![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
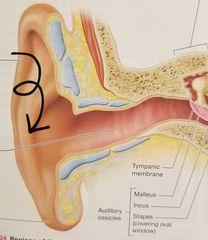
Auricle (pinna) |
|
|
External auditory canal |
|
|
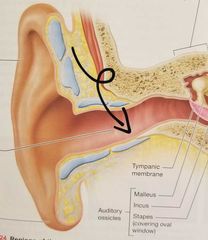
Tympanic membrane |
|
|
Malleus |
|
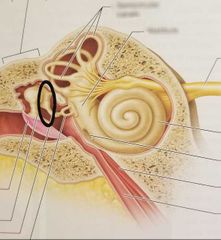
|
Incus |
|
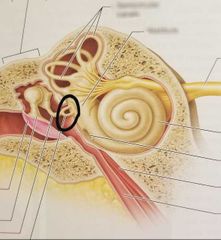
|
Stapes |
|
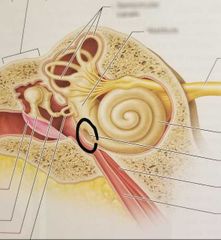
|
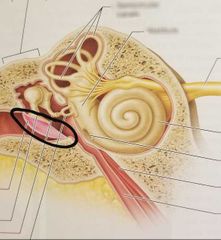
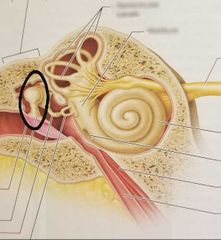
Round window |
|
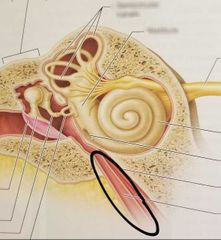
|
Pharyngotympanic tube |
|
|
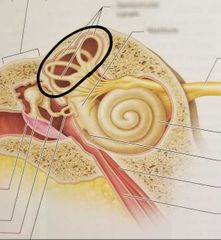
Semicircular canals |
|
|
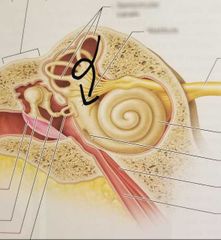
Vestibule |
|
|
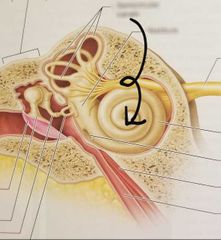
Cochlea |
|
|
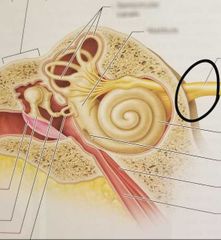
Vestibulocochlear nerve (Cranial nerve VIII) |
|
|
Which part of the ear funnels sound waves into the ex. auditory canal? |
Auricle |
|
|
Which part of the ear transmits sound waves to the tympanic membrane? |
External auditory canal |
|
|
Which part of the ear transmits vibrations to the auditory ossicles? |
Tympanic membrane |
|
|
Is the tympanic membrane part of the external or middle ear? |
External |
|
|
Three small bones that amplify and conduct sound |
Auditory ossicles |
|
|
Membranous opening connected to the stapes |
Oval window |
|
|
Membranous opening that relieves pressure in cochlea |
Round window |
|
|
Passage that connects the middle ear with the back of the throat |
Pharyngotympanic tube |
|
|
Fluid found in the membranous labyrinth |
Endolymph |
|
|
Fluid found between the mem. and bony labyrinths |
Perilymph |
|
|
Contains the ampulla which functions in dynamic equilibrium |
Semicircular canals |
|
|
Contains otoliths which function in static equilibrium |
Vestibule |
|
|
Houses the organ of Corti which contain "hair" cells, the sensory receptors for hearing |
Cochlea |
|
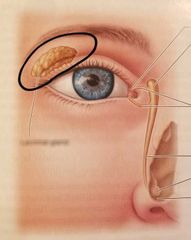
|
Lacrimal gland Creates tears |
|
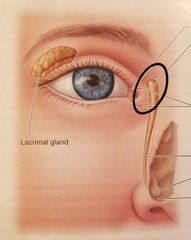
|
Lacrimal sac |
|
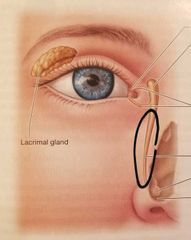
|
Nasolacrimal duct Drains tears into nasal cavity |
|
|
Which membrane lines eyelid and covers anterior surface of the eye? |
Conjunctiva |
|
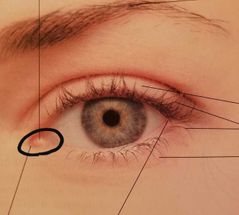
|
Lacrimal caruncle Lubricates the eye |
|
|
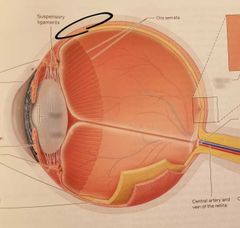
Sclera |
|
|
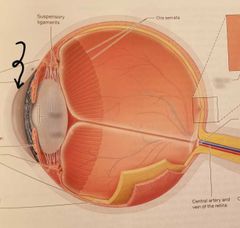
Cornea |
|
|
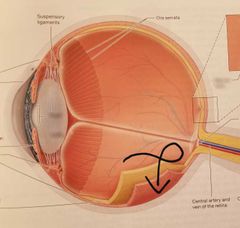
Choroid Highly vascular, pigmented |
|
|
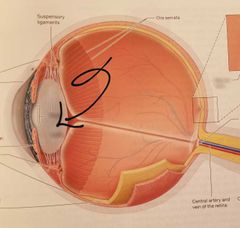
Lens |
|
|
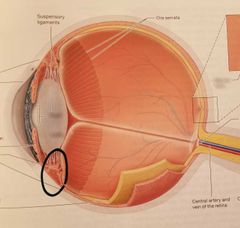
Ciliary body Controls shape of lens |
|
|
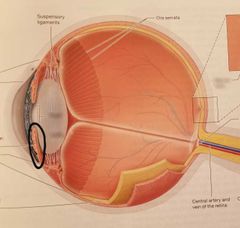
Iris Controls size of pupil |
|
|
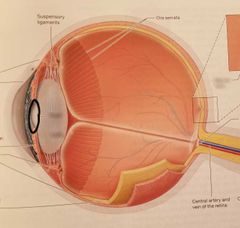
Pupil Opening within the iris |
|
|
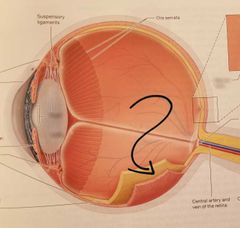
Retina Two layers - pigmented, neural |
|
|
Non-color receptors; work best in dim light; highly concentrated along periphery of retina |
Rods (Rods > cones) |
|
|
Color receptors; work best in bright light; highly concentrated in center of retina |
Cones |
|
|
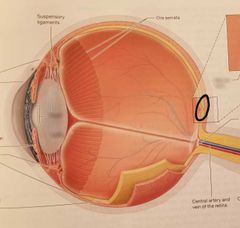
Fovea centralis Highest concentration of cones |
|
|
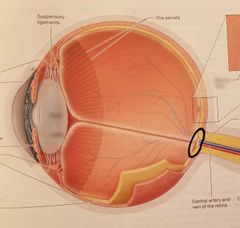
Optic disc (blind spot) |
|
|
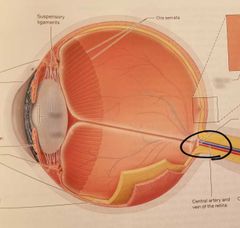
Optic nerve (Cranial nerve II) |
|
|
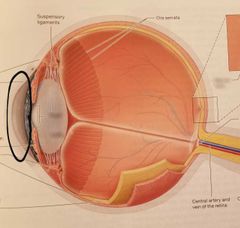
Anterior segment, aqueous humor |
|
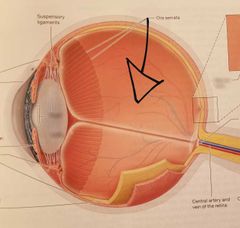
|
Posterior segment, vitreous humor |
|
|
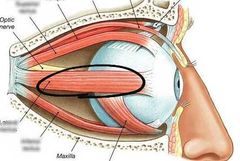
Lateral rectus |
|
|
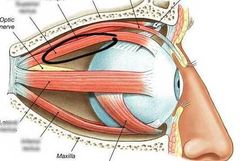
Superior rectus |
|
|
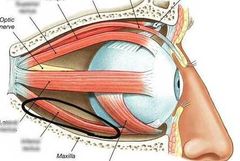
Inferior rectus |
|
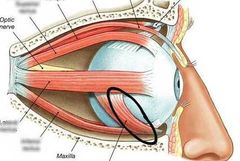
|
Inferior oblique |
|
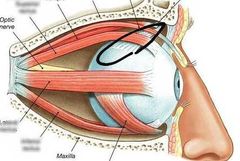
|
Superior oblique |
|
|
Which eye muscles are controlled by the oculomotor nerve (III)? |
Medial, superior, inferior rectus Inferior oblique |
|
|
Which eye muscle is controlled by the trochlear nerve (IV)? |
Superior oblique |
|
|
Which eye muscle is controlled by the abducens nerve (VI)? |
Lateral rectus |

