![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Litosphere |
Composted of the crust (oceanic and continental - mainly of BASALT, GRANITE and other rocks) and the most upper mantle. Rigid outermost layer which cannot convect. -Internal heat is carried through it by conduction. -It also can be transported by advection on geologically active planets (such as Earth and Io) - below the Mohorovičič discontinuity from ~70 - 150 km - the low velocity zone divides it from the Asthenosphere
|
|
|
What is plate tectonics? |
Heat transfer by wholesale recycling of the lithosphere |
|
|
Asthenosphere |
- The zone where pressure and temperature are sufficiently high to allow a material to flow, even in its solid state - The internal heat is mainly transfered surface wards by convection - consists of 2 parts, mainly composed of PERIDOTITE: • upper mantle (from the low velocity zone until 670km) • lower mantle (from 670km to 2,900km-Guttenberg discontinuity) - From ~150km - 2,900 km until the Guttenberg discontinuity which decides the Asthenosphere from the core |
|
|
Core |
- The Guttenberg discontinuity at 2,900km divides it from the Asthenosphere - The core can be divided in 2 sections: • liquid outer core (from 2,900km to 5,154km), which composed of mainly iron, nickel and other heavier elements. • solid inner core from 5,154km to 6,371km, which composed of mainly iron with approx. 4% nikkel |
|
|
Describe the composition of the Earth |

|
|
|
Convection |
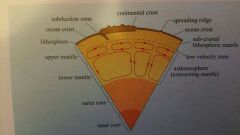
Process of heat transfer where a liquid in a gravitational field is heated by from below to the point where the hotter, less dense fluid rises upwards, displacing the cooler, denser fluid downwards |
|
|
Conduction |
The transfer of heat by means of internal kinetic energy on the atomic scale |
|
|
Advection |
Transferring heat by physically moving molten material - magma - up through fractures in the lithosphere |

