![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the six fibromyalgia drugs? Which ones are used "off label?" |
Duloxetine Milnacipran Pregabalin
Amitripyline* Cyclobenzaprine* Fluoxetine* |
|
|
What is a suspected cause of fibromyalgia? |
Elevated neurotransmitter function in the ascending pathways of the spinal cord and dimishined levels in the descending, modulatory pathways
Amplification of all nociceptive signals arriving in the brain from peripheral tissues |
|
|
What are some fibromyalgia symptoms? |
Stiffness Unrefreshing sleep Tension headache IBS Difficulty concentration and cognitive function Depression/mood disorders RLS Vaginal pain and dryness Painful menstrual periods Irritable bladder and urinary complaints |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action for Duloxetine and Milnacipran? What category of drugs?
Differences between action on neurotransmitters? |
Serotonin-Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
Duloxetine = SER >NE Milnacipran = NE > SER |
|
|
How is Duloxetine metabolized and eliminated? How is this different from Milnacipran? |
Duloxetine = CYP2D6 metabolism and inhibition => urinary metabolites
Milnacipran = no CYP metabolism => urinary elimintion |
|
|
What patients should not receive duloxetine and milnacipran? |
Severe liver dysfunction, chronic alcoholics, pre-existing CV issues, closed angle-glaucoma |
|
|
What class of drugs should you never use with duloxetine and milnacipran? |
MAOIs |
|
|
What are adverse affects of both duloxetine and milnacipran?
BBWs for what? |
Mild HR and BP increases, hyponatremia from SIADH
BBW = Suicidal ideation |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Pregabalin? What drug class is it related to? |
Anti-seizure durgs
Inhibits presynaptic alpha-2-delta subunits of L-type calcium channels => inhibit excitatory transmission by glutamate => alleviates neuropathic pain, anxiety, and pain syndromes |
|
|
Pregabalin is a schedule ____ drug. |
V |
|
|
How is pregabalin eliminated?
Should you reduce dose if renal dysfunction/failure?
|
Unchanged renal, renal tubular absorption
Yes! |
|
|
What are some AEs from Pregabalin? (think depression medication) |
Withdrawal => rebound worsening of symptoms Monitor for depression/suicide Dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, xerostomia |
|
|
What are the four skeletal muscle relaxer drugs? |
Carisoprodol Cyclobenzaprine Methocarbamol Tizanidine |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of carisoprodol? |
CNS action in reticular activating system and spinal cord => sedation and altered perception of pain
NO DIRECT EFFECT ON neuronal conduction, neuromuscular transmission, or muscle excitability |
|
|
How is carisoprodol metabolized/eliminated? Should you worry about hepatic and renal dysfunction? |
CYP2C19 = > less active compounds eliminated in urine
YES! |
|
|
What are some AEs/cautions with Carisoprodol? |
CNS drug so think CNS effects => dizziness, drowsiness, other CNS manifestations (agitation, insomnia, vertigo, ataxia, etc.)
DON'T COMBINE WITH OTHER SEDATIVES! |
|
|
Mechanism of action of cyclobenzaprine? |
Central action at level of brainstem |
|
|
Metabolism/elimination of cyclobenzaprine? Should you worry about old people and liver dysfunction? |
Enterohepatic recirculation, extensive CYP metabolism (3A4, 1A2, 2D6). YES! |
|
|
Side effects of cyclobenzaprine (general) and two serious things to watch out for! |
General = anticholinergic effects (TCA) = drowsiness, xerostomia, fatigue, N/V
Paralytic ileus and QT prolongation! |
|
|
What should you not combine with cyclozenaprine? |
Additive effects with anticholinergics Additive CNS depression with depressant drugs and alcohol |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of methocarbamol? How is it administered? |
Generalized sedative effect (no direct effect on muscle or excitation-contraction coupling).
Oral, IM, IV |
|
|
How is methocarbamol metabolized/eliminated?
Should you worry about toxicity with impaired kidney or liver? |
HEPATIC dealkylation and hydroxylation with URINARY elimination
Yes yes! |
|
|
What are some AEs associated with methocarbamol? (nothing really out of the ordinary) |
Additive CNS depression with other depressant drugs and alcohol
Common AEs = N/V, etc. |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Tizanidine?
It reduces muscle_______ but NOT ________.
|
Pre-synaptic alpha-2 agonist => decreased activation of polysynaptic spinal cord motor neurons
Reduces muscle TONE but NOT STRENGTH |
|
|
How is tizanidine eliminated?
Should you titrate the dose in the elderly or renal patients? |
First pass metabolism -> short half life, renal clearance of long-lasting metabolites!
YES!
|
|
|
What are some AEs of Tizanidine? What should you monitor?
What is a weird thing about administration of this drug?
With what drugs should you worry about additive effects?
What are the common side effects typical of? |
Hepatocellular toxicity (LFTs)
Need to TAPER drug to avoid rebound hypertonicity, tachycardia, hypertension
Additive CNS Additive HYPOTENSION with clonidine, methyldopa, guafacine, or guanabenz
Alpha-2 agonist effects (dizziness, asthenia, xerostomia, sedation, etc.)
|
|
|
What are the four drugs used for spasticity? |
Baclofen Botulinum toxin Dantrolene Tizanidine |
|
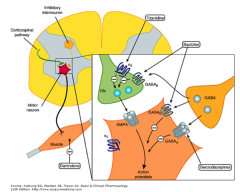
Notice where each spasticity drug acts! |
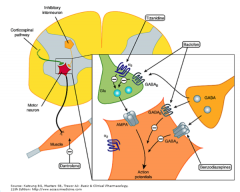
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Baclofen? |
GABA agonist = inhibitory signals or hyperpolarizing => reduces excitatory (aspartate and glutamate) polysynaptic pathways
Pain relief from inhibition of substance P action |
|
|
How is Baclofen eliminated? What can drug accumulation lead to? |
Renally!
Encephalopathy, abdominal pain, seizures, and respiratory depression |
|
|
What are some AEs of baclofen? BBW? Additive effects with what? What is increased in the blood with baclofen (think diabetics)? |
BBW = abrupt discontinuance = crazy CNS effects, taper for 2 or more weeks
Additive CNS depression with other depressants Additive hypotension with antihypertensive agents and MAOIs
Dose adjust diabetic therapy = increased BLOOD GLUCOSE
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Dantrolene?
What unusual condition is it useful in treating (think "hot")? |
Decreases muscle contraction by interfering with ryanodine receptor with calcium ion release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum within skeletal muscle cells.
Malignant hyperthermia |
|
|
What is the dosing route of dantrolene? |
Oral or IV dosing (thrombophlebitis sometimes) |
|
|
What does dantrolene produce if used during Caesarean section? Why? |
"Floppy child syndrome"
Crosses placenta! |
|
|
What are some cautions for dantrolene? Think common stuff. What happens when combined with Ca2+ blocker (that's a lot of calcium you are stopping)?
Think about what would happen if you gave too much! |

|
|
|
Don't forget botulinum toxin! |
Botulinum toxin! |
|
|
How are all the fibromyalgia drugs classified? |
Centrally acting! Sedating, little evidence that they do any good at all. |
|
|
How does pregabalin work? |
Blocks glutamate presynaptically |
|
|
Which characteristic is common to drugs used to relax skeletal muscle? |
Sedation |
|
|
Which drug also produces anticholinergic effects? |
Cyclobenzaprine |
|
|
Which drug produces an effect on the same family of receptors as diazepam? |
Baclofen (acts on GABA-B instead of GABA-A like valium) |
|
|
Should a patient taking baclofen stop drug therapy without physician guidance? What is the adverse effect? |
NO! => seizures, pyschiatric distrubanes, hallucinations, etc. (become a crazy person...) |

