![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of a radar rating?
|
A rating authorising the holder of the rating to provide or supervise the provision of, such radar services, in such areas, as are specified in the rating.
|
|
|
What does a radar rating enable the holder to perform?
|
1. Provision of all radar services
2. Use of all associated tools 3. Resolution of traffic management problems associated with radar systems or radar failure |
|
|
What are the radar ratings associated with TWR, TMA & ENR?
|
TWR - Aerodrome Control Rating / Approach Control Rating
TMA - Approach Radar Control Rating ENR - Area Control Rating / Area Radar Control Rating |
|
|
What is a radar coupling?
|
The link between a system track and a flight data record.
|
|
|
At what FPL stage is the route created in the flight data record?
|
PRE-ACTIVE
|
|
|
What are the 4 tolerances for radar coupling?
|
1. Within 20 mins of estimated position
2. A circle of 20nm radius for ADEP / ADES in the FDRG (accounting for SID / STAR) 3. A circle of 20nm at each enroute turning point 4. Corridor 10nm either side of the calculated route |
|
|
What does VSP stand for?
|
Variable System Parameter
|
|
|
What 4 conditions must exist for auto-coupling?
|
1. FDR must exist
2. Must be an SSR or ADS-B return squawking / squittering 3. Must be within coupling corridor 4. FPL state must be COORD or later (will not couple in INACTIVE / PRE-ACTIVE) |
|
|
State 4 reasons for using coupling corridors?
|
1. Reduces incorrect coupling
2. Prevents false updates of FDP (APR) 3. Enables off-track alert processing - RAM 4. Enables multiple use of same SSR code within FDRG |
|
|
Give 5 examples of when an Automatic Position Report (APR) is sent?
|
1. On automatic and manual coupling
2. Over a significant reporting point 3. At pre-defined intervals 4. Upon loss of system track 5. Upon leaving and re-entering RAM corridor |
|
|
Give 3 examples of when an Automatic Position Report is not sent?
|
1. If the track is not coupled
2. FDR is in HOLD status 3. The track is outside the RAM corridor |
|
|
How can you re-establish a track within the coupling the corridor if the aircraft is no longer on its initial route?
|
Using the RER function to change the route
|
|
|
If the aircraft status changes and one of the coupling requirements no longer applies, is coupling lost?
|
No, there will be a warning alert.
|
|
|
What 3 conditions must be met before a surveillance control service can be provided?
|
1. Check airspace class
2. Check type of flight 3. Aircraft must be identified |
|
|
What are the 4 considerations regarding the number of aircraft that can be safely handled when providing a surveillance control service?
(irrespective of control experience and skill) |
1. Functions required
2. ATC workload and sector capacity 3. Reliability of comms / navaids / surveillance 4. Structural complexity - routes / boundaries / aerodromes |
|
|
Under normal circumstances are identified or non-identified aircraft given priority?
|
Identified
|
|
|
What is the difference between SNAP-SHOT and FLIGHT FOLLOWING information services?
|
SNAP-SHOT service is terminated immediately after information is given, FLIGHT FOLLOWING is ongoing until terminated.
|
|
|
Must an aircraft be identified to receive a Surveillance Information Service?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Can a FLIGHT FOLLOWING information service be transferred to an adjacent sector?
|
Yes, with the new sector controller's concurrence
|
|
|
How many SSR codes are available?
|
8 x 8 x 8 x 8 = 4096
|
|
|
What is the difference between a discrete SSR code and a non-discrete SSR code?
|
A discrete code is allocated to a specific flight until that flight ends or instructed by ATC.
A non-discrete code is applied to a category of aircraft |
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil flights in classes A, C & D airspace, or IFR flights in class E airspace?
|
3000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil IFR flights in class G airspace?
|
2000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil VFR flights in class E or G airspace?
|
1200
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for military flights in class A, C, D or E airspace?
|
5000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for military flights in class G airspace?
|
6000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil flights not involved in special operations or SAR, operating in class G airspace in excess of 15nm off-shore?
|
4000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code of civil flights engaged in littoral surveillance?
|
7615
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for ground testing by aircraft maintenance staff?
|
2100
|
|
|
What is the SSR code assigned by Tower ATC for Tower airspace?
|
0100
|
|
|
Can an ATC manually choose an SSR code to assign to an aircraft?
|
Yes, but the practice is not recommended due to the risk of duplicating a TAAATS assigned code in the same sector.
|
|
|
If an aircraft is already under ADS-B surveillance, is an SSR code allocated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
How is an SSR code assigned to an international flight?
|
ASSR is transmitted with the DEP message
|
|
|
What is the process for allocating SSR codes to formation flights?
|
1. Assign discrete code to the lead aircraft
2. Other aircraft 'SQUAWK NORMAL' 3. Can be helpful to identify rear aircraft as well when in convoy |
|
|
'SQUAWK CODE 5423' - Is this correct?
|
No, do not use the word 'CODE'
|
|
|
Prior to providing a surveillance service what must ATC do?
|
Identify the aircraft
|
|
|
If an aircraft's radar ident is lost, what must ATC do?
|
Inform the pilot
|
|
|
Once radar identity is established what do ATC need to inform the PIC?
|
[callsign]
IDENTIFIED [position] - unless identification established using discrete SSR code where position is consistent with current flight plan |
|
|
What does the acronym PADLI stand for?
|
Pressure Altitude Derived Level Information
|
|
|
What should a controller do during identification to assure the accuracy of PADLI?
|
Level verification
|
|
|
When should level verification be attempted?
(4) |
1, As early as practicable
2. Whenever monitoring has not been continuous 3. Hand-off of surveillance track infers verification completed unless otherwise advised 4. Continues if changing between ABL and MCL |
|
|
Level verification is accomplished through simultaneous comparison with...?
|
a) ...altimeter derived level information received from the same aircraft by radio-telephony
b)...the aerodrome elevation during the take-off roll, provided that the level information subsequently indicates a positive climb after take-off MATS 9.8.5.4 |
|
|
Can level be verified by requesting the pilot to REPORT PRESENT LEVEL?
|
No, this permits the pilot to journalise slightly.
The request must be VERIFY LEVEL |
|
|
If requesting level verification outside of the identification process how should a controller respond to a successful verification?
|
Callsign
|
|
|
What is the tolerance for verification?
|
+/- 200ft
|
|
|
What steps should be taken if tolerance is exceeded during level verification?
|
1. Advise pilot
2. Request check of pressure setting 3. Confirm current level MATS 9.8.5.5.1 |
|
|
A verified Mode C level may be used to...?
|
a)...apply vertical separation
b)...determine whether aircraft have maintained, vacated, passed or reached a level MATS 9.8.5.1 |
|
|
PADLI: If MCL is blank what actions can be taken?
|
Maybe a pilot or avionics problem request "SQUAWK CHARLIE"
If unable to fix, enter Pilot Reported Level in LABEL DATA |
|
|
PADLI: If MCL is incorrect what actions can be taken?
|
Maybe pilot or avionics problem request "CHECK ALTIMETER SETTING AND CONFIRM LEVEL"
If unable to fix - "STOP SQUAWK CHARLIE, WRONG INDICATION", enter Pilot Reported Level in LABEL DATA |
|
|
Can Pilot Reported Level be updated on surveillance tracks?
|
No
|
|
|
What is the criteria for using verified PADLI to determine when a level is being maintained?
|
Within +/- 200 ft for three consecutive updates or 15 seconds.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the criteria for using verified PADLI to determine when a level has been vacated?
|
A change of 400 ft or more in the anticipated direction from the previously assigned level.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the criteria for using verified PADLI to determine when a level has been passed?
|
Passed the level in the required direction by 400 ft or more.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the criteria for using PADLI to determine when a level has been reached?
|
Within +/- 200 ft of the assigned level for the greater of three consecutive updates or 15 seconds.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the monitoring requirement for using PADLI to determine level occupancy?
What further information can be used to validate PADLI? |
When only PADLI is used, the read-outs must be monitored continuously.
PRL (REPORT WHEN LEAVING / REACHING / PASSING [level]) |
|
|
How does the transition from PADLI to PRL work when leaving surveillance coverage?
|
Eurocat automatically populates the last valid PADLI into the PRL field.
The PRL field becomes usable for ATC purposes. |
|
|
When providing SIS, can both verified and unverified PADLI be used? What phraseology should be used to convey this to the PIC?
|
Yes. Unverified level information should be prefixed by the words UNVERIFIED LEVEL.
MATS 9.1.6.6 |
|
|
What does it mean if the PADLI shows 'INV'? What should you do?
|
Sometimes upon entering surveillance there is a short period where MCL data has not been validated.
No manual update is permitted at this time and the problem will rectify itself after a few updates. |
|
|
Unverified PADLI can be disregarded for traffic or avoidance at what point?
|
When it is greater than 2000 ft above or below, unless further information indicates a potential problem.
MATS 9.1.6.6.1 |
|
|
When should traffic information be provided to aircraft leaving CTA?
|
a) The aircraft is on descent and PADLI of observed traffic is operating within 2000 ft of the base of CTA
b) Other information indicates a potential conflict exists MATS 9.1.5.8 |
|
|
What is the minima for lateral RADAR separation? What are the exceptions?
|
5nm
a) Parallel approaches in VMC (less) b) UFB (Ultimate Fall Back) degraded mode (more) c) Wake turbulence separation (more) d) TCU application (less) e) Definite passing longitudinal time standard T7d (less) MATS 10.2.2.1 |
|
|
When can 3nm separation be used in a TCU?
|
You may reduce the horizontal radar separation minimum to 3 NM, provided that
a) the aircraft are in communication with and b) under the control of either a TCU or an associated control tower providing Class C or Class D services, and are: i) within 100 NM of an MSSR sensor; or ii) within 30 NM of a radar sensor using military high definition Terminal Approach Radar (TAR) or primary data from a civil high definition TAR. MATS 10.2.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what is the required separation between two position symbols / PSR blips?
|
The centres of the position symbols / PSR blips is never less than the prescribed minimum.
MATS 10.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what is the required separation between a position symbol / PSR blip and an SSR response?
|
Centre of the position symbol / PSR blip and the nearest edge of the SSR response is never less than the prescribed minimum.
MATS 10.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what is the required separation between two SSR responses?
|
The closest edges of the SSR responses is never less than the prescribed minimum.
MATS 10.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what are the conditions relating to the overlap of position symbols / PSR blips / SSR responses?
|
Do not allow the position indications to touch or overlap, under any circumstances, unless vertical separation is applied between aircraft, irrespective of the type of position indication used and the separation minimum applied.
MATS 10.2.1.1.1 |
|
|
What is the display limitation on using the BRL?
|
The BRL can only be used to establish or monitor horizontal separation between RADAR, ADS-B and ADS-C position symbols when the display range does not exceed 3500nm.
NAPM 14-15-5 |
|
|
What is the wake turbulence envelope?
|
Directly behind (within 760m laterally) another aircraft at the same level or less than 1000 ft below.
MATS 10.7.1.2 |
|
|
Are separation assurance standards different between procedural and surveillance environments? Explain?
|
No. Having surveillance is no justification to not apply separation assurance.
|
|
|
What aircraft are considered to be wake turbulence category Heavy if leading and Medium if following?
|
B757 - Boeing 757
H47 - Chinook H53 - Sea Stallion (Navy version of Chinook) |
|
|
Under what 5 circumstances is wake turbulence separation not required?
|
a) When a Light aircraft will cross or follow the track of a Medium fixed win aircraft of less than 25000 kg MTOW
b) Between an aircraft landing behind an aircraft taking off on the same runway c) If a pilot has initiated a waiver of the relevant departure wake turbulence separation minima d) For VFR flights in relation to a preceding Heavy or Medium aircraft, except on departure e) When the pilot of an IFR flight has reported the preceding aircraft in sight and has accepted responsibility for visual separation with that aircraft, except on departure MATS 10.7.1.4 |
|
|
What wake turbulence category is a C550?
|
Light
|
|
|
What wake turbulence category is a C560?
|
Medium
|
|
|
What appears in the label of a Super Heavy wake turbulence category aircraft?
|
J
|
|
|
What are the distance based wake turbulence standards behind a Super Heavy?
|
Super Heavy - 4nm*
Heavy - 6nm Medium - 7nm Light - 8nm * just because you can, doesn't mean you should - there are other reasons for keeping 2 super heavies more than 4nm apart. MATS 10.7.3 |
|
|
What are the distance based wake turbulence standards behind a Heavy?
|
Heavy - 4nm
Medium - 5nm Light - 6nm |
|
|
What are the distance based wake turbulence standards behind a Medium?
|
Light - 5nm
|
|
|
What is the anomaly with the DHC Dash-8 with regards to wake turbulence?
|
The Dash-8 Delta is considered a Medium as a leading aircraft for wake turbulence purposes as it has a MTOW of about 32000 kg.
Other Dash-8 models are under 25000 kg. |
|
|
When may you separate an identified surveillance track from a procedural track using RADAR?
|
The identified track can be separated from the navigational tolerances of a flight not receiving a surveillance control service, providing the procedural navigation tolerances are shown on the ASD.
MATS 10.2.1.7 |
|
|
Can the BRL be used to display an angular navigation tolerance for separation?
|
Yes, provided a 2 degree correction is applied to the derived angle.
NAPM 14-15-7 |
|
|
What is the radar track type for CANCELLED?
|
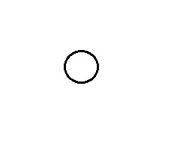
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for COMBINED TRACK?
|
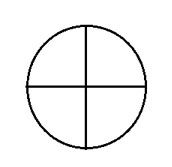
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for LAST RADAR POSITION?
|
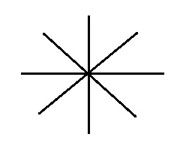
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for PRIMARY TRACK?
|
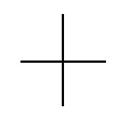
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SECONDARY TRACK?
|
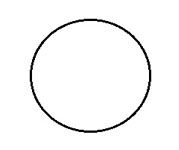
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SITE TRACKS?
|

|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 0001?
|
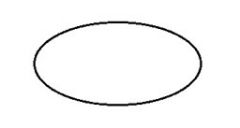
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 2000?
|

|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 0100?
|
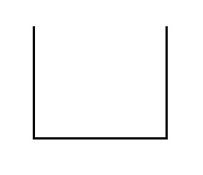
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 1200?
|
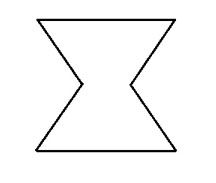
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for TEST TRACKS?
|
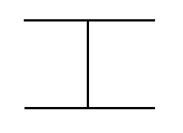
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for TRACK IN EXTRAPOLATED STATUS?
|
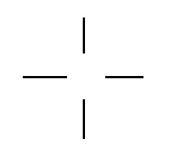
|
|
|
What is the separation criteria for aircraft leaving RADAR surveillance on the same track?
|
Non-RADAR separation must be established before the following aircraft arrives within 5nm of the last RADAR position of the proceeding aircraft.
MATS 10.2.1.6 |
|
|
What is the separation criteria for an aircraft leaving RADAR surveillance on a reciprocal track?
|
RADAR separation exists when identified aircraft has passed the last RADAR observed position of an outbound aircraft by the RADAR standard.
MATS 10.2.1.6 |
|
|
When may you apply ATS surveillance system separation between aircraft about to leave controlled airspace?
|
a) When the horizontal separation is not less than the prescribed minimum
b) Mutual traffic information is passed to the aircraft concerned prior to them leaving controlled airspace MATS 10.2.1.5 |
|
|
When should you apply the standard of half the applicable ATS surveillance standard minimum separation?
|
a) the adjacent sector, in controlled airspace, has the same ATS surveillance system processing and display system;
b) the Restricted Area activity is designated with a non-flying classification type; or c) the Restricted Area activity is classified as 'military flying' and by local agreement the ADF will apply the following separation between the activity and the Restricted Area boundary: i) half the applicable ATS surveillance system separation minimum; or ii) an appropriate procedural navigation tolerance. |
|
|
What are you providing to aircraft when you vector?
|
Navigational guidance
|
|
|
Give 6 reasons why you would vector?
|
a) Apply surveillance separation
b) Flow traffic c) Maximum airspace utilisation d) Noise abatement e) Hazardous weather avoidance f) Facilitate approaches MATS 9.8.10.1 |
|
|
What are prohibitions on vectoring?
|
a) Must not vector a flight plan track or an ADS-C track
b) Must not vector RADAR / ADS-B identified aircraft to avoid a flight plan track or ADS-C track c) Do not vector Special VFR except in an emergency d) Do not vector aircraft outside controlled airspace, except in an emergency. MATS 9.8.10.2 |
|
|
What are considerations that need to be made when vectoring?
|
a) Vector aircraft along or in close proximity to routes, making navigation easier if RADAR fails
b) Advise the pilot 1) reason 2) extent of & 3) expectation after the vector c) Repeat, I say again repeat, the direction of turn when 180 degrees or more; d) Agree turn rates with a pilot who reports unreliable directional instruments to make all turns at an agreed rate immediately when requested e) ensure that adequate terrain clearance exists at all times pilot resumes own navigation; f) Advise pilot sufficiently to permit own navigation in the event of radio or RADAR failure; g) Ensure that intervals between transmissions are brief, where terrain or traffic separation occur no more than 30s h) Avoid areas of known hazardous weather MATS 9.8.10.3 |
|
|
Who is responsible for terrain clearance of an aircraft in receipt of an advisory service?
|
The pilot, although ATC still have a duty of care.
|
|
|
When TCU control is vectoring an aircraft, what should be used to assign the minimum assignable altitude?
|
RTCC - RADAR Terrain Clearance Chart
|
|
|
What information is provided to the pilot when terminating a vector?
|
a) A heading as necessary to intercept the nominal track of a pilot interpreted navaid appropriate to the cleared route
b) A clearance direct to a pilot interpreted navaid for interception of the cleared route c) A clearance direct to an area navigation waypoint for interception of the aircraft's cleared route for approved SCNS aircraft |
|
|
What type of heading does the BRL tool give?
|
True
|
|
|
What is the 1 in 60 rule?
|
Each degree of track variation will result in a cross track displacement of 1 nm every 60 nm
|
|
|
Subtracting the speed of one track from another will gave the amount of closure for how long?
|
6 minutes
|
|
|
What are the considerations for speed control?
|
a) It is an ATC instruction, be specific
b) Turbulence can affect ability to fly fast or slow c) Range of acceptable speed changes with altitude (if you need to slow an aircraft consider an early descent) d) Consider profile and aircraft capabilities |
|
|
If you have a faster following aircraft but want to move the slower leading aircraft out of the way, what must you consider.
|
Turning the slower aircraft reduces its along track speed even more, so make the turn very early.
|

