![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Minerals |
a naturally occurring chemical compound that's the building of blocks |

|
|
|
Ores |
a useful mineral that is a metal mineral or rock |

|
|
|
Fossil Fuels |
remains of living things that are burned to produce energy |

|
|
|
Physical Property |
things that are observed and measured without changing the substance |
|
|
|
Chemical Property |
a substance that is observed and does have change |

|
|
|
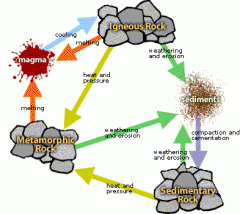
Rock Cycle |
a group of changes for rocks in all shapes and sizes |
|
|
|
Sediments |
a piece of matter that settles to the bottom of a liquid |

|
|
|
Sedimentary Rock |
forms of compaction/cementation of rock pieces called sediments |

|
|
|
Metamorphic Rock |
when rocks are changed into different rocks by heat and pressure |

|
|
|
Extrusive Igneous Rock |
when cooling takes place rapidly on the earths surface |

|
|
|
Intrusive Igneous Rock |
when cooling is taking place slowly beneath the earths surface |

|
|
|
Mechanical Weathering |
the breaking down of rock into smaller pieces |

|
|
|
Chemical Weathering |
the decomposition of rock caused by chemical reactions, resulting in new compounds |

|
|
|
Erosion |
the transportation of a rock from one area to another |

|
|
|
Deposition |
this is the dumping of sediments into layers |

|
|
|
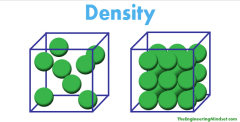
Density |
mass per unit of volume in an object |
|
|
|
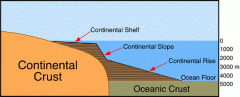
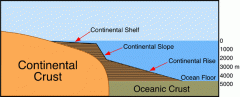
Continental crust |
thick part of the earth's crust that forms large land masses. |
|
|
|
Oceanic crust |
thin part of the earth's crust that underlines the ocean |
|
|
|
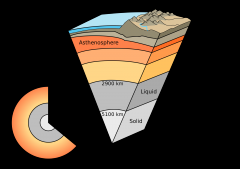
Lithosphere |
it's the rigid outer part of the earth |
|
|
|
Asthenosphere |
it's the upper layer of the earth's mantle |
|
|
|
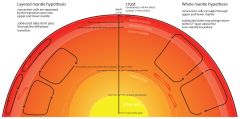
Mantle |
liquid layer between the crust and the outer core |
|
|
|
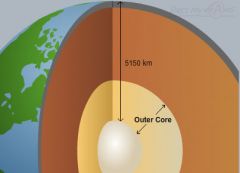
Outer core |
a liquid layer that's above the core and below the mantle |
|
|
|
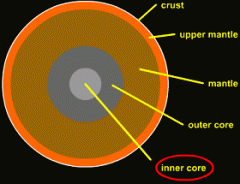
Inner core |
the hard middle of all the layers of the earth |
|
|
|
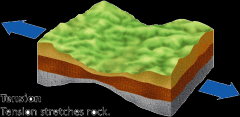
Tension |
applying force for something to stretch |
|
|
|
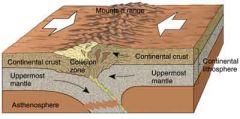
Compression |
to push things together with a great force |
|
|
|
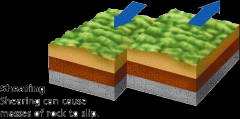
Shearing |
when things grind past each other |
|
|
|
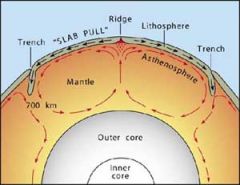
Convection currents |
the transfer of heat by the mass movement
|
|
|
|
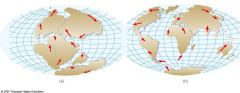
Theory of Plate Tectonics |
finish this |
|
|
|
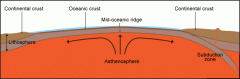
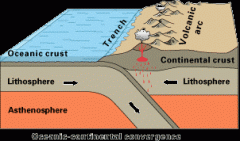
Subduction |
sideways and downward movement of the edge of a plate
|
|
|
|
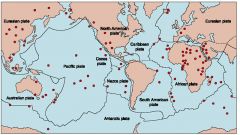
Hot Spots |
area in the mantle from which heat rises from deep in the Earth.
|
|
|
|
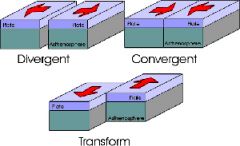
Convergent plate Boundary |
when 2 or more plate tectonics collide |
|
|
|
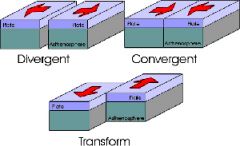
Divergent plate Boundary |
when 2 plate tectonics move away from each other |
|
|
|
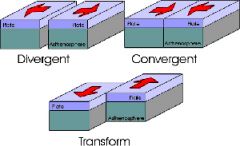
Transform plate Boundary |
when 2 plate tectonics grind past each other |
|
|
|
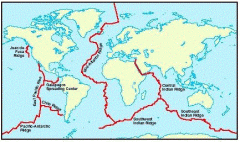
Mid-ocean Ridges |
underwater mountain system formed by plate tectonics
|
|
|
|
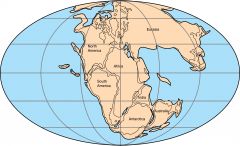
Pangaea |
the name of a supercontinent that existed long ago |
|
|
|
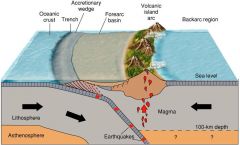
Island Arcs |
curved chain of volcanic islands located at a tectonic plate
|
|
|
|
Faults |
planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock
|

|
|
|
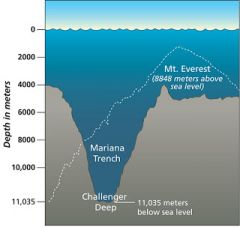
Trenches |
a deep and long narrow ditch |
|
|
|
Folded Mountains |
mountains that form mainly by the effects of folding on the top layer
|

|
|
|
Pacific Ring of Fire |
an area of a great amount of volcanoes |
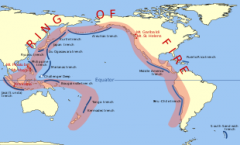
|
|
|
Seismic Activity |
frequency and size of earthquakes that happen over a period of time
|
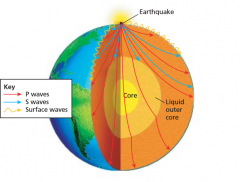
|
|
|
Landforms |
a natural feature of the earth's surface
|

|
|
|
Seafloor Spreading |
where new crust is formed and it moves away |
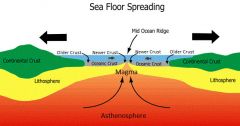
|
|
|
San Andreas Fault |
an example of a transform plate boundary |

|
|
|
Continental Drift |
a theory that all continents were connected but moved away |
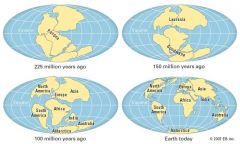
|

