![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Apparent magnitude |
A measure of the brightness of a star as it appears to an observer on earth |
|
|
What magnitude does a bright star have? Brightest stars? what magnitude does a dim star have? |
Bright Star: low magnitude Brightest Stars: negative magnitude Dim Star: high magnitude |
|
|
What scale is apparent magnitude measured on? |
A Logarithmic scale |
|
|
What are the 2 main factors that determine a stars apparent magnitude? |
- How much light the star emits - The distance between the star and earth - the greater the distance, the dimmer the star will appear |
|
|
What are interstellar distances? What are they measured in? |
The distance between stars Light Years (l.y) |
|
|
What is a light year? |
1 l.y = the distance that light will travel in 1 year (under 9.5 trillion kilometers) |
|
|
What is the name of another commonly used astronomical unit of length? What is it equivalent to in light years? |
Parsec (pc) Equivalent to 3.26 l.y |
|
|
How to convert between light years and parsecs |
l.y -> parsecs distance in light years / 3.26 parsecs -> distance in parsecs x 3.26 |
|
|
Define Parallax |
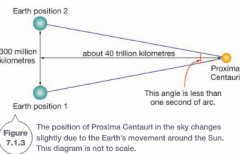
Technique used to measure the distance to other stars |
|
|
What is parallax used for? |
To measure the distance between the sun and other stars. As the earth moves around the sun, our changing point of view means that the positions of stars in the sky change very slightly over the course of a year |
|
|
Define Stellar Parallax |
The shift in position of stars that are close to earth (less than one-thousandth of 1 degree) the apparent change in the position of a star throughout the year due to the earths motion around the sun |
|
|
Define Absolute Magnitude |
A measure of how bright a star would appear if it was 10 parsecs from earth |
|
|
What does the Absolute magnitude allow? |
It allows for the brightness of stars from different parts of the galaxy, to be meaningfully compared |
|
|
List the energies in the electromagnetic spectrum, from low energy, to high energy |
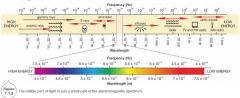
AM Radio, Radio waves, TV & FM Radio, Microwaves/radar, Infrared, Ultraviolet, X-Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays |
|
|
How does light work? |
Your eyes collect the visible light from stars and your brain performs a complex averaging process that results in you perceiving the star as a particular colour |
|
|
What do scientists use to analyse the colour of a star? |
this is done by comparing the magnitude of the star when viewed through coloured filters, therefore, allowing for its colour to be precisely measured |
|
|
How is a star's spectrum determined? Compare & contrast the energy cooler stars and hot stars emit |
Its surface temperature - cooler stars emit most of their energy in the infrared and red parts of the spectrum - very hot stars emit a lot of energy in the violet and ultraviolet part of the spectrum and appear blue - stars with temperatures in between these extremes emit light across a range of wavelengths and can appear orange, yellow or white |
|
|
What is another device that is used to analyse star light? What does it do? |
Spectrometer --> splits light into a spectrum to reveal its component colours |
|
|
How do scientists analyse spectrums of radiation? |
Scientists can determine what chemical elements are present in a star from distinctive lines that appear in its spectrum. particular elements emit colours of particular wavelengths. These can be measured precisely to determine the elements in a star. they also see dark lines showing missing colours. This is due to light interacting with atoms in the outer layers of the star. the light energy is absorbed by electrons in atoms of all the elements in the outer gas layers. these electrons absorb light energy of particular wavelengths. the absorption occurs at exactly the same wavelength that the same element would emit when its extremely hot. |
|
|
What is spectral class? |
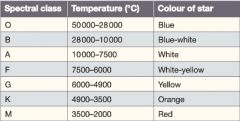
It indicates the elements present in the star, the temperature and colour of a star |
|
|
abc |
abc |

