![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which week of gestation does the ear start to form? Which 2 branchial arches does it form from? |
First (mandibular) and second (hyoid) branchial arches are responsible for auricular development1 (Fig. 27-1). ▀During sixth week, external ear begins to develop around the dorsal end of the first branchial cleft. The ear arises from six buds of mesenchyme in the first and second branchial arches, known as the six hillocks of His. |
|
|
What is the mildest manifestation of hemifacial microsomia? |
Microtia |
|
|
85% of ear development by age x? |
Age of external ear maturity •85% of ear development is attained by age 4. •Ear width continues to grow until age 10. |
|
|
When in relation to autogenous ear reconstruction should a BAHA be placed? |
This is usually done with external hearing aids in early childhood followed by atresia repair or a bone-anchored hearing aid (BAHA) later in life. |
|
|
What causes cryptotia? |
Cryptotia is a congenital ear deformity in which the upper pole appears buried beneath the mastoid skin. It is a common auricular malformation in Asians. Children with this condition often present when they are in elementary school, and are unable to wear eyeglasses. The cause of this condition is the abnormal distribution of the intrinsic auricular muscle. |
|
|
Why is auricular molding started 3 days of life? |
Maternal estrogen concentrations are highest in the first 3 days of life and begin to decrease thereafter. In order to achieve good results with auricular molding, treatment must be initiated while maternal estrogen concentrations are increased and therefore cartilage pliability is high. |
|
|
Which ear deformity has a third crus, a flat helix, and a malformed scaphoid fossa? |
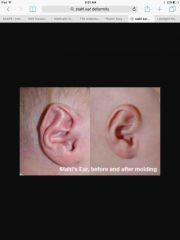
Stahl ear, also known as Spock ear. |
|
|
A 22-year-old man comes to the office because he is dissatisfied with the appearance of his ears. Physical examination shows bilateral effacement of the antihelical folds, conchal hypertrophy, and severe prominence of the lobules. Otoplasty is performed with a posterior incision and placement of permanent sutures from the scaphal cartilage and helical sulcus cartilage to the mastoid fascia. Following surgery, the patient is satisfied with the appearance of the upper and middle parts of the ears but notes persistent prominence of the lobules. Which of the following is the most likely cause? A ) Inadequate reduction of the antitragus B ) Inadequate reduction of the cavum conchae C ) Overtightening of the scapha-mastoid sutures D ) Suturing the triangular fossa to the temporal fascia |
The correct response is Option B.
As the cartilage angle between the cavum conchae and the antitragus becomes more acute, hypertrophy of the cavum conchae projects the lower third of the ear, forcing the lobule outward. Failure to adequately reduce the cavum conchae before suture placement will lead to persistent prominence of the lobule. |
|
|
What is the most common postop complication of otoplasty done for prominent ears? |
Recurrence of deformity |
|
|
A 53-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 2-year history of a lump on her right ear. Physical examination shows a 2.5 × 2 × 1.5-cm neurofibroma on the concha. Resection of the skin of the entire conchal bowl and the underlying conchal cartilage is planned. Which of the following flaps is most appropriate for reconstruction of the defect? |
Postauricular island flap |
|
|
Primary blood supply to the anterior surface of the ear? |
The primary blood supply to the anterior surface of the ear is the posterior auricular artery. |
|
|
Normal helical rim to head measurements at the apex, midpoint and lobule? |
Normal helical rim-to-head measurements for each third of the ear are 10 to 12 mm at the helical apex, 16 to 18 mm at the midpoint, and 20 to 22 mm at the lobule. |
|
|
A 6-year-old boy with microtia is evaluated for single-staged alloplastic reconstruction. In addition to the prosthesis itself, discussing with the parents soft-tissue reconstruction should focus on tissues dependent on which vasculature? |
D) superficial temporal In general, the superficial temporal/temporoparietal fascia flap is the work-horse flap and is based on the superficial temporal vasculature. This requires incisions into the hair-bearing scalp; alopecia and irregular parting of the hair are possible negative outcomes. Additional skin grafting must also be discussed |
|
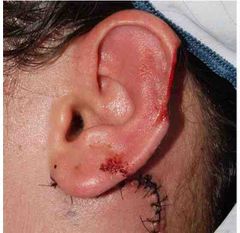
Best method of reconstruction? |
Postauricular flap and conchal cartilage graft |

