![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do 20% of patients with jaundice and DILD progress to? |

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
When can drug injury occur with DILD (days)? What is the triad (rare)? |

|
|
|
Is DILD a diagnosis of exclusion? |

|
|

What might you suspect? |
DILD |
|
|
Is repeated exposure required for DILD? Can even small doses result in severe liver injury? |

|
|

|

|
|
What is the drug? |
Very reproducible injury from carbon tetrachloride => often unpredictable in humans however. |
|

What type of hepatotoxin? |
Idiosyncratic => OFTEN VERY UNPREDICTABLE IN HUMANS |
|

What can all of these drugs cause? |
DILD |
|

What can all of these cause? |
Hepatocellular injury DILD can mimic all of these. |
|

What can all of these cause? |
Cholestatic injury |
|
|
What extremely commonly used drug can cause liver injury? |

|
|
|
What type of injury is caused by oral contraceptives? What type of cholestasis? What is estrogen's effect on membrane fluidity? What pump is affected? |

|
|

Generally don't do liver biopsy on oral contraceptive induced cholestasis => just stop the drug and see how they do. |

|
|
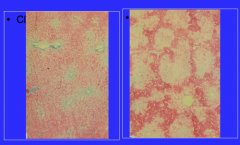
What can all of these be caused by? |
Oral contraceptives Budd Chiari = blood goes to the liver and cannot leave => becomes blood filled and enlarged |
|

What can these be caused by? |
Oral contraceptives |
|

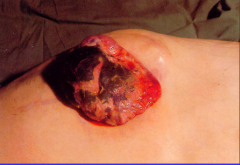
Person on oral contraceptive with hypotension. What is going on? |
Bruise on right side => hepatic adenoma => sometimes have spontaneous hemorrhage |
|

What is this? |
Hepatic adenoma => spontaneous hemorrhage sometimes |
|

What is shown? |
Hepatic adenoma with hemorrhage |
|

What is shown? |
Hepatic adenoma with hemorrhage |
|

|

|
|
What is the tumor type? |
Angiosarcoma |
|
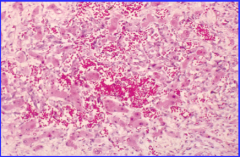
Tumor type? (notice all the blood) |
Angiosarcoma |
|
|
Patient present with hepatomegaly, elevated alkaline phosphatase, >70% pathogenesis unknown, 25 patients diagnosed per year in the US? |
Angiosarcoma |
|
|
Does angiosarcoma often have cirrhosis in addition to angiosarcoma? |
Yep |
|
|
What chemical caused an increased in angiosarcoma? |

|
|

What is the drug? |

Acetaminophen |
|
|
What drug causes 85% of OTC poisonings? |

|
|

|
? |
|
|
What were the top three causes of acute liver failure? |

|
|
|
What patients had the greatest transplant survival rate? (what type of liver injury) |

Most acetaminophen injuries survive without transplant. |
|
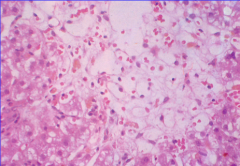
What is shown here? |
Acetaminophen injury around central zone (3). Shotgun blast of injury. |
|

Elevation of liver enzymes after acetaminophen injury |
? |
|

Understand this pathway. |
Most will be oxidized safely If system overloaded => toxic metabolite bound to glutathione (safe way) or everything else will be oxidized => high levels of toxic metabolites. |
|
|
What are the effects of acetaminophen and ethanol on glutathione, P450 induction, toxic metabolites? |

|
|
|
What is unsafe at low doses in alcoholics (drug)? Patients with cirrhosis from other causes often have decreased _____ activity and normal ____ levels. |

Fever from bacterial pneumonia, cirrhosis => probably want to avoid aspirin, acetaminophen should be a safe alternative (even through they have cirrhosis). LIVER PATIENTS OFTEN HAVE IMPAIRED OXIDATION! Patients must be ACTIVELY drinking to have decreased glutathione levels. |
|

Table for overdoses (completely useless now) |

|
|
|
What is the treatment for ethanol+acetominophen injury? |

IV dose now also |
|

Where does antidote act? |
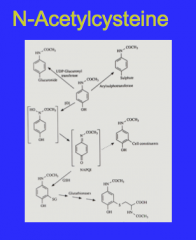
Repletes glutathione |
|
|
Can you give N-acetylcysteine even with late presentation? |

Works even if given late. |
|

|

|
|
|
With acute liver injury, always consider what at low doses in the setting of ethanol abuse?
If you are not sure, what drug do you give anyway? |

|
|
|
What should you always consider in every patient with liver disease? |

|
|

|

|
|

What are some of the various components of drug-induced liver injury? |

|
|
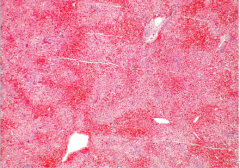
What is this necrosis from? |
Massive hemorrhagic hepatic necrosis due to acetaminophen with only a few periportal hepatocytes surviving. |
|
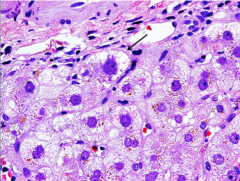
What type of degeneration (worst at arrow) can be due to drugs? |
Hepatocyte hydropic degeneration |
|
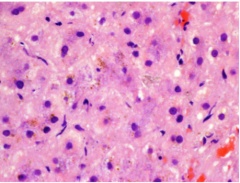
What are the golden granules in the hepatocytes? What is the condition due to the drug chlorpromazine? |
Cholestasis |
|
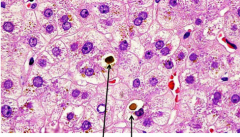
Can cholestais be canalicular too? |

|
|
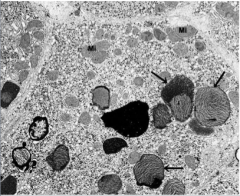
What drug can cause steatohepatitis, Mallory-Denk bodies, or granulomas, but its most distinctive hepatotoxicity is phospholipidosis?
What is the mechanism? |

|
|
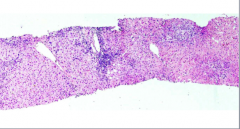
What is the condition shown here? |

|
|
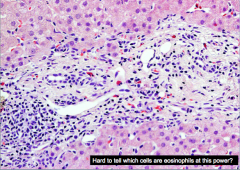
What type of damage shown here? (what condition)? |

|
|
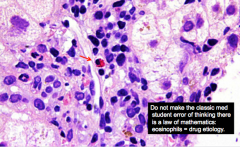
What is shown at the red arrow? |
Eosinophil |
|
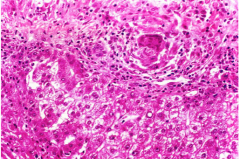
What type of hepatitis? |

|
|
|
What can be used to determine the morphologic type of drug-induced liver disease? Is it necessary? What are some of the risks? |

|
|
|
Again, what are the four hepatotoxins? |

|

