![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
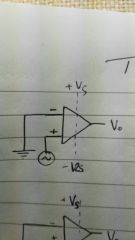
|
Simple op amplifier |
|
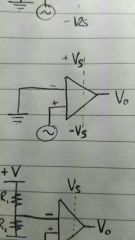
|
Comparator - Converts sinusoidal input to square wave because Av is large and op amp is operating in saturation. |
|
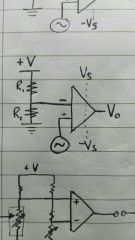
|
Non-zero level comparator - compares sinusoidal input voltage against the Vref (v across R2) |
|
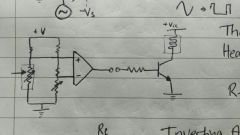
|
Input voltage varies due to external circumstance. Output puts the transistor into either saturation or cutoff when needed. |
|
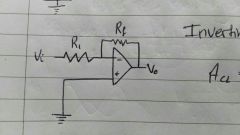
Also, gain=? |
Inverting Amplifier. Acl (closed loop gain) = vo/vi = -Rf/R1 |
|
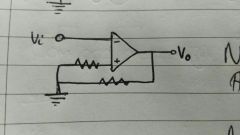
|
Non inverting Amplifier. Acl = vo/vi = 1+(Rf/R1) |
|
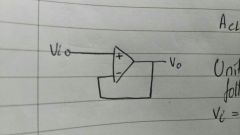
|
Unity or Voltage follower. vo=vi I=0. Used to transfer voltage between circuits while isolating their seperate currents. |
|
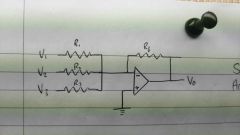
|
Summing Amplifier. vo = Σvi |
|
|
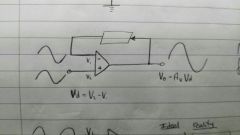
Negative feedback loop - theory for following circuits |
|
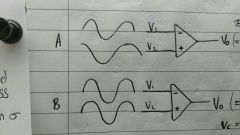
Note - two separate circuits. Comparison essential. |
A: vo is the difference between the two vi. So vo=Av Vd. In reality, due to noise, vo=Av Vd + Ac Vc B: v1=v2 so in theory, vo=0 In reality, due to noise, vo=Ac Vc Error correction: remove vob from voa to achieve corrected output. |
|
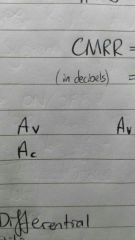
Define CMRR, Ac and Av |
CMRR, Common mode rejection ratio, =Av/Ac, more often represented in Decibels so =20log(Av/Ac) Av is 'Differential gain' or 'Internal gain' Ac is 'Common mode gain' The larger the CMRR the better the component: ( Ac(noise)<<Av(usefulgain) ) |
|
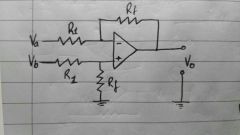
|
Differential amplifier. vo=(vb-va)Rf/R1 |
|
|
Golden op amp rules? (With external feedback) |
I. Vo aims to minimise Vd. Vd-->0 II. Ii = 0 no current flows between inputs |

