![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
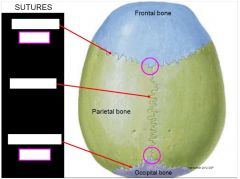
|
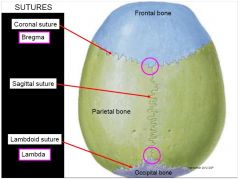
|
|
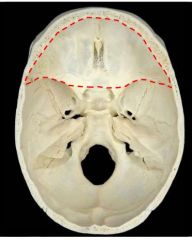
Which fossa is this, what is contained here, and what forms its borders??
|
Anterior cranial fossa
Houses the frontal lobes Anterior border is formed by the cribriform plate from the ethmoid bone - Crista galli dividing it in half Posterior border is formed by the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone |
|
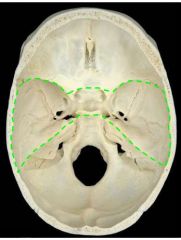
What fossa is this, what is contained here, and what forms its borders?
|
Middle cranial fossa
Houses the temporal lobes Formed by the body of the sphenoid - Cella turcica - Central air sinus - Clinoid processes Lateral borders: - Anterior: lesser wing of sphenoid - Posterior: superior edge of petrous bone - Lateral: squamous part of temporal bone Floor: - Greater wing of sphenoid - Anterior surface of petrous bone |
|
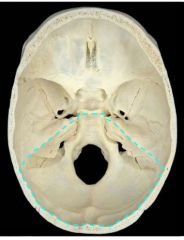
What is this fossa, what is contained in it, and what forms its borders?
|
Posterior cranial fossa
Anterior border: - Superior petrous and temporal Floor: - Posterior petrous, squamous, and basal occipital Contains foramen magnum |
|
|
|
|
|
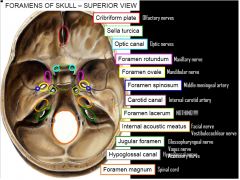
What goes through the cribriform plate?
|
CN I (olfactory)
|
|
|
What goes through the optic canal?
|
CN II (optic)
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen rotundum?
|
V2 (maxillary) of CN V (trigeminal)
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen ovale?
|
V3 (mandibular) of CN V (trigemial)
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen spinosum?
|
Middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
What goes through the carotid canal?
|
Internal carotid artery
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen lacerum?
|
Internal carotid artery (from carotid canal)
|
|
|
What goes through the internal acoustic meatus?
|
CN VII (facial)
CN VIII (vestibulocochlear) |
|
|
What goes through the jugular foramen?
|
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
CN X (vagus) CN XI (spinal accessory) |
|
|
What goes through the hypoglossal canal?
|
CN XII (hypoglossal)
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen magnum?
|
Spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the four paranasal sinuses?
|
Frontal
Ethmoid Sphenoid Maxillary |
|
|
Where are the frontal sinuses found and what are their drainage patterns?
|
Found between outer and inner tables of the frontal bone
Drainage: - Frontonasal duct - Middle nasal meatus |
|
|
Where are the ethmoid sinuses found and what are their drainage patterns?
|
Found between the orbit and nasal cavity
Drainage: - Anterior and middle groups through the middle nasal meatus - Posterior group through the superior nasal meatus |
|
|
Where are the sphenoid sinuses found and what are their drainage patterns?
|
Found in the body of the sphenoid bone
Drainage: - Sphenoethmoidal recess - Superior nasal meatus |
|
|
Where are the maxillary sinuses found and what are their drainage patterns?
|
Found above the maxilla and palate
Drainage: - Middle nasal meatus |
|
|
What are the layers of the scalp?
|
Skin
Connective tissue Aponeurosis - Between frontalis and occipitalis muscles Loose connective tissue Pericranium |
|
|
What supplies arterial blood to the anterior and superior aspects of the scalp?
|
Branches from the ophthalmic artery
- Supratrochlear - Supraorbital |
|
|
What supplies arterial blood to the scalp, not including the anterior and superior aspects?
|
Branches from the external carotid
- Superficial temporal - Posterior auricular - Occipital |
|
|
What are the layers of the head from outermost to innermost?
|
Scalp
Skull Extra/epidural space Dura mater (2 layers) Subdural space Arachnoid mater Subarachnoid space Pia mater |
|
|
What are the layers of the dura mater?
|
Outer periosteal layer
Inner meingeal layer |
|
|
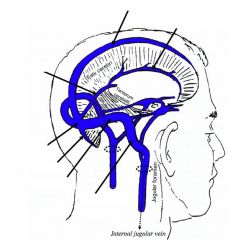
What are the dural partitions?
|
Falx cerebri
Falx cerebelli Tentorium cerebelli Diaphragma sellae - Above pituitary |
|
|
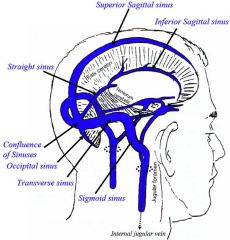
|
|
|
What is found in the cavernous sinuses?
|
Internal carotid artery
CN III (oculomoter) CN IV (trochlear) V1 (ophthalmic) of CN V (trigeminal) V2 (maxillary) of CN V (trigeminal) CN VI (abducens) |
|
|
What supplies the dura mater with arterial blood in these areas:
- Anterior cranial fossa - Middle cranial fossa - Posterior cranial fossa |
Meningeal arteries in the outer periosteal layer
Anterior cranial fossa: - Anterior meningeal artery (ethmoidal arteries) Middle cranial fossa - Middle meningeal artery (maxillary artery) - Accessory meningeal artery (maxillary artery) Posterior cranial fossa - Posterior meningeal artery (ascending pharyngeal artery) - Other meningeal branches from the ascending pharyngeal artery, occipital artery, and vertebral artery |
|
|
What innervates the dura mater?
|
Small meningeal branches of:
- V1 (ophthalmic) of CN V (trigeminal) - V2 (maxillary) of CN V (trigeminal) - V3 (mandibular) of CN V (trigeminal) - CN X (vagus) - Spinal nerves C1, C2, C3 |
|
|
Through what does CSF flow in the subarachnoid space?
|
Cisterns
|
|
|
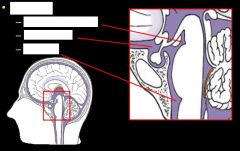
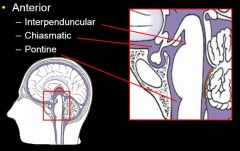
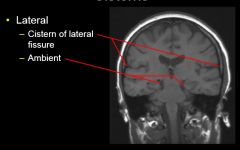
What are the four major subarachnoid cisterna?
|
Anterior
Posterior Lateral Lumbar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What produces CSF and where is this found?
|
Choroid plexus
Found in the superior parts of all ventricles except for the cerebral aqueduct |
|
|
What are the ventricles found in the brain?
|
Lateral (2)
Third Fourth |
|
|
What is the path of CSF flow through the ventricles?
|
1. Begins in the lateral ventricles
2. Flows through the interventricular foramen of monro to the third ventricle 3. Flows down the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle |

