![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
SEQUESTRUM
- remaining dead bone - the center of the infection (initial target) - sequestrum is surrounded by involucrum |
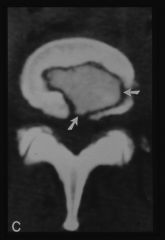
|
|
|
what is an involucrum?
|
the body's attempt to wall off the infected bone (bone may be larger in measurement)
_ often MR and CT can demonstrate a draining sinus |
|
|
what is the opening to a draining sinus (from osteomyelitis)
|
cloaca
|
|
|
What is this?
|
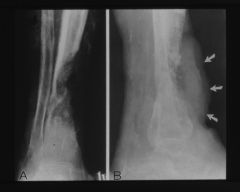
mariolin's ulcer - squamous cell carcinoma (a potential complication of osteomyelitis)
(if chunk of bone is coming out of hole in skin, then osteomyelitis) |
|
|
what are 2 possibilities when you see local lucency
|
tumor or infection
|
|
|
what is the fundamental difference between tumor and infection
|
the speed of progression
- infection - days to weeks - tumor - months to years |
|
|
respects boundaries
|
tumor
|
|
|
doesn't give a crap for any boundaries
|
infection
|
|
|
how much bone loss can you assume before any changes are seen on plain film
|
30-50%
|
|
|
what is the ideal imaging tool to recognize infection
|
MRI
|
|
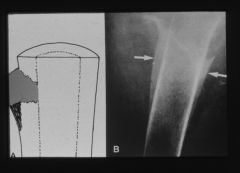
|
codman's triangle
|
|
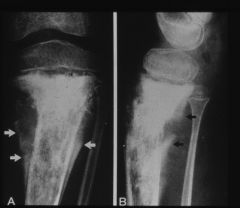
|
codman's reactive triangle and osteosarcoma of the proximal tibia
|
|
|
what is codman's cuff or triangle
|
raised periostium
*worry about aggressive process first *area will be warm, red, hyperemic, painful, tumor (swollen mass of infected tissue) |
|
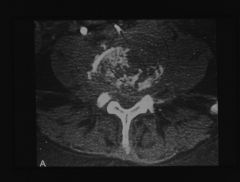
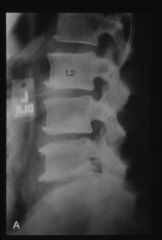
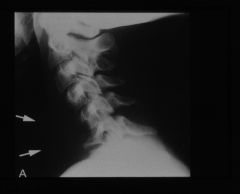
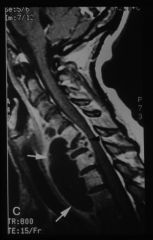
diabetic presenting with low back pain
|
sponylodiscitis
|
|
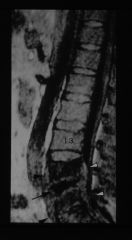
L4-L5 MRI
T2 weighted |
spondylodiscitis
|
|
|
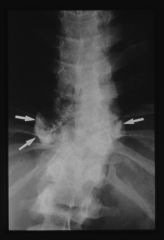
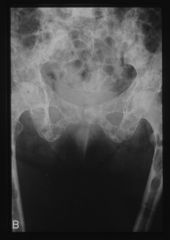
pubic diastasis
|
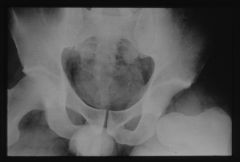
|
|
|
features of osteomyelitis
|
-corticomedullary jxn should be clear
-moth eaten (the step after permeative) -permeative - pinholes -loss of cortex **if cortical destruction, can't be benign ***must put infection first WBC and ESR probably elevated if infection |
|
|
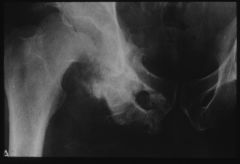
OSTEOMYELITIS OF THE ISCHIOPUBIC CHONDROSIS AP Pelvis
|
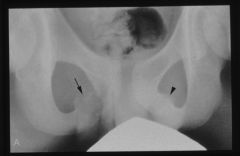
|
|
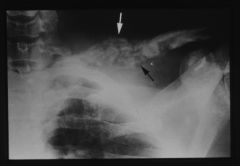
what is going on here
|
osteomyelitis of clavicle
|
|
|
what is the most common cause of osteomyelitis in the lower extremity
|
diabetes
|
|
|
2 common conditions on lower extremities
|
1- neurotrophic joint disease (atrophic or hypertrophic)
2- osteomyelitis |
|
|
bone scan for an infection is "hot"
what does a bone scan for tumor show as? |
looks normal
|
|
|
2 categories of infection
|
bacterial (suppurative)
non suppurative (tb, syphilitic) |
|
|
80-90% of all bone/jt infx are traced back to
|
staph aureus
|
|
|
pseudomonas has a reputation for affecting which joints
|
the "S" joints
spine, sacrum, sc, symphisi pubis |
|
|
infant presents with an infection involving the humerus.
|
streptococcus (as opposed the staph)
|
|
|
may show as bilateral symmetric.. passed from mother during birth
|
syphilitis
|
|
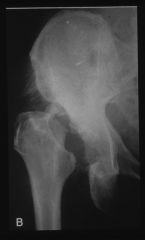
|
hypertrophic pattern neurotrophic jt disease..pt has syphilis
|
|
|
syphilis neurotrophic joint dis. atrophic pattern
|
|
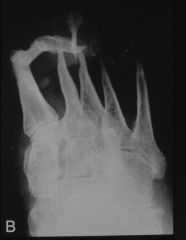
|
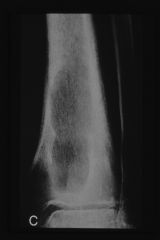
neurotrophic
atrophic pattern diabetic foot |
|
|
lumbar neurotrophic jt disease
syphilis |
|
|
brodies abscess
|
|
|
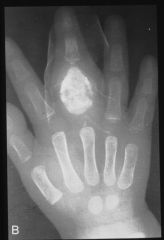
what the heck is brodie's abscess
|
suppurative
lucency w/in the medullary cavity walled off suppurative infx (ie staff) tx is to dig it out aspirin provides relief |
|
|
night pain relieved by aspirin
|
brodies abscess or osteoid osteoma.
need MRI to distinguish (brodies-intramedullary, osteoid osteoma-periosteal) |
|
|
target sign, bull's eye sign
|
ie: proximal tibia
subtle lucency that is magnified on bone scan and MRI |
|
|
use of coca and crack is exacerbating the problem with
|
resistant strains of TB
|
|
|
TB will effect lung or bone first
|
lung - upper lobe (pulmonary nodules and ghon complex)
|
|
|
primary skeletal sight for TB
|
TL jxn
|
|
|
TB suppurative or non-suppurative
|
nonsuppurative
|
|
|
potts paraplegia
progressive myelopathy (cord damage) |
|
|
what happens when TB invades and damages tissue
|
distrophic calcification
|
|
|
tubercular dactylitis
|
|
|
|
facts assoc with TB dactylitis
|
inflamm of fingers and toes, resulting in sausage shaped appearance of digits
soft tissue swelling looks like infx but long duration of symptoms |
|
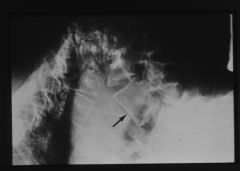
|
TB gibbus deformity
|
|
|
wimberger's signs of syphilis
|
erosion of medial, proximal part of tibia
(wimberger's sign of scurvey--epiphysis has a bright white ring) |
|
|
saber shin
(syphilis) |
the organism weakens the bone -> anterior bowing of the tibia
solid periosteal reaction that ossifies and adds to the impression of diameter increase |
|
|
stages of syphilis
|
periostitis
metaphysitis osteitis |
|
|
blastomycosis
|
|
blastomycosis
|
|
|
|
blastomycosis
|
|
|
blastomycosis
|
blastomycosis
|
|
|
mostly found on us canadian border
starts in the lungs |
blastomycosis
|
|
|
coccidiomycosis
|
dry climates of SW
starts in lung and disseminates to skeleton attacks bony projections remember that poodles leg pic he showed in class |
|
|
histoplasmosis
|
not a skeletal complaint
polk-a-dots in the chest mississippi river valley lung, liver, and spleen are prime targets |
|
|
most frequent form of osteoporosis
|
post menopausal
|
|
|
_____ will soon replace post menopausal osteoporosis as life expectancy increases
|
senile osteoporosis
|
|
|
w/ osteoporosis what structurally stands out
|
accentuation of the vertical trabeculae
|
|
|
most frequent site of compression fracture
|
T12, T11, L1
compression fractures at unusual locations are a possible sign of pathology |
|
|
facts about regionalized osteoporosis
|
reflex sympathetic dystrophy
(RSD) unilateral trab bone loss in phalanges, metacarpals raynauds translucent skin tactile sensitivity suicide is frequent cause of death smiths or colles fx common no known tx, but chiro can help |
|
|
most common benign tumor of the spine
|
hemangioma
(corduroy vertebra) thickened trab bone due to coalescence |
|
|
bowed long bones
zpc is blended with surrounding bone rosary bead appearance (bumps at costochondral junctions) |
rickets
|
|
|
rickets rarifies the zpc and _____ sclerosis the zpc
|
scurvy
|
|
|
sandwich vertebra
|
osteopetrosis
|
|
|
rugger jersey spine
|
hyperparathyroid
|
|
|
primary hyperparathyroidism
|
tumor
metastatic calcification |
|
|
secondary hyperparathyroidism
|
kidney disease
|
|
|
tertiary hyperparathyroidism
|
end stage renal failure
pt on dialysis (dialysis wastes calcium) pt should be on Ca & vit D otherwise too much Ca is taken from the bones |
|
|
lantern jaw
|
prognathism
assoc w/ acromegaly |
|
|
lead intoxication
|
in growing bone, lead is easily integrated
*very dense zpc |
|
|
examples and facts about histiocytosis x
|
eosinophilic granuloma
silver dollar sign in the spine spontaneous resolution is common missing bone appearance --expect it to self resolve and fill in on its own |
|
|
3 patterns of osteopenia
|
generalized
regionalized localized |
|
|
generalized
|
osteopenia affecting the majority of the skeleton
senile ost.. post menopausal hpt cushings wide spread malignancy |
|
|
regionalized
|
osteopenia affecting one limb or section of the body
disuse atrophy reflex sympathetic dystrophy transient regional osteo regional migratory osteo |
|
|
localized
|
focal osteopenia in one or multiple discrete locations in bone (most worrisome)
lytic metastasis osteomyelitis inflammatory arthritides |
|
|
ant aspect of vertebral body is smaller than the post portion
|
wedged shaped fx
|
|
|
uniform vertebral body height
aggressive pattern of collapse most either tumor or infx |
vertebra plana
|
|
|
angular end plate deformity (aka check sign)
|
most are path fx
a small # are simple benign compression deformity, but must first rule out the aggressive diagnosis |
|
|
as the femur is devoid of visible trabeculae, we lose the sight of
|
ward's triangle
(lucent triangle formed by 3 diff tab pattern in the femur) |

