![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The snowshoe hares predator is what? |
Snowshoe crab |
|
|
Population cycles involve a lot of what? |
Species |
|
|
Without dispersal, what would happen to the prey as a result of the predator? |
They would go extinct |
|
|
How can prey survive? |
Long distance dispersal, prey survive |
|
|
What is the mite predator prey reaction mentioned in the slide? |
Western predatory and six spotted mice |
|
|
What does the coexistance of predator prey cycles in the lab depend on? |
Rate of predator feeding on prey |
|
|
A model of predator prey interactions that produces oscillations in predator and prey populations |
Lotka-Volterra model |
|
|
Prey equation for lotka volterra model |
Dn/dt=rN-cNP |
|
|
Explain Prey equation for lotka volterra model |
C= consumption rate of prey by predator N= prey size P=Predator size |
|
|
What is NxP in the lotka volterra ? |
Law of mass action |
|
|
Predator equation for lotka volterra model |
dP/dt=acNP-mP |
|
|
Explain Predator equation for lotka volterra model |
a= efficient of consumer prey converted into new predators m= mortality rate of predation |
|
|
When is prey population stable? |
When its rate of change is zero |
|
|
When is prey increasing? |
dN/dT > 0 and p<r/c |
|
|
When are predators increasing? |
dP/dT>0 N> m/ac |
|
|
Population sizes that cause one population to be stable |
Equilibrium (zero growth isocline) |
|
|
Suppose you wanted to kepp prey population from crashing too low during its cycle in order to prevent possible extinction. Which scenario below is most likely to accomplish this? |
Increase m (if you decrease m prey go lower) |
|
|
Lotka voltera model graph |
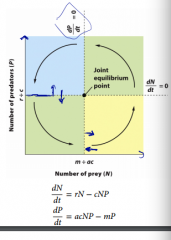
|
|
|
the relationship between the density of prey and an individuals predators rate of food consumption |
Functional response |
|
|
a change in the number of predators through population growth (due to consumption of prey) or through immigration or emigration |
Numerical response |
|
|
time spent moving around looking for prey |
Active hunting strategies |
|
|
lie in wait for prey to pass by |
Ambush (sit and wait) hunting strategies such as carnivores plants |
|
|
What are some of the way predators trap prey? |
Detection, pursuing, catching, handling, consumption |
|
|
camo that either allows an individual to match its environment or to blend in better with backgroud |
Crypsis |
|
|
Reduce a predators ability to capture, attack or handle prey |
Structural defenses |
|
|
Some organisms release what to deter predators? |
Chemicals |
|
|
Distastefulness to predators evolves in association with very conspicuous colors and patterns |
aposematism |
|
|
palatable species evolve warning coloration that resembles unpalatable species |
Batesian mimicry |
|
|
Several unpalatable species evolve a similar pattern of warning coloration |
Mullerian |
|
|
T or FL behavioral defense are rarely costly |
False, usually costly |
|
|
Why are behavioral defenses costly? |
result in reduced feeding activity or crowding in location away from predators |
|
|
What type of defense are often very energetically expensive to produce? |
Mechanical |
|
|
What can defense costs reduce? |
Growth, development and reproduction |
|
|
Two or more species evolve in response to traits in one another |
Coevolution |
|
|
Some plants have phenotypically plastic defenses induced by what? |
Attack |
|
|
Some plants have what? |
Fixed defenses |
|
|
What do structural defenses deter? |
Herbivores from consuming leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits |
|
|
What are some example of chemical defenses? |
Sticky resins and latex compounds that are hard to consume and alkaloids that have toxic effects |
|
|
What are some alkaloids? |
Caffeine, nicotine, morphine |

