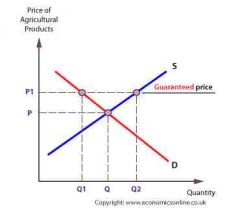
1) Minimum guaranteed prices 2) what does Q1 to Q2 show? |
1) Minimum price from particular commodity guaranteed to producers 2) surplus |
|
|
|
2 advantages of minimum guarantee prices |
1) produces know amount they will receive in advance 2) allows them to plan investment and output |
|
|
|
3 disadvantages of minimum guaranteed prices |
1) if minimum guaranteed price set to high surpluses each year 2) costs of storage and disposal burdened by taxpayers 3) encourages overproduction may therefore result in inefficient allocation of resources |
|
|
|
2 advantages of minimum guarantee prices |
1) produces know amount they will receive in advance 2) allows them to plan investment and output |
|
|
|
3 disadvantages of minimum guaranteed prices |
1) if minimum guaranteed price set to high surpluses each year 2) costs of storage and disposal burdened by taxpayers 3) encourages overproduction may therefore result in inefficient allocation of resources |
|
|
|
Situation in which one party in a transaction has more or superior information compared to another |
Asymmetrical information |
|
|
|
3 examples of asymmetrical information |
1) housing markets – estate agents may know more than potential buyer 2) life-insurance – consumers may withhold aspects of health profile 3) Financial services – bank may be unaware of likelihood of default by borrower |
|
|
|
3 methods of dealing with asymmetrical information |
1) State provision 2) public information /advertisements 3) private sector organisations, the media and the Internet: information which informs consumers |
|
|
|
Government intervention results in net welfare loss… |
Government failure |
|
|
|
Why agricultural stabilisation schemes might be an example of government failure |
Schemes could result in surpluses involving huge storage costs, surpluses imply resources may not be an allocated efficiently |
|
|
|
Why housing policies might be an example of government failure |
Although state provisions of housing desirable for those on low income, housing substitutes prevent market from working efficiently, little incentive for people so limits geographical mobility of labour |
|
|
|
And example of why an environmental policy might be an example of government failure |
Windfarms – expensive, environmental problem in itself (eyesore) |
|
|
|
Why the labour market might be an example of government failure |
Could result in unemployment if wages set above free-market wage, rate of unemployment depends on whether minimum wage is above equilibrium wage and on price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply of labour |
|

