![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Measures the sensitivity of a quantity demanded of a product to a change in its own price... |
Price elasticity of demand |
|
|
|
Equation for PED |
% change in QD/ % change in P |
|
|
|
When demand is price inelastic, where will the value of PED be between? |
0 and 1 |
|
|
|
When will the value of PED be greater than 1? |
When demand is price elastic |
|
|
|
PED=1 |
Unit elastic |
|
|
|
PED=0 |
Perfectly inelastic |
|
|
|
PED = infinity |
Perfectly elastic demand |
|
|
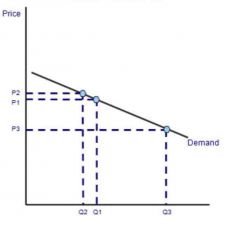
What is this an example of? |
Relatively price elastic |
|
|
|
Total revenue |
Value of goods sold by a firm, calculated by P X Q sold |
|
|
|
5 factors that influence PED |
1) availability of substitutes - if substitutes available, strong incentives to shift to these if price of product rises - substitutes= demand elastic 2) proportion of income spent on product - small % = demand inelastic, large % = demand elastic 3) nature of product - addictive (alcohol) demand inelastic 4) durability of product - long wearing = demand elastic, non durable = demand inelastic 5) length of time - takes time for consumers to adjust their expenditure patterns - demand more elastic in short run then long run |
|
|
|
Which one is correct? A) products are elastic B) demand for a product is elastic |
B |
|
|
|
4 points of significance for firms |
1) The effect of change in price on total revenue & expenditure on product. 2) price volatility in market following changes in supply – important for commodity producers who suffer price and revenue shifts from different time periods 3) change in an indirect tax on P&Q demanded, also whether the business is able to pass on some or all of the tax onto the consumer. 4)Information on PED can be used by a business as part of a policy of price discrimination- supplier decides to charge different prices for the same product to different segments of the market e.g. peak and off peak rail travel |
CPIP |
|
|
When will businesses usually charge a higher price to consumers? |
When demand is inelastic |
|
|
|
4 points of significance for firms |
1) The effect of change in price on total revenue & expenditure on product. 2) price volatility in market following changes in supply – important for commodity producers who suffer price and revenue shifts from different time periods 3) change in an indirect tax on P&Q demanded, also whether the business is able to pass on some or all of the tax onto the consumer. 4)Information on PED can be used by a business as part of a policy of price discrimination- supplier decides to charge different prices for the same product to different segments of the market e.g. peak and off peak rail travel |
|
|
|
What is 3 significance points for governments? |
1) can determinate rate of foreign exchange which is based on the elasticity of imports and exports, based on elasticity of imports and exports. 2) max tax revenue, increase tax on demand price inelastic products (cigarettes), consumers bear most of tax burden 3) May tax products and services whose demand is price elastic, producers bear higher proportion of tax burden |
|
|
|
Cross elasticity of demand |
Sensitivity in demand for one product to a change in price of another product |
|
|
|
Difference between PED and XED |
XED deals with more than one product |
|
|
|
Difference between PED and XED |
XED deals with more than one product |
|
|
|
Formula for measuring XED |
% change in QD of product Y / % change in P of product X |
|
|
|
1) + sign XED = 2) - sign XED = |
1) Products are substitutes 2) Products are compliments |
|
|
|
What will a rise in price of a substitute do? |
Increase in demand for the other |
|
|
|
What will a decrease in price for a complement do? |
Increase in demand for the other |
|
|
|
What are in joint demand? |
Complements |
|
|
|
XED is useful for... |
1) setting prices for products (product with close substitute, demand is therefore sensitive to price change) 2) complementary goods can command higher prices (printers cheap, cartridges expensive) |
|
|
|
Sensitivity of demand for a product to a change in real income |
Income elasticity of demand |
|
|
|
What is the formula for YED? |
% change in QD / % change in real income |
|
|
|
1) + sign for YED 2) - sign for YED |
1) normal good 2) inferior good |
|
|
|
Do normal goods or inferior goods have more expensive substitutes? |
Inferior goods |
|
|
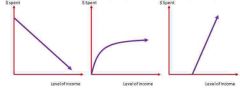
What does 1, 2 and 3 represent? |
1 - inferior good 2 - normal good 3 - superior good |
|
|
|
Price elasticity of supply |
Sensitivity of supply of a product to a change in its price |
|
|
|
PES > 1 |
supply is price elastic |
|
|
|
PES < 1 |
supply is price inelastic |
|
|
|
PES = 0 |
supply is perfectly inelastic |
|
|
|
PES = infinity |
Supply is perfectly elastic |
|
|
|
If supply is elastic, producers can... |
increase output without a rise in cost or a time delay |
|
|
|
If supply is inelastic, firms will... |
find it hard to change production in a given time period. |
|
|
|
Sensitivity of demand for a product to a change in real income... |
Income elasticity of demand |
|
|
|
If S increases and D is perfectly inelastic... |
then price falls and quantity doesn't change. |
|
|
|
If D increases and S is perfectly elastic, |
then price stays the same and quantity rises. |
|
|
|
If S increases and D is perfectly elastic... |
then price stays the same and quantity rises. |
|
|
|
3 influencing factors of PED |
1) Time - longer the time period the more elastic supply is (difficult to change in short period of time) 2) stocks - if stocks available, supply relatively elastic ( respond quickly) 3) spare capacity - (under utilised machinery) supply likely to be elastic |
|
|
|
Difference between how much consumers are willing to pay and how much they actually pay for a product... |
Consumers' surplus |
|
|
|
2 factors affecting size of consumer surplus |
1) gradient of demand curve (steeper, greater CS) 2) changes in conditions of demand |
|
|
|
Producer surplus |
Difference between cost of supply and price received by producer for product |
|
|
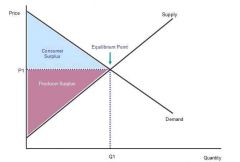
1) above the supply curve... 2) below the supply curve... |
1) consumer 2) producer |
|
|
|
2 factors affecting size of producer surplus |
1) gradient of supply curve (steeper, greater surplus) 2) condition of supply increase supply increases surplus |
|

