![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a radar coupling?
|
The link between a system track and a flight data record.
|
|
|
What are the 4 tolerances for radar coupling?
|
1. Within 20 mins of estimated position
2. A circle of 20nm radius for ADEP / ADES in the FDRG (accounting for SID / STAR) 3. A circle of 20nm at each enroute turning point 4. Corridor 10nm either side of the calculated route |
|
|
What 4 conditions must exist for auto-coupling?
|
1. FDR must exist
2. Must be an SSR or ADS-B return squawking / squittering 3. Must be within coupling corridor 4. FPL state must be COORD or later (will not couple in INACTIVE / PRE-ACTIVE) |
|
|
State 4 reasons for using coupling corridors?
|
1. Reduces incorrect coupling
2. Prevents false updates of FDP (APR) 3. Enables off-track alert processing - RAM 4. Enables multiple use of same SSR code within FDRG |
|
|
How can you re-establish a track within the coupling the corridor if the aircraft is no longer on its initial route?
|
Using the RER function to change the route
|
|
|
If the aircraft status changes and one of the coupling requirements no longer applies, is coupling lost?
|
No, there will be a warning alert.
|
|
|
What 3 conditions must be met before a surveillance control service can be provided?
|
1. Check airspace class
2. Check type of flight 3. Aircraft must be identified |
|
|
Under normal circumstances are identified or non-identified aircraft given priority?
|
Identified
|
|
|
Must an aircraft be identified to receive a Surveillance Information Service?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Can a FLIGHT FOLLOWING information service be transferred to an adjacent sector?
|
Yes, with the new sector controller's concurrence
|
|
|
How many SSR codes are available?
|
8 x 8 x 8 x 8 = 4096
|
|
|
What is the difference between a discrete SSR code and a non-discrete SSR code?
|
A discrete code is allocated to a specific flight until that flight ends or instructed by ATC.
A non-discrete code is applied to a category of aircraft |
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil flights in classes A, C & D airspace, or IFR flights in class E airspace?
|
3000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil IFR flights in class G airspace?
|
2000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil VFR flights in class E or G airspace?
|
1200
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for military flights in class A, C, D or E airspace?
|
5000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for military flights in class G airspace?
|
6000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for civil flights not involved in special operations or SAR, operating in class G airspace in excess of 15nm off-shore?
|
4000
|
|
|
What is the SSR code of civil flights engaged in littoral surveillance?
|
7615
|
|
|
What is the SSR code for ground testing by aircraft maintenance staff?
|
2100
|
|
|
What is the SSR code assigned by Tower ATC for Tower airspace?
|
0100
|
|
|
'SQUAWK CODE 5423' - Is this correct?
|
No, do not use the word 'CODE'
|
|
|
Prior to providing a surveillance service what must ATC do?
|
Identify the aircraft
|
|
|
If an aircraft's radar ident is lost, what must ATC do?
|
Inform the pilot
|
|
|
Once radar identity is established what do ATC need to inform the PIC?
|
[callsign]
IDENTIFIED [position] - unless identification established using discrete SSR code where position is consistent with current flight plan |
|
|
Level verification is accomplished through simultaneous comparison with...?
|
a) ...altimeter derived level information received from the same aircraft by radio-telephony
b)...the aerodrome elevation during the take-off roll, provided that the level information subsequently indicates a positive climb after take-off MATS 9.8.5.4 |
|
|
Can level be verified by requesting the pilot to REPORT PRESENT LEVEL?
|
No, this permits the pilot to journalise slightly.
The request must be VERIFY LEVEL |
|
|
What is the tolerance for level verification for PADLI?
|
+/- 200ft of the level given by the PIC
|
|
|
What steps should be taken if tolerance is exceeded during level verification?
|
1. Advise pilot
2. Request check of pressure setting 3. Confirm current level MATS 9.8.5.5.1 |
|
|
A verified Mode C level may be used to...?
|
a)...apply vertical separation
b)...determine whether aircraft have maintained, vacated, passed or reached a level MATS 9.8.5.1 |
|
|
PADLI: If MCL is blank what actions can be taken?
|
Maybe a pilot or avionics problem request "SQUAWK CHARLIE"
If unable to fix, enter Pilot Reported Level in LABEL DATA |
|
|
PADLI: If MCL is incorrect what actions can be taken?
|
Maybe pilot or avionics problem request "CHECK ALTIMETER SETTING AND CONFIRM LEVEL"
If unable to fix - "STOP SQUAWK CHARLIE, WRONG INDICATION", enter Pilot Reported Level in LABEL DATA |
|
|
What is the criteria for using verified PADLI to determine when a level is being maintained?
|
Within +/- 200 ft
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the criteria for using verified PADLI to determine when a level has been vacated?
|
A change of 400 ft or more in the anticipated direction from the previously assigned level.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the criteria for using verified PADLI to determine when a level has been passed?
|
Passed the level in the required direction by 400 ft or more.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the criteria for using PADLI to determine when a level has been reached?
|
Within +/- 200 ft of the assigned level for the greater of three consecutive updates or 15 seconds.
MATS 9.8.5.2 |
|
|
What is the minima for lateral RADAR separation? What are the exceptions?
|
5nm
a) Parallel approaches in VMC (less) b) UFB (Ultimate Fall Back) degraded mode (more) c) Wake turbulence separation (more) d) TCU application (less) e) Definite passing longitudinal time standard T7d (less) MATS 10.2.2.1 |
|
|
When can 3nm separation be used in a TCU?
|
You may reduce the horizontal radar separation minimum to 3 NM, provided that
a) the aircraft are in communication with and b) under the control of either a TCU or an associated control tower providing Class C or Class D services, and are: i) within 100 NM of an MSSR sensor; or ii) within 30 NM of a radar sensor using military high definition Terminal Approach Radar (TAR) or primary data from a civil high definition TAR. MATS 10.2.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what is the required separation between two position symbols / PSR blips?
|
The centres of the position symbols / PSR blips is never less than the prescribed minimum.
MATS 10.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what is the required separation between a position symbol / PSR blip and an SSR response?
|
Centre of the position symbol / PSR blip and the nearest edge of the SSR response is never less than the prescribed minimum.
MATS 10.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what is the required separation between two SSR responses?
|
The closest edges of the SSR responses is never less than the prescribed minimum.
MATS 10.2.1.1 |
|
|
On a TAAATS display what are the conditions relating to the overlap of position symbols / PSR blips / SSR responses?
|
Do not allow the position indications to touch or overlap, under any circumstances, unless vertical separation is applied between aircraft, irrespective of the type of position indication used and the separation minimum applied.
MATS 10.2.1.1.1 |
|
|
What is the wake turbulence envelope?
|
Directly behind (within 760m laterally) another aircraft at the same level or less than 1000 ft below.
MATS 10.7.1.2 |
|
|
What aircraft are considered to be wake turbulence category Heavy if leading and Medium if following?
|
B757 - Boeing 757
H47 - Chinook H53 - Sea Stallion |
|
|
Under what 5 circumstances is wake turbulence separation not required?
|
a) When a Light aircraft will cross or follow the track of a Medium fixed wing aircraft of less than 25000 kg MTOW
b) Between an aircraft landing behind an aircraft taking off on the same runway c) If a pilot has initiated a waiver of the relevant departure wake turbulence separation minima d) For VFR flights in relation to a preceding Heavy or Medium aircraft, except on departure e) When the pilot of an IFR flight has reported the preceding aircraft in sight and has accepted responsibility for visual separation with that aircraft, except on departure MATS 10.7.1.4 |
|
|
What wake turbulence category is a C550?
|
Light
|
|
|
What wake turbulence category is a C560?
|
Medium
|
|
|
What are the distance based wake turbulence standards behind a Super Heavy?
|
Super Heavy - 4nm*
Heavy - 6nm Medium - 7nm Light - 8nm * just because you can, doesn't mean you should - there are other reasons for keeping 2 super heavies more than 4nm apart. MATS 10.7.3 |
|
|
What are the distance based wake turbulence standards behind a Heavy?
|
Heavy - 4nm
Medium - 5nm Light - 6nm |
|
|
What are the distance based wake turbulence standards behind a Medium?
|
Light - 5nm
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for CANCELLED?
|
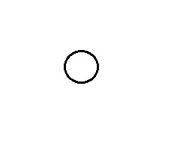
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for COMBINED TRACK?
|
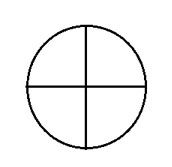
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for LAST RADAR POSITION?
|
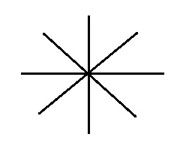
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for PRIMARY TRACK?
|
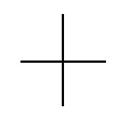
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SECONDARY TRACK?
|
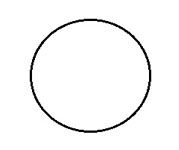
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SITE TRACKS?
|

|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 0001?
|
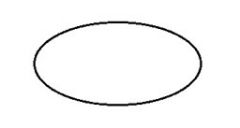
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 2000?
|

|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 0100?
|
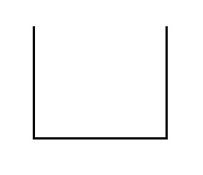
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for SSR Code 1200?
|
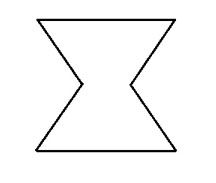
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for TEST TRACKS?
|
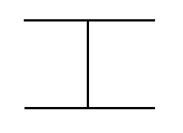
|
|
|
What is the radar track type for TRACK IN EXTRAPOLATED STATUS?
|
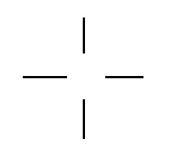
|
|
|
Give 6 reasons why you would vector?
|
a) Apply surveillance separation
b) Flow traffic c) Maximum airspace utilisation d) Noise abatement e) Hazardous weather avoidance f) Facilitate approaches MATS 9.8.10.1 |
|
|
What are prohibitions on vectoring?
|
a) Must not vector a flight plan track or an ADS-C track
b) Must not vector RADAR / ADS-B identified aircraft to avoid a flight plan track or ADS-C track c) Do not vector Special VFR except in an emergency d) Do not vector aircraft outside controlled airspace, except in an emergency. MATS 9.8.10.2 |
|
|
What are considerations that need to be made when vectoring?
|
a) Vector aircraft along or in close proximity to routes, making navigation easier if RADAR fails
b) Advise the pilot 1) reason 2) extent of & 3) expectation after the vector c) Repeat, I say again repeat, the direction of turn when 180 degrees or more; d) Agree turn rates with a pilot who reports unreliable directional instruments to make all turns at an agreed rate immediately when requested e) ensure that adequate terrain clearance exists at all times pilot resumes own navigation; f) Advise pilot sufficiently to permit own navigation in the event of radio or RADAR failure; g) Ensure that intervals between transmissions are brief, where terrain or traffic separation occur no more than 30s h) Avoid areas of known hazardous weather MATS 9.8.10.3 |
|
|
Who is responsible for terrain clearance of an aircraft in receipt of an advisory service?
|
The pilot, although ATC still have a duty of care.
|
|
|
When TCU control is vectoring an aircraft, what should be used to assign the minimum assignable altitude?
|
RTCC - RADAR Terrain Clearance Chart
|
|
|
What information is provided to the pilot when terminating a vector?
|
a) A heading as necessary to intercept the nominal track of a pilot interpreted navaid appropriate to the cleared route
b) A clearance direct to a pilot interpreted navaid for interception of the cleared route c) A clearance direct to an area navigation waypoint for interception of the aircraft's cleared route for approved SCNS aircraft |
|
|
What is the 1 in 60 rule?
|
Each degree of track variation will result in a cross track displacement of 1 nm every 60 nm
|
|
|
What are the considerations for speed control?
|
a) It is an ATC instruction, be specific
b) Turbulence can affect ability to fly fast or slow c) Range of acceptable speed changes with altitude (if you need to slow an aircraft consider an early descent) d) Consider profile and aircraft capabilities |
|
|
What is a Surveillance Information Service?
|
An on request traffic, position or navigation information service provided to assist pilots of VFR flights, within ATS surveillance system coverage in Class E & G airspace
|
|
|
What is the latest an aircraft can be established on final approach?
|
The aircraft must be established on final approach at least 2NM before commencement of the final approach (Initial Approach Fix)
|
|
|
What is the maximum angle between the intercept track and the final approach track?
|
45 degrees or less
|
|
|
When can terrain clearance be assigned to the pilot in a RADAR environment?
|
In VMC by day only, when ATC assigns responsibility for arranging obstacle clearance specifically to the pilot.
|
|
|
State the circumstances where a pilot may turn a transponder off, on onto standby?
|
Prior to departure
After arrival When changing codes |
|
|
What must be included in a Class C departure report?
|
a) Direction of turn
b) Initial heading c) altitude at which the aircraft is passing to the nearest 100ft d) last assigned level |
|
|
What is an aircraft tracking via a SID required to include in a departure report?
|
An aircraft tracking via a SID which does not incorporate initial heading instructions is only required to advise altitude passing and confirm assigned level.
|
|
|
Which flights receive a separation service in Class C airspace?
|
IFR from IFR / VFR / S.VFR
VFR from IFR S.VFR from S.VFR |
|
|
Which flights receive a separation service in Class G airspace?
|
Nil separation service provided
|
|
|
Which flights receive a separation service in Class D airspace?
|
IFR from IFR / S.VFR
S.VFR from S.VFR |

