![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
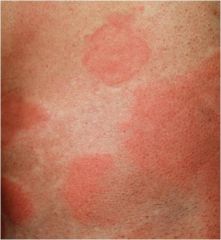
?
|
urticaria
|
|
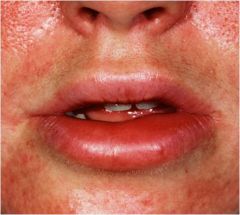
?
|
Angioedema
|
|
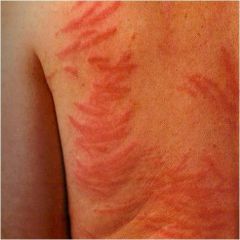
?
|
urticaria
|
|
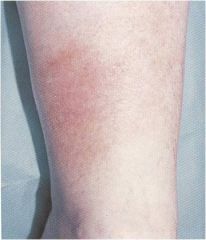
?
|
erythema nodosum
Panniculitis Red, painful subcutaneous nodules Shins, extensor surfaces of UE, dorsum of feet Peak incidence 3rd decade Fever, malaise, arthralgia (50%) esp. ankles Self-limited, 4-6 wk duration Caused by drugs, infections, inflammatory dz |
|
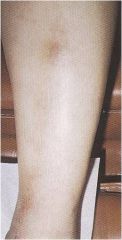
?
|
erythema nodosum
|
|
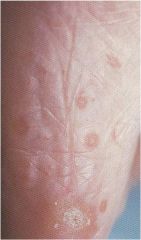
?
|
Erythema multiforme
Self-limiting (1 mo) Target lesions Symmetrical, round, red or purple Caused by infections and drugs Treat by removing drug and giving steroids Severe variant = Stevens-Johnson Syndrome |
|
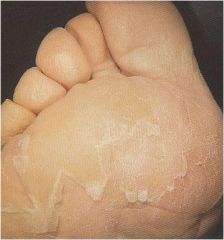
?
|
acroexfoliate dermatitis
Mild, exfoliative changes to hands & feet No erythema Rapid healing when drug has been eliminated |
|
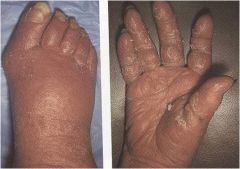
?
|
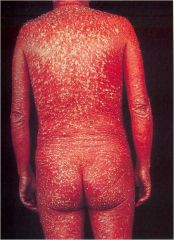
Exfoliative erythroderma
Acute onset with rapid progression Reaction to drugs and disease Exfoliation with erythematous base All meds must be stopped Steroids begun ASAP E.E. Syndrome is full body and can be life-threatening |
|
?
|
Exfoliate erythroderma
|
|
|
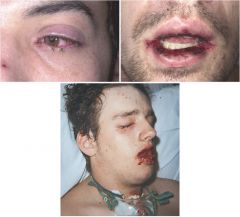
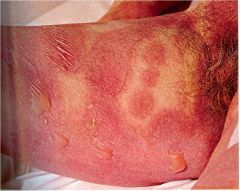
Steven Johnsons syndrome
AKA Erythema Multiforme Major Mucocutaneous tenderness and erythema followed by necrosis and sloughing Potential for severe morbidity and death Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity Etiology: viral infections, drugs, malignancies Treat as severe burn |
|
|
Steven Johnsons syndrome
|
|
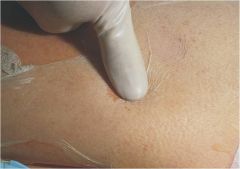
sign?
|
Nikolskys sign
|
|
|
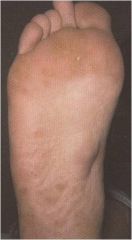
drug induced plantar keratoses
Arsenic & lithium well known causes Multiple, small, punctate hyperkeratoses on the palms and soles May convert to SCC May treat with sharp debridement, cryotherapy, electrodessication |
|
|
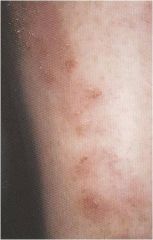
Eczematous Drug Reaction
Pruritic reaction Vesicles and papules Crusting and scaling if drug use continues Stop drug! |
|
|
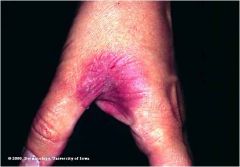
fixed drug reaction
Well-defined, sharply marginated lesion Occurs in the same location each time the patient is exposed to the sensitizing medication Dermatitis develops within minutes of exposure Remove drug and treat itching |
|
|
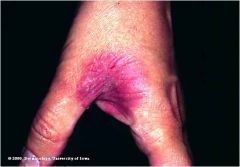
fixed drug reaction
Well-defined, sharply marginated lesion Occurs in the same location each time the patient is exposed to the sensitizing medication Dermatitis develops within minutes of exposure Remove drug and treat itching |
|
|
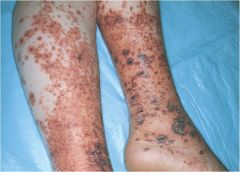
drug induced purpura
schambergs disease |
|
|
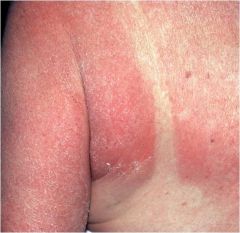
photosensitivity reaction
Caused by ultraviolet light exposure after taking certain medications Sunburn-like erythema, papules, vesicles are possible Present only in sun exposed areas Prevent sun exposure and/or stop drug exposure |
|
|
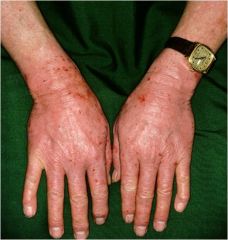
photoallergic
type IV hypersensitivity, may spread to unexposed areas |
|
|
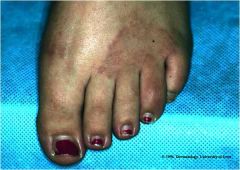
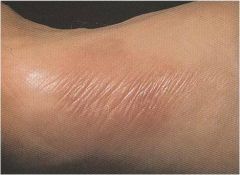
Granuloma annulare
Benign, inflammatory, granulomatous condition of the dermis of unknown origin Occurs in all age groups but most common in young women < 30 years old Skin-colored, violaceous, raised, oval lesions on hands, feet, legs, ankles Asymptomatic Single or multiple |
|
|
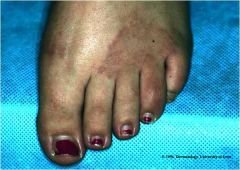
Granuloma annulare
Benign, inflammatory, granulomatous condition of the dermis of unknown origin Occurs in all age groups but most common in young women < 30 years old Skin-colored, violaceous, raised, oval lesions on hands, feet, legs, ankles Asymptomatic Single or multiple |
|
|
erythema nodosum
|
|

|
Dr Jenkins house
|

