![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the potential problems which may be aggravated by or associated with bruxing? |
Excessive wear (including abfracture)
Tooth fracture Restoration failure Aggravate periodontal problems: pockets and mobility Muscle tenderness Joint disturbances |
|
|
4 components of history taking:
|
Medical History:
Family History: Social History: Dental History: ----Include Screening Questions for Potential occlusal problems: -------More Detailed Questions for Positive Answers to Screening Questions |
|
|
What is the purpose of asking the question: "Does your jaw ever lock open or closed, get stuck, or go out?"
|
Jaw ever lock: it’s the hinge is locked while it’s open. On the other hand if they can’t open it may be muscles
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the question: Have you noticed any recent changes in your bite?
|
Recent changes in bite: acromegaly.
Trauma: change in the bite due to jaw fracture. Muscles can cause change in disc |
|
|
What are you looking for when you palpating the Muscles and TMJ? |
pain, deviation, displacement, clicks, crepitus, limitation
|
|
|
What are the anatomical structures palpated in an exam?
|
TMJ, temporalis (origin, insertion, anterior, middle and posterior portion), coronoid process (contains temporal tendon), Masseters(internally, and externally),
Both temporalis and Masseters should be palpated |
|
|
What is the Normal range of motion of the mandible?
|
53-58mm (for class I incisial relationship)
|
|
|
At what point is the range of motion of the mandible considered restricted?
|
<40mm
|
|
|
What does a hard stop and soft stop suggest in a patient with restricted opening
|
hard stop=joint issue
soft feel=muscle problem |
|
|
What is the normal range for lateral and protrusive excursions?
|
8 mm + laterally and protrusively
< 8 mm = restricted |
|
|
Distinguish between deviation and deflection
|
DEVIATION: As the mandible opens, if it goes towards one side, then returns to centre as it continues to open.
DEFLECTION: If it does NOT return to the midline after opening |
|
|
What do Deviation and Deflection indicate?
|
Deviation and deflection are often indicative of joint disturbances.
The condyle on the side the mandible is moving towards may be unable to translate during opening, resulting in movement towards the affected side. In the case of deviation, the return to the centre/midline on further opening may be accompanied by a click in the TMJ on the affected side. |
|
|
How do you record a joint sound?
|
Record the vertical dimension between incisors when you hear click
|
|
|
What is a click?
|
Clicks are a single sound of short duration
|
|
|
When do clicks most often occur
|
Clicks occur most frequently as the mandible opens beyond the range of rotation of the condyles, i.e. during the translation portion of mandibular opening.
|
|
|
What is a reciprocal click?
|
A click that happens on both opening and closing
|
|
|
what's a pop?
|
A pop is a particularly loud click
|
|
|
What's crepitation?
|
, is a series of sounds, often described as “gravelly” or “grating”. It suggests the sound of two dry bones rubbing together. Sounds terrible but not often painful
-> Associated with disk deterioration and osteoarthritis |
|
|
What should you see clinically if the the pterygoid muscles are the source of pain?
|
If a muscle is a source of pain, both stretching and contracting the muscle should elicit pain, or increase existing pain.
|
|
|
What should you see clinically if the the INFERIOR lateral pterygoid muscles are the source of pain?
|
Contraction:
Protruding the mandible against resistance should cause pain (muscles have to work harder to open) Stretching: Biting maximally in MI should cause pain Biting on separators should not be painful or reduce pain |
|
|
What should you see clinically if the the SUPERIOR lateral pterygoid muscles are the source of pain?
|
Contraction:
Biting maximally in MI should cause pain. Biting on separators will also cause pain. Masseter & Temporalis will give same result Stretching: Biting maximally in MI should cause pain (same as Masseter & Temporalis. Opening the jaw wide will NOT cause pain in the Superior Lateral Pterygoid. |
|
|
What is the test that distinguishes the source of pain is due to superior lateral pterygoids and NOT the masseter and temporalis?
|
Opening the jaw wide will NOT cause pain in the Superior Lateral Pterygoid. Masseter & Temporalis will be painful during this exercise. Superior lateral pteryoid is relaxed in this state, but the other two are being stretched.
|
|
|
What should you see clinically if the the MEDIAL pterygoid muscles are the source of pain?
|
Contraction:
Biting maximally in MI should cause pain. Biting on separators will also cause pain. Masseter & Temporalis will give same result Stretching Opening the jaw wide will cause pain in the Medial Pterygoid. Masseter & Temporalis will be painful during this exercise. |
|
|
What would you observe in a patient with Intracapsular (Joint) Disorders?
|
Movement of the Condyle and increased loading will cause pain, or an increase in pain:
Biting maximally in MI. Opening widely. Protruding against resistance . Decreasing the loading on the condyle may cause a decrease or elimination of pain: Biting on a unilateral separator. Protruding against resistance with a separator on painful side |
|
|
What teeth are used to measure Overbite?
|
Distance between Incisal Edges of 11 and 41, measured VERTICALLY
|
|
|
What landmarks are you using if your over jet value consists of one number?
|
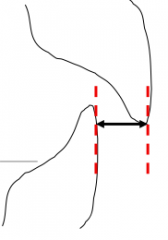
Horizontal Distance between Facial Surfaces of 11 and 41, measured at incisal edge of 11
|
|
|
What landmarks are you using if your over jet value consists of two numbers?
|
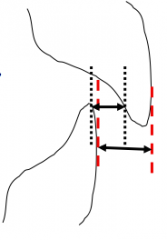
1st number: Facial of 41 to Lingual of 11, measured at incisal edge of 41 (black lines). Indicates if there is contact between the two incisors.
2nd number: Horizontal Distance between Facial Surfaces, measured at incisal edge of 11 (red lines) |
|
|
Why is it important that the patient be upright when trying to locate MI contacts?
|
Places the patient in Alert feeding position. (More accurate)
|
|
|
Why is it important to note if wear facets are flat or cupped?
|
Flat: Wear is still on enamel
Cupped: Wear is into Dentin and needs to be restored (Class VI). Dentin wears much faster, potential to be carious |
|
|
How do we check for Fremitus?
|
Check for FREMITUS in excursions and MI by placing finger over root and sliding sideways, forwards, and tapping teeth together. Feel for vibrations or movement.
|
|
|
What is Total Cross-Bite? What is the biggest problem with this?
|
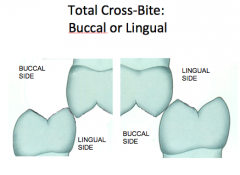
Overtime there is over eruption of both teeth, creating a heavy interference
|
|
|
Other names for Occlusal Splints?
|
Bite Plane
Nightguard Bruxism Splint Orthotic |
|
|
What are the 3 categories of splints?
|
Diagnostic
Preventative Therapeutic |
|
|
Features of a maxillary nightguard
|
Flat Plane
No cusp indentations Freedom of movement |
|
|
When is a mandibular nightguard useful?
|
Some patients with Class III occlusion
Some posterior cross-bites Daytime use Some patients who find maxillary splint hard to wear. |
|
|
What's the purposing of rinsing before inserting impression?
|
This removes excessively thick saliva, which can interfere with impression accuracy for fine detail
|
|
|
Why is it important to protect opposite teeth with a finger on the handle of the impression tray when you're removing the impression?
|
You can chip an incisor during the "snap" removal action.
|
|
|
List the criteria for a good impression:
|
Adequate tissue roll
All teeth in impression No voids or bubbles No “burn-through” to metal CHECK FOR PERIPHERAL DISTORTION ! If you see metal rim, alginate may have distorted. |
|
|
List some problems that can make taking a impression hard
|
Gagging
Orthodontic hardware Bridges (use block out wax) Exostoses and Tori (Use a plastic tray and cut out the sides) |
|
|
Alternate names for Jadestone and Microstone
|
Jadestone: Densite
Microstone: Hydrocal |
|
|
What's the problem of leaving the cast in the alginate for more than an hour?
|
If you let it sit more than an hour, the stone will start absorbing water from the alginate. Hard to remove and increases risk for breakage
|
|
|
What is the purpose of using a knife to trim retromolar areas on the stone cast?
|
Prevent interferences when we are occluding the casts
|
|
|
What are the function of keyways?
|
Keyways allows lab to separate the cast from the plaster and then remounted in the same manner at a later time.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Jaw relation records?
|
Allows mounting casts
Programming the articulator |
|
|
What is the purpose of the facebow record?
|
records relationship between maxillary teeth and the TMJ
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the CR record?
|
Mandibular Teeth to Maxillary
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Protrusive record?
|
Setting Condylar Guidance
|
|
|
Features of the WhipMix 3000 series articulator
|
Semi-adjustable
Adjustable Condylar Guidance Average Anatomical Shape Fixed Inter-condylar distance. Arcon Condyle on Mandible Arbitrary facebow Arbirary Hinge Axis |
|
|
What are the references that are used for the Arbitrary Hinge Axis Facebow?
|
1. External Auditory Meatus (EAM)-Minimum 5mm error
2. Anterior reference point is the Nasion |
|
|
What other options can be used besides PVS to obtain the facebow record?
|
Wax, White compound.
|
|
|
Should the fossae be included when you are taking the facebow record?
|
No! Just the cusp tips should indent the record. Including Fossae will cause inaccuracies. There should also be no rocking!
|
|
|
List the articulator settings when you are mounting your cast
|
Lock articulator in CR
Trapeze ON Condylar inclination set at 30 degrees Side Shift 0 |
|
|
Describe operator guided Disc-oriented CR
|
Patient reclined 30-45º
Bilateral pressure to seat disc Downward pressure on the chin CR taken at highest point when patient can rotate without pain or tenderness |
|
|
Describe Operator guided ligament-Dominated CR
|
“Capture” a repeatable reference position
Patient seated upright Patient closes with light chin-point guidance on softened recording material |
|
|
Power Centric
|
Patient’s elevator muscles seat condyles
Patient upright Anterior wax wafer stop CR measured on posterior wax record with patient closing against anterior stop *(ie. The deprogramming jig) |
|
|
Criteria for a good cast?
|
No nodules
No grinding slurry No interferences of soft-tissue/land area, esp. in posterior Should be able to hand-articulate in a stable Maximum Intercuspation (MI) |
|
|
Why do you want to trim the buccal area of the CR record?
|
You want the record to create as little interference with occlusion as possible
|
|
|
Why do you not want the teeth to perforate the wax when taking the CR record?
|
The teeth will have a natural tendency to want to slide into MI if this occurs
|
|
|
How do you check that you've taken a accurate CR record?
|
When you place the CR record in between the casts, the MANDIBULAR red line should be posterior to the maxillary red line
|
|
|
Steps to mounting the cast using the CR record
|
Lock centric latch
Condylar Inclinations set at maximum Increase vertical dimension 3 mm at incisal guide pin, to allow for the thickness of the wax record. |
|
|
What are some better method of stabilizing casts for mounting
|
Stabilize with popsicle sticks and sticky wax, or
Hold casts steady with hands (assuming wax record holds cast reliably). |
|
|
How far should the patient protrude when taking a Protrusive record?
|
5-6mm
|
|
|
Is perforation of wax a problem when taking a protrusive record?
|
No. Unlike CR, you don't have to worry about slide.
|
|
|
Steps for setting condylar inclination
|
CR Latch OFF
Trapeze OFF Pin UP Condyle path inclines set to 0 Seat casts in record Should be 5-6mm forward of CR Loosen condylar Inclines and rotate until they touch condyles Tighten Condylar Inclines |
|
|
Conditions for mounting in MI?
|
There is no pathology related to the slide, just go with MI
If MI is small (<0.5mm) IF there are a lot of teeth present to give stable MI Most situations involve restoring natural teeth. We still may have to deal with other occlusal problems in MI (like working And NW but not the slide. |
|
|
Conditions for Mounting in CR:
|
For Dx to allow analysis of premature contacts and slides
For restorative situations where there is not a stable or measureable MI: Complete dentures Full mouth reconstruction Multiple missing teeth Flat plane occlusal splints (allow patient to go back into CR) In therapeutic situations where it has been determined that the existing MI position is contributing to pathology and a decision has ben made to adjust the patient’s position of MI to one in CR, with no sldie present. |
|
|
Why do I have the same point of prematurity on the articulated models as I found in the mouth, but the articulated models do not close into a proper MI on the articulator, even after I unlatch the condyles?
|
The articulator is only an approximation of the mouth.
|
|
|
What are the regulations concerning keeping casts?
|
Study models: used in diagnosis only. Need to be kept as part of patients clinical record
Clinical records need to be kept at least 10 years after the last visit of the patient, or 10 years after the patient has attained the age of 18 |
|
|
Potential problems that Bruxing may cause or exacerbate
|
Excessive wear (including abfracture)
Tooth fracture Restoration failure Aggravate periodontal problems Muscle tenderness Joint disturbances |
|
|
Causes of Bruxism?
|
Occlusal interferences-No good evidence that this is a factor
Emotional stress: Type “A” people (Dr. Noble thinks this is a issue) “Hurry and Worry” Other factors: Some medications Genetic factors CNS disturbances |
|
|
Name some characteristics of Normal Functional Activity
|
Vertical Forces
Normal amount of force Normal Muscle contraction/relaxation (Isotonic) – good blood flow Protective Reflexes In or near MI Forces distributed over many teeth Condyles in stable position Food between teeth |
|
|
Name some characteristics of Normal Functional Activity
|
Horizontal Forces
Amount of force> 3x normal Sustained Muscle contractions (Isometric) –poor blood flow No Protective Reflexes Eccentric positions Forces distributed over few teeth Condyles in unstable position Tooth – Tooth contact |
|
|
Variables in Occlusal Splint Design?
|
Purpose / Uses:
Function / Mode of Action: Material Arch: which arch? Full Arch or Partial Arch: |
|
|
Benefits of coverage of occlusal surfaces?
|
Cuspal coaverage.
Places material between teeth which is softer than teeth= less force being exerted on teeth and supporting structures including periodontium, muscles and joints. -allows control of intercuspation |
|
|
Which situations may require a splint with intercuspation?
|
1) If the Mandible needs to be held in MI
2) Repositioning splint |
|
|
When would you want to hold the mandible in MI with a occlusal splint?
|
May be used in surgical positioning splints used in orthognathic surgery, and treatment of maxillofacial trauma.
|
|
|
What is a repositioning splint and when should you prescribe one?
|
Orthopedic device altering normal jaw closure.
Has the potential to cause permanent changes in a patient’s TMJ function or occlusion, requiring further extensive and expensive restorative treatment and occlusal therapy. Generally we SHOULD NOT MAKE REPOSITIONING SPLINTS |
|
|
What is a Flat plane occlusal splint and what are the benefits?
|
Flat Plane, no cusp indentations.
Disengages teeth from normal MI position. Allows freedom of movement of mandible. Used more for preventative splint to protect teeth and other structures from bruxing. Can also be used as a therapeutic splint. Can be useful as a diagnostic aid in the diagnosis of TMD, because it eliminates occlusal factors. |
|
|
When is it most important to allow retrusive movement?
|
-> Any Flat plane splint should allow mandible to go into CR (along with protrusive without interference).
-->This is especially important for diagnostic splints, and patients with large CR-MI discrepancies. |
|
|
What is the main benefit of increasing vertical dimension with splints?
|
Tends to decrease muscle tension.
Some feel this is the most important part of therapeutic splints. Useful as part of full-mouth rehabilitation, esp. in the diagnostic and treatment stages. Useful for treating cases of restricted jaw-opening. |
|
|
Benefits of Canine Ramps?
|
Discluding ramps in canine area will cause separation in lateral and protrusive movements.
This will protect posterior teeth in excursions (mutually protected occlusion). Thprois also reduces Muscle Force, which means potentially less damage, and possibly less muscle pain. |
|
|
What some potential problems if Canine Ramp isn't placed properly?
|
may tend to force mandible posteriorly, creating pain in retro-discal tissues
and interfering with freedom of movement, especially in patients with long “slides” and mounted in CR. Pushes mandilbe posteriorly |
|
|
What is the occlusal disengagement theory of occlusal splints?
|
Use Flat plane splint to eliminate dental interferences
|
|
|
What is the vertical dimension theory of occlusal splints?
|
Use a Bite-opening splint to Increase vertical dimension reduces muscle tension
|
|
|
What is the Joint repositioning theory of occlusal splints?
|
Uses a repositioning splint to Places TMJ’s in more comfortable position (Not a good idea)
|
|
|
What is the Cognitive awareness theory of occlusal splints?
|
Similar to occlusal disengagement
Decreases “dental awareness” Flat plane splint |
|
|
What are the different material options for occlusal splints?
|
1)Hard Acrylic with clasps
2) Soft Flexible Acrylic (similar to sportsguard) 3) Thermoplastic Acrylic – softens when warmed 4) Hard Acrylic Occlusal bonded to Thermoplastic base (Dual Laminate) |
|
|
What is the benefit of a thermoplastic splint?
|
Comfortable.
Flexible when heated in hot water but cools in mouth and becomes rigid. Doesn't require clasps because it engages embrasures of teeth |
|
|
What is the advantages and disadvantages of Maxillary Dual-Laminate Splint?
|
Hard Acrylic Occlusal surface (easy to adjust like dentures) on a thermoplastic base.
Biggest issue: Longitudinal cracks (last only 2-3 years) |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of maxillary occlusal splint
|
+: all mandibular teeth contact on a flat surface
+:eccentric guidance easier to achieve - : esthetics - : Phonetics |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of mandibular occlusal splint
|
+: phonetics
+:Esthetics -:difficult to establish vertical occlusal contact with maxillary incisors (good for class three) |
|
|
What is the potential problem with partial arch coverage?
|
Can have over eruption of the teeth that you didn't cover.
|
|
|
List the things that should be on your night guard prescription
|

|
|
|
If an occlusal split does not seat properly during delivery, what is the most likely problem and how would you fix it?
|
check acrylic in the embrasures – especially in the anterior.
This can be relieved with a straight-shank fissure or round bur in the slow speed handpiece. |
|
|
If you find your occlusal splint is lacking adequate canine ramp, what should you do?
|
you can add cold-cure orthodontic resin (clear). You can use the same technique to add a "centric" contact
This technique is useful for repair future defects |
|
|
Why don't we want contacts on non-centric cusps on a night guard?
|
they are the ones that tend to break (Buccal upper and lingual of lower)
|
|
|
Patient has trouble sleeping or drooling. What are some solutions?
|
Try wearing it earlier to start getting used to the drooling thing. Some may prescribe sleep medication…have to be careful because it can be habit and not real sleep.
|
|
|
Patient notices tissue irritation. What do you do?
|
Tell them to stop wearing it and bring it to you so you can relieve the impingement area
|
|
|
Patient notices pressure from nightguard on teeth?
|
Tell them to stop wearing it and bring it to you so you can relieve the impingement area
|
|
|
Patient thinks teeth have moved?
|
Stop immediately. Maybe have them leave it for a couple days until it returns to natural position. Then relieve it. Can’t see it but patient can know even it is a little bit off.
|
|
|
Patient wakes up with pain in jaw joint?
|
Stop wearing. It may be opening them up too much. May have to reduce it.
If it’s not completely flat. May have to relieve ramp for relief |
|
|
Patient says bite feel different in the morning. No pain. Feels normal again after about 30 minutes?
|
Bite deprogramming. It allows the jaw to move back to their most relaxed position. So no need for occlusion correction!! Just get patient to come in to check if it’s a repositioning splint
|
|
|
Patient needs a filling after splint is made
|
Don't Forget that you made a splint for them! so if they need a filling, get them to bring their splint (and make a note that they have a splint in your records!!) so you can adjust afterwards. Hollow out where the filling/restoration is going to be, fill the hole with ortho resin, place vaseline on the filling and fit. If it fits ok, cure the ortho resin
|
|
|
What are some considerations for patients for TMD?
|
1) Short appointments
2) Use a Bite block/mouth prop |

