![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are barriers to drug uptake?
|
Gut mucosa
Liver |
|
|
How are drugs returned from the liver to the gut?
|
Bile
|
|
|
What is hepatic clearance?
|
The rate of removal of drugs/xenobiotics from the blood
|
|
|
What are the factors that effect hepatic clearance?
|
Liver blood flow
Liver intrinsic clearance Fraction of drug not bound to albumin |
|
|
What's the formula for hepatic clearance of drugs?
|

|
|
|
What is the hepatic clearance formula for high extraction drugs?
|
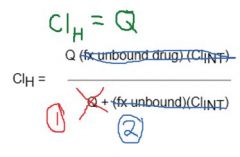
|
|
|
What are drugs that are high extraction?
|
Nitroglycerine
Lidocaine Propanolol (10% makes it through.) Bile acids |
|
|
What's the difference in dosing for proparnolol IV vs. oral? Why?
|
Oral is 10x higher
Only 10% makes it through the liver. |
|
|
Why is the liver highly efficient at extracting drug-like compounds?
|
It doesn't want bile acids in systemic circulation
|
|
|
What is the formula for low-extraction drugs?
|

|
|
|
What are some drugs that are low-extraction?
|
Diazepam
Phenytoin Theophylline Bilirubin |
|
|
What is the bioavailability of a drug that is low extraction?
|
High! You want to give these drugs orally
|
|
|
How does the liver get rid of drugs?
|
Uptake
Biotransormation! Phase I: P450s Phase II: Conjugation |
|
|
Typically what kinds of compounds are taken care of by the liver?
|
Large
Lipophilic Liver |
|
|
After the liver, where do biotransoformed drugs go?
|
Biliary excretion
Efflux to blood for eventual renal excretion |
|
|
Where do the biotransormation reactions take place in the cell?
|
On the outside of the ER
|
|
|
What are the phase 1 reactions?
|
Oxidative reactions
CYP-mediated reactions Add reactive/hydrophilic groups |
|
|
What are the phase 2 reactions?
|
Conjugation to a polar ligant
Glucuronyl transferases Sulfotransferases Glutathione-S transferases |
|
|
What occurs during the phase 1 reactions of biotransofmration?
|
Direct modification of primary structure
Often, because there are a limited amount of enzymes, there are drug-drug interactions |
|
|
What accounts for variability in peoples response to drugs?
|
Genetic polymorphisms in the phase 1 reactants of biltransformation
|
|
|
What are the most important CYPs?
|
CYP3A4
CYP2D6 CYP2C |
|
|
What does the differential effects of codeine on different people explain about biotransformation?
|
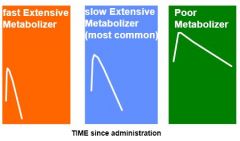
Some people metabolize fast, some slow
If the drugs isn't effective, it could be that they never convert the prodrug (codeine) into the active form (morphine) |
|
|
What groups are often added during phase 2 of biotransofmation?
|
Glucuronic acid
Sulfate Glutathione AAs |
|
|
What is the overall effect of conjugation during phase II of biotransformation?
|
Increase water solubility
|
|
|
What are some examples of endogenous conjugation?
|
Bilirubin and glucuronide
Bile acids and glycine/taurine |
|
|
What other molecules are transported by the bilirubin trasnporter?
|
Organic anions
Glutathione S-conjugates |
|
|
What transporter causes cells to be resistant to chemo?
|
MDR
|
|
|
What other part of the body is involved in drug metabolism?
|
Gut!
it has CYPs, MDR transpoters |
|
|
What are the principles of drug-drug interactions?
|
Competitive inhibition of a CYP
Induction of CYP by certain drugs |
|
|
What P450 metabolizes cyclosporin? Why is this a problem with transplants?
|
CYP3A4
Lots of other drugs are metabolized by 3A4...leads to toxic effects of cyclosporin (kidney disease, neurologic signs) |
|
|
What is the effect of rifampin on CYP3A4? What is the effect?
|
Induces CYP3A4 RAPIDLY!!!
You're going to have super low levels of drugs in your body |
|
|
What is the most important thing to remember with Drug-Drug interactions?
|
Quite frankly, you've just got to keep them in mind.
Data is given about what 3A4s are used for different compounds...look them up! |
|
|
What are the different causes of drug-induced liver disease?
|
Hepatocellular injury
Autoimmune hepatocellular injury Cholestatis liver injury |
|
|
What drugs can cause hepatocellular injury?
|
Isoniazid
Acetaminophen |
|
|
What drugs can cause autoimmmune hepatocellular injury?
|
Halothane
|
|
|
What drugs can cause cholestatis liver injury?
|
Estrogen
|
|
|
What's the cause of acetaminophen toxicity?
|
Creation of toxic metabolites by the CYPS instead of being glucuronidated.
This is caused by too high levels of the drug shunting compounds down a toxic pathway |
|
|
What's the antidote to acetaminophen toxicity? How does it work?
|
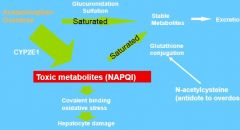
N-acetylcysteine
You induce glutathione production, which allows to creation of stable metabolites |
|
|
What part of the liver has all the P450's?
|
The pericentral area
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of drug-induced autoimmune liver disease in halothane hepatitis?
|
You get a binding of the drug to the CYP at a site that causes antigen formation.
Then, you have a problem that the antigen recognizes the CYP and starts to kill liver cells |
|
|
What are some other types of drug-induced liver injury/
|
Bile duct injury
Steatosis Vascular injury neoplasms |
|
|
What is the effect of alcohol on the liver?
|
Induction of CYP2E1
This is the cytochrome that creates toxic metabolites of acetaminophen |
|
|
How do you dose drugs in people with liver failure?
|
If it's an efficiently cleared drug: lower levels!
Low clearance drug: little effects until ESLD |
|
|
Why is it that cirrhotic patients have problems with high-clearance drugs?
|
There are shunts around the liver!
|
|
|
What is the effect of cirrhosis on:
Susceptibility to idiosyncratic drug reactions? Likelihood of autoimmune-mediated drug reactions? |
NOTHING!
|
|
|
How do you tell if a drug is high extraction?
|
IV dose vs. the Oral dose
If the oral dose is higher than the IV, high extraction |

