![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plate Tectonics:
Subduction zones |
Denser oceanic crusts descends beneath the less dense continental crust and in the process causes earthquakes |
|
|
Plate Tectonics:
Batholiths |
-Large magma chambers - Roughly elliptical or circular outline; more than 100 Km^2 in cross-sectional area - Discordant (cut across country rock) |
|
|
Earth History
What is the Law of Original Horizontality? |
Majority of sedimentary rocks are deposited horizontally (or at an angle <2 degrees
If there are any layers inclined to the horizontal, we can assume that there was a period of disturbance |
|
|
Earth History
What is the law of Principle of Superposition? |
Oldest rock layers are on the bottom; Newest or youngest layers are on top
We look for evidence (upside-down, ripples, cross bedding...) to see if sequence is overturned |
|
|
Earth History
What is the Principle of Inclusions? |
Inclusions of other rock units must be younger than the rocks from which the inclusions were derrived |
|
|
Earth History
What is the Principle of Cross-cutting relationships? |
Igneous intrusive rocks will always be younger than the rocks through which they cut |
|
|
Earth History
Stock |
- Type of intrusive body what cuts across country rocks - roughly elliptical or circular outline; less than 100 Km^2 in cross-sectional area |
|
|
Earth History
Dyke |
- Type of intrusive body what cuts across country rocks - Narrow band, following joint or fault patterns |
|
|
Earth History
Sill |
- Type of intrusive body that does not cut across beds - Lenticular, elliptical or circular outlines, paralleling the outcrop of country rocks |
|
|
Earth History
Laccolith |
-Type of intrusive body that does not cut across beds - Lenticullar, elliptical or circular outlines, paralleling the outcrop of country rocks - Connected to underneath the Batholith |
|
|
Earth History
Lopolith |
-Type of intrusive body that does not cut across beds - Lenticullar, elliptical or circular outlines, paralleling the outcrop of country rocks - connected to the stock |
|
|
Earth History
Law of Faunal Sucession |
- Fossilized fauna and flora that succeed each other in a definte sequence - obtain relative age of dates for sedimentary layers |
|
|
Explain the major events of Precambrian Era |
- Geologic time older than this is called the Hadean Eon - Divided into two Eons: Archean and Protozoic |
|
|
What is the oldest rocks found to date? |
Acasta Gneiss 4.0 billion year old during the Precambrian Era.
Found in Northwest territories of Canada |
|
|
Name two North American principal Archean Cratons (continental cores) |
- Slave: contains Acasta Gneiss rocks - Superior: forms the nucleus of our continent |
|
|
Archean crustal rocks are characterized by... |
- deformed granite-gneiss complexes - Greenstone belts (low grade metamorphosed volcanic rocks) |
|
|
Oldest life forms that eventually evolved into blue-green algal mounds (stromatolites)
During which Era, Eon? |
Prokaryotes
During the Precambrian, Proterozoic era |
|
|
Proteozoic Eon... |
- 2.5 bya - Shallow seas opened and closed, causing sedimentary sequences to accret around the edges of cratons - Formation of Rodinia (1st super continent) - Formation of of Grenville region of Precambrian Shield - Produce the largest mountain ranges that Earth has ever had |
|
|
When did Rodinia split apart to create large ocean basins between the continental fragments |
750 mya
|
|
|
True or false
There was an ice age, as Proterozoic glacial deposits have been found on all the continents except Antarctica |
True |
|
|
True or false.
The early Precambrian atmosphere contained no oxygen. Sedimentary Precambrian deposits that contain unoxidized iron and uranium. |
True |
|
|
True or false.
Due to photosynthesizing bacteria, the percentage of oxygen steadily increased until about the Devonian. |
True |
|
|
True or false.
During the Proteozoic Era, the first eukaryotic cells appeared |
True |
|
|
What big event occured during the Ediacaran period? |
- Fossil evidence of multicellular organisms (Ediacaran Fauna) - Spans the last 90 million years of the Precambrian |
|
|
What large events occured during the Cambrian period? |
- Fossils show "hard" calcium cabonate, Silica, Phosphate or Chitin - Trilobites, brachiobods and acheocyathids (sponge like reef builder) are common - Age of the Trilobite - Primary continents: Laurentia, Gondwanam Siberia and were at or near the Equator and both poles were water covered |
|
|
What large events occurred during the Ordovician period? |
- Ordovician, Gondwanda moved towards South Pole resulting in glaciation - Consolidated glacial deposits (tillites) in the region of the Sahara desert, are remnants of this time -Corals, brachiopods, nautiloid cephalopods, and trilobite fossils; graptolite and trilobite dominated in synclines
|
|
|
Which time period is the first fish seen? |
Ordovician period |
|
|
What time period is known as The Age of Nautiloid |
Ordovician |
|
|
What are the main events during the time period of Silurian? |
- Coral reefs, crinoids (sea lillies) - Land plants and fish more common - Graptolites became extinct at the end of Silurian; known as The Age of Grapolite - Dominated by trilobite - Devonian, Baltica collided with Laurentia forming Laurasia - Lapetus Sea began to close - Taconic Orogeny during late Ordovician in Laurentia - Caledonian Orogeny during the Silurian in Baltica |
|
|
What is the period that comes after Silurian? |
Devonian period |
|
|
Describe the major events during the Devonian period? |
- Northern Lapetus sea continued to narrow, causing Acadian Orogeny - Mountain formation in areas now known as NE America, Britain and Western Scandinavia - Common invertebrates: Brachiopods, corals, crinoids, and nautiliod cephalopods - Known as Age of Fishes - Development of forests - Transition of fish into amphibian |
|
|
What period is known as "Age of Fishes" |
Devonian Period |
|
|
In which period did the transition of fish to amphibians occur? |
Devonian Period |
|
|
What period followed the Devonian period? |
The Carboniferous (Mississippian and Pennsylvanian) |
|
|
Describe the major events during the Carboniferous period? |
- Gondwana in the South Pole = extensive glaciation - advance and retreat of glaciers changed seal levels - Gondwana began to move northward and collided with Laurasia causing the Allegenian Orogeny (Appalachian) |
|
|
What common species were seen during the Carboniferous period? |
- Crinoids, bachiopods and corals - Cephalopods (both nautiloids and ammonoids) - Presence of insects - Sharks and bony fishes evolving - Age of amphibians; becoming more diverse, ex. Labrinthodont - Gave rise to the first reptiles in late Pennsylvanian - Age of Great Coal forests; plants increased coal swamps |
|
|
What are the three types of Carboniferous plants? |
1) Ferns and seed ferns 2) Scale trees 3) Scouring rushes |
|
|
What time period was the supercontinent Pangaea formed? |
Permian Period |
|
|
When was the largest mass extinction? |
Permain period - invertebrate faunas (trilobite, blastoids, tabulate corals, and rugrose corals), carboniferous plant (scale trees) - Dominance of reptiles over amphibians |
|
|
Describe the main events during the Triassic period? |
- Seperation of Laurasia to the north from Gondwana to the south - India seperated from Gondwana and moved north - Age of the Ammonite (Ammonite was very common, two types: Ammonite Cephalopod, Ammonoid Cephalopod) - Gymnosperms (seed baring) - Reptile domination, including dinosaurs - Therapsid (type of true mammal) occurred in Triassic |
|
|
The Mesozoic Era consists of which 3 time periods.
Clue: Thisis known as the Age of Reptiles |
1) Cretaceous 2) Jurassic 3) Triassic |
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Two walking legs or bipedal; the front limbs were very short and could only be used for grasping; meat eater or carnivore with very sharp teeth |

Order: Saurischian (reptile-hipped) Suborder: Theropod
|
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Long neck with small head and long tail; plant eater (herbivore) with flat shaped teeth; most were very large and walked on four legs |

Order: Saurischian (reptile Hipped) Suborder: Sauropod
|
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Body was armored or covered with plates and had many bony lumps and spikes; herbivore and quadruped with short legs |

Order: Ornithischian (bird-hipped) Suborder: Ankylosaur
|
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Massive heads with horns and neck frills and beak-shaped jaw; quadruped and herbivore |

Order: Ortnithischian (Bird-hipped) Suborder: Ceratopsian
|
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Herbivore; front legs were somewhat shorter than back but could walk on 2 legs or 4 legs; stiff tail; many had a "duck bill" shaped skull (the hadrosaurs) with some also evolving head crests |

Order: Ortinithischian (Bird-hipped) Suborder: Ornithopod
|
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Heavy domed bony skull with a fringe of bony knobs or spikes on the skull; bipedial with wide hips |

Order: Ornithischian (Bird-hipped) Suborder: Pachycephalosaur
|
|
|
Dinosaur distinguishing features:
Double row of upright plates down its back; quadruped with narrow head; herbivore |

Order: Ornithischian (bird-hipped) Suborder: Stegosaur
|
|
|
Describe the main events during the Jurassic period |
- South America began to separate from Africa, and NA began to separate with Eurasia - Formation of Atlantic ocean - Formation of Cordillean mountains - Ammonites and belemnites, bivalves, gastropods and corals dominant invertebrates - Flying lizards (reptiles) |
|
|
Describe the main events during the Cretaceous period |
- Australia and Antarctica separated - SA and Africa separated; NA and Eurasia still in separation process - More mountain building in Cordillera - Interior seaway formed in NA - Dominant invertebrates: Ammonites, belemnites, echinoids, bivalve, gastropods, sponges - Age of dinosaurs - Mass extinction |
|
|
What time period did the mass extinction of pterosaurs (flying reptiles), ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs (marine) and many other reptile and invertebrate groups occur? |
This occurred in the Cretaceous period
2nd largest mass extinction |
|
|
The Cretaceous period is known as the age of... |
Age of the Dinosaurs |
|
|
The Paleogene and Neogene periods were formally known as... |
The tertiary period |
|
|
What are the 5 Epochs of the Tertiary period? |
Making up the Paleogene period: 1) Paleocene (oldest) 2) Ecocene 3) Oligocene
Making up the Neogene period: 4) Miocene 5) Pilocene (youngest) |
|
|
Which Epoch in the Paleogene period did the Laramide Orogeny of the Cordillera region continue (begun in Cretaceous)? |
Ecocene
- Subduction of Pacific Oceanic Plate moving NA Plate |
|
|
When was the Age of Mammals? |
Paleogene |
|
|
True or false:
Mammals and birds became more refined and specialized during the Paleogene Period.
It is known as the Age of Mammals. |
True |
|
|
True or False:
A sudden increase of grassland habitats was caused by warm dry climate during the Micoene Epoch. |
True |
|
|
Angiosperms (flowering plants) dominated in the last 100 million years. |
True |
|
|
Global cooling and glaciation of Earth occured in the Pleistocene Epoch during which Period? |
Quaternary Period |
|
|
Our present interglacial stage began 11,000 years ago during which Epoch? |
Holocene or Recent Epoch |
|
|
Describe the human lineage in respect to evolution. |
- began 2 mya in Africa with the evolution of tool making Hominid Homo habbilis - 1.8 mya Homo erectus spread to India, China, Indonesia and Europe - Homo sapiens evolved from archaic Homo sapiens 300,000-200,000 years ago |
|

What is a Disconformity? |
The Strata below unconformity are parallel to the strata above it |
|
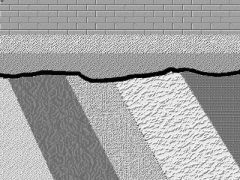
What is an Angular Unconformity? |
Strata below unconformity are at an angle to a strata above it |
|
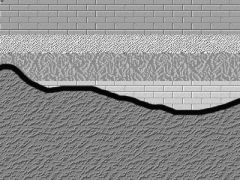
What is a nonconformity? |
Sedimentary strata overlie OLDER plutonic igenous or metamorphic rock |
|

What kind of fossil is this? |
Rugose Coral |
|

What kind of fossil is this? |
Tabulate Coral |
|

What kind of fossil are these? |
Bryozoa - look for very tiny openings (autopores) regularly arranged on the structure surface |
|

Is this a Brachiopod or a bivalve? |
This is a Brachiopod because it has bilateral symmetry |
|

Is this a Brachiopod or bivalve? |
This is a bivalve as there are two halves: right and left. It is asymmetrical |
|

What kind of fossil is this? |
This is a gastropod - key feature is the arrangement of spines and nodes |
|

What kind of fossil is this? |
Gastropod
- Key features are the arrangements of spines and nodes |
|

Is this a Nautiloid cephalopod or a Ammonoid Cephalopod? |
This is a Nautiloid cephalopod |
|

Is this a Nautiloid cephalopod or an ammonoid cephalopod? |
Ammonoid Cephalopods |
|

Is this a Nautiloid cephalopod or an ammonoid cephalopod? |
Ammonoid Cephalopods |
|
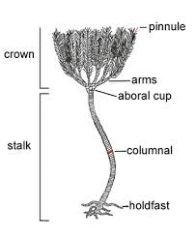
What fossil is this? |
Crinoid - common in the Paleozoic period |
|

What kind of fossil is this? |
Trilobite |
|

True or false This is Graptolites |
Graptolites
This is true |

