![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does a normal P Wave show? |
Arterial depolarization |
|
|
What does the QRS wave show you? |
Ventricular Depolarizarion |
|
|
What does the T Wave show? |
Ventricular Repolarization |
|
|
What does normal sinus rhythm look like? |
Regular spacing between R Waves means it’s a regular heart rate |
|
|
What is the Rule of 300? |
Divide 300 by the number of boxes between each QRS to get the heart rate |
|
|
What is normal sinus rhythm? |
60-100 bpm |
|
|
What is bradycardia and when do you see it? |
< 60 bpm Normal in athletes or those taking beta blockers |
|
|
What is Tachycardia and when do you see it? |
> 100 bpm Seen in peds patients, those who may be anxious, caffeine |
|
|
What do you see on an EKG with Zone of Ischemia |
Depression of ST segment with or without T wave inversion |
|
|
What do you see on EKG with Zone of Injury |
ST segment elevation Seen with acute MI |
|
|
What do you see on an EKG with Zone of Infarction |
Deep Q Waves ST elevation Significant MI |
|
|
What is a PVC and what does it look like? |
Extra heartbeats in the ventricles Can be unifocal or multifocal QRS complex spikes up (Higher R and S) More than 3 in a row = not normal (V Tach) Keep exercising and closely monitor if seen in clinic |
|
|
What is a PAC |
Premature Atrial Contraction |
|
|
What do you call more than 3 PVCs in a row? What are some other characteristics? |
V-Tach Rate of 100-200 bpm Can lead to V Fib/ decreased cardiac output |
|
|
What is ventricular Fibrillation and what should you do if you see it? |
Quivering of the heart; no longer pumping blood Medical emergency: call 911 |
|
|
What does atrial flutter look like? |
“Saw tooth pattern” I cell is irritated beating fast results in > BPM Multiple P waves |
|
|
Atrial Fibrillation |
Multiple cells are irritated (multiple ecetopic) Pattern is irregular, irregular More than 3 |
|
|
What is an AV Node Block? |
Damage or fibrotic changes to the AV node that leads to varying degrees of AV node block 1st, 2nd, or 3rd degree (complete block) |
|
|
What does a 1st degree AV block look like? |
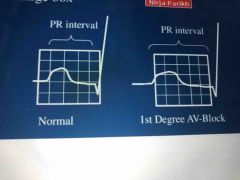
PR interval is > .2 seconds (1 large block) |
|
|
What does a 2nd degree AV block look like? |

2-3 P waves to every QRS complex |
|
|
What are the 2 types of 2nd Degree AV block? |
Wenckebach and Mobitz II |
|
|
Describe the Wenckebach 2nd Degree Heart Block EKG |
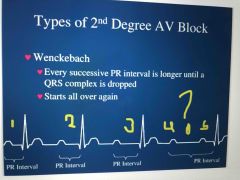
Every successive PR interval is longer and longer until a QRS interval is dropped |
|
|
Describe the Wenckebach 2nd Degree Heart Block EKG |
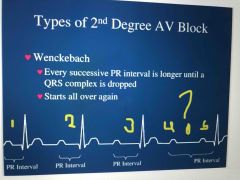
Every successive PR interval is longer and longer until a QRS interval is dropped Then pattern starts over again |
|
|
N |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Describe the Mobitz II 2nd degree AV Block |

PR interval stay the same but QRS interval will be dropped Then pattern starts again |
|
|
Describe the EKG of a 3rd degree AV block |

No relationship between p waves and QRS complexes (no coordination anymore) |

