![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Minerals |
Naturally occurring organic material found in the Earth. |
|
|
|
Ores |
A useful mineral found deep deep deep deep deep deep underground |

|
|
|
Fossil fuels |
ancient organism parts that have been pressed down on to create fuel for electricity |
|
|
|
Physical properties |
Properties that can determine the mineral without changing the substance |

|
|
|
Chemicals properties |
Properties that change the substance |

|
|
|
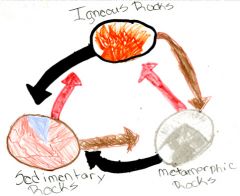
Rock cycle |
The order of rock transformation from one to another |
|
|
|
sediments |
broken down rocks; are cemented into sedimentary rocks |

|
|
|
sedimentary rock |
rocks created by sediments eroding, depositing, and cementing |

|
|
|
metamorphic rock |
rock created by heat and pressure |

|
|
|
extrusive igneous rock |
rock formed from the cooling of magma AFTER it has left the volcano |
|
|
|
intrusive igneous rock |
rock formed from the cooling of magma WHILE IT IS STILL INSIDE the volcano |
|
|
|
mechanical weathering |
the physical break down of rocks |
|
|
|
chemical weathering |
the chemical break down of rocks |
|
|
|
erosion |
the carrying away/transportation of sediments |
|
|
|
deposition |
the sediments are deposited after being eroded |
|
|
|
density |
the measure of mass in an object |
|
|
|
continental crust |
the outermost layer of earth. the lest dense layer. |
|
|
|
oceanic crust |
the inner layer of the crust; the more denser part. |
|
|
|
lithosphere |
the very bottom of the crust |
|
|
|
asthenophere |
the top of the mantle |
|
|
|
mantle |
the largest layer of earth; it made mostly of molten rock |
|
|
|
outer core |
the second innermost layer of earth; is made of liquid iron and nickle |
|
|
|
inner core |
the innermost layer of earth; is made of solid iron and nickle |
|
|
|
tension |
the force applied at divergent plate boundaries |
|
|
|
compression |
the force applied at convergent plate boundaries |
|
|
|
shearing |
the fore applied at transform plate boundaries |
|
|
|
convection currents |
the rotation of hot and cold magma in the mantle; is the cause of tectonic plates moving |
|
|
|
theory of plate tectonics |
the belief that the earth has plates that are constantly moving |
|
|
|
subduction |
when a older, more denser plate converges with a younger, less dense plate; the older one slides under the the younger one; this will cause trenches and volcanic arcs |
|
|
|
hot spots |
volcanoes that do not appear on a fault line; these occur when the magma from the mantle leak though the crust; volcano island arcs; example is hawaii |
|
|
|
converging plate boundaries |
when two plates push together at a fault line |
|
|
|
diverging plate boundaries |
when two plates push away from each other at a fault line |
|
|
|
transform plate boundaries |
when two plates push beside each other scrapping against one another; California is an example of this |
|
|
|
mid-ocean ridges |
small mountain ranges that appear at divergent plate boundaries |
|
|
|
Pangaea |
a super continent that is believed to have been created once long ago; it is supporting evidence of the theory of plate tectonics |
|
|
|
island arc's |
a small arc of islands; typically from a hot spot |
|
|
|
faults |
the area between two plates |
|
|
|
trenches |
large, deep valleys that are found in the ocean at a subduction zone |
|
|
|
folded mountains |
large mountains that appear at convergent plates |
|
|
|
pacific ring of fire |
a large ring of volcanoes in the pacific ocean |
|
|
|
seismic activity |
the time and size of earthquakes |
|
|
|
landforms |
large natural structures; i.e: mountains, valleys, trenches, volcanoes, etc. |
|
|
|
sea-floor spreading |
happens at divergent plate boundaries; the oceanic crust gets thinned out |
|
|
|
San Andrea's Fault |
Major transform fault line in California |
|

