![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Processes that Structure Communities (DINS) |
- Dirsturbance - Interactions - Niche requirements - Stochastic (unpredictable) processes |
|
|
|
Ecological Disturbance |
An event which kills organisms or removes biomass and opens up space in a community. - eg: fire |
|
|
|
Disturbance Types |
- Geomorphic: relating to landscape form (eg, volcanoes, earthquakes, floods) - Climatic: eg, wind, drought, snow/ice. - Animal: eg, burrowing, trampling and wallows. - Anthropogenic: eg, human-caused disturbances. eg, deforestation. |
|
|
|
Primary Succession |
- Primary: On a new un-inhabited substrate. Over time chemical and physical weathering by lichens and mosses builds up soil for larger plants. Eg, rangitoti island, sand dunes. |
|
|
|
Secondary Succession. |

The original vegetation is destroyed but soil is intact. Some life still remain, such as seeds. Eg, fire, cyclone, snowfall. |
|
|
|
Succession Adaptive Traits |
- Pioneer species: first arrivals, fast growing and hardy. - Late successional species: slow growing, delicate, shade tolerant, good competitor. |
|
|
|
Disturbance Adapted Communities |
- rely on regularly occurring disturbances (eg eucalypt forest fires) - require disturbance for regeneration or to complete their life cycle. |
|
|
|
Succession Community Structure |
- Species richness increases - Species comp changes as species shift from early to late succession. - Species change their environment (eg soil) |
|
|
|
Wave Regeneration |
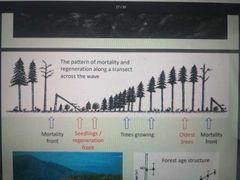
|
|
|
|
How Wave Regeneration Occurs (OPEN HINT) |
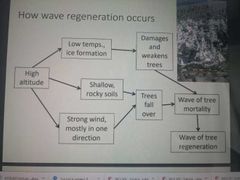
|

|

