![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What illicits an immune response?
|
antigens
|
|
|
What are the four hallmarks to the Specific Immunity
|
1. SPECIFICITY - for one antigen
2. DIVERSITY - able to recognize millions of different molecules as antigens 3. LEARNED - response (adaptation - antigen presenting cells such as macrophages) 4. MEMORY - remembered response 1st encounter/exposure gives rise to long term memory response |
|
|
____ aka Specific Immunity
|
Adaptive or Acquire Immunity
|
|
|
Which response is this:
1. extremely specific 2. adaptation period |
Primary Response
(1st encounter) |
|
|
Which response is this:
1. long-term memory (exposure) 2. rapid and powerful |
Secondary Response
(Most PROTECTIVE) |
|
|
These are ____
gamma globulins = imunnoglobulins (Igs) = antibodies (Abs) |
immune proteins
B-Cells |
|
|
Describe the B-Cell cycle
|
a recombination of mitosis of lymphocytes gives great diversity
1. produce antibodies 2. naive lymphocytes never encounter their antigen (Ag) 3. Upon encounter, triggers protective development and maturation |
|
|
What is the antigenic determinant?
|
EPITOPE
the part that is recognized by the antibody |
|
|
What is the symbol for antibody?
|
a Y
|
|
|
What are the three parts of the antibody structure (think Y)
|
Antigen binding site
Hinge region (disulfide bonds) Fc Stem Region (aka constant region) |
|
|
What part of the antibody structure flags for phagocytosis opsonins?
|
The CONSTANT or Fc STEM region
|
|
|
Which region of the antibody structure is able to BIND to different regions?
|
The VARIABLE region of the Y (the arms of the structure)
|
|
|
What is
Agglutination |
binding; when two or more antigens are bound simultaneously by the same antibody
|
|
|
Igs
|
Immunoglobulins which are gamma globulins which are antibodies (Abs)
|
|
|
What are the five classes of Igs?
|
IgG - Monomer *smallest, passes through placenta, present in baby's blood*
IgM - Pentamer *very large, major agglutinator, first produced in immuno response* IgA - Dimer in secretions *ie breast milk provides protection of mucous membranes* IgD - Monomer *antigen receptor on B lymphocytes* IgE - Monomer *involved in many allergic rxns* |
|
|
Which class of Igs is
very large and the first produced in immune response? |
IgM a pentamer shape
|
|
|
What is the life of and total blood serum level
IgM |
10 days
5 to 10% |
|
|
What is the life of and total blood serum level
IgG |
80 to 85%
21 days (this one crosses the placenta!) |
|
|
What is the life of and total blood serum level
IgA |
10%
6 days Secretions |
|
|
What is the life of and total blood serum level
IgD |
<1%
3 days |
|
|
What is the life of and total blood serum level
IgE |
smallest percent of blood <.01%
allergic rxn over release of histamines 2 days |
|
|
At birth does a baby have IgGs?
|
No, child will obtain in mother's milk while bone marrow matures and produces cells (about 2 years for immune system to develop)
|
|
|
Humoral Immunity
(ie blood, interstitial) |
found in body fluids
|
|
|
Cellular Immunity
|
extracellular fluids
|
|
|
Which cells are involved in antibody mediated immunity?
|
B-Cells
undergo clonal selection that leads to MEMORY cells and PROLIFERATION of EFFECTOR cells which go into PLASMA Cells |
|
|
List the 6 protective outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding
|
1. Agglutination
2. Opsonization 3. Neutralization 4. Activation of Complement 5. Inflammation 6. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) |
|
|
What is ADCC?
|
Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity
or TOUCH KILLING of large parasites |
|
|
With regards to outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding describe
Agglutination |
enhances phagocytosis thereby reducing the # of infectious units to be dealt with
|
|
|
With regards to outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding describe
Opsonization |
coats antigen with antibody to enhance phagocytosis
|
|
|
With regards to outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding describe
Neutralization |
Blocks adhesion of bacteria and viruses to mucosa and
blocks active site of toxin |
|
|
With regards to outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding describe
Activation of Complement |
cell lysis
causes cell to split |
|
|
With regards to outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding describe
Inflammation |
w/ complement activation
disruption of cell protein attracts phagocytic and other defensive immune system cells |
|
|
With regards to outcomes of Ag-Ab Binding describe
Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) |
antibodies attach to target cell cause destruction by non-specific immune system cells
|
|
|
ADCC
Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity |
Fc or Constante Region of the Ab cell is drawn to parasite
1. RECOGNITION of surface 2. ATTACHES leaving Fc FLAG to attract eosinophils and macrophages |
|
|
Which cell releases cytokines and lytic enzymes:
Macrophages or Eosinophils? |
Macrophages
|
|
|
Which cell releases perforin and lytic enzymes:
Macrophages or Eosinophils? |
Eosinophils
|
|
|
Apoptosis
|
touch killing
|
|
|
What are the two circumstances for NK cells?
|
1. Fc receptors on NK cells bind to attached Ab on cells
2. Host cells do not have MHC markers proclaiming "cells" |
|
|
NK Cells
|
Natural Killer Cells destroy Ab coated infected or tumor cells and parasites by touch killing
|
|
|
MHC markers
|
lead to self tolerant of cells that are self (unique to each person)
|
|
|
Which immune cell is an extracellular antigen?
|
T-Cytotoxic cell
|
|
|
Define Perforin
|
Perforin found in cytotoxic T cells create holes which allow proteases entry into cytoplasm inducing apoptosis
|
|
|
What are the three antigen presenting cells (MHC II)?
|
Macrophages
Dendritic Cells B-Cells |
|
|
MHC I
|
marker cells that identifies cells as "self"
|
|
|
Which cells activate B-Cells?
|
T-Cells
also may release NK cells |
|
|
Which cells act as judges?
|
Th cells determine which cells go to clonal selection or are non-self for destruction.
|
|
|
Of the bloods cells which ones do not carry MHC I markers?
|
Red Blood Cells or
ERYTHROCYTES |
|
|
CD4+
|
Th cells
T helper cells (a "marker" type of WBC) |
|
|
CD8+
|
Tc cell receptor (a "marker" type of WBC)
|
|
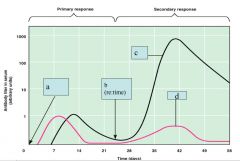
Identify the letters.
|
A. Initial exposure to antigen
B. Second exposure to antigen C. IgG (smallest of antibodies) D. IgM (largest of antibodies) |
|
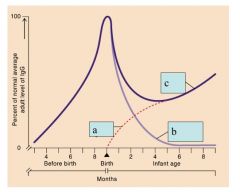
Identify the letters.
|
A. Infant IgG
B. Maternal IgG C. Total IgG |
|
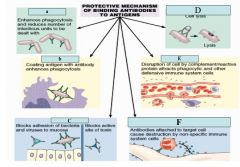
Identify each letter.
|
A. Agglutination
B. Opsonization C. Neutralization D. Activation of complement E. Inflammation F. Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity |

