![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Union of sperm and ovum to produce a zygote, also called conception. |
Feritilization |
|
|
One-celled organism resulting from fertilization. |
Zygote |
|
|
Sex cells; male - sperm; female - ovum |
Gametes |
|
|
The rupture of a mature follicle in either ovary and the expulsion of its ovum-- occurs once every 28 days until menopause. |
Ovulation |
|
|
Twins from two different zygotes, genetically different. |
Dizygotic Twins Fraternal Twins |
|
|
Twins from the division of one zygote. Genetically identical. |
Monozygotic Twins Identical Twins |
|
|
Chemical that carries inherited instruction for the development of all cellular forms of life. |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) |
|
|
Sequence of bases within the DNA molecule; governs the formation of proteins that determine the structure and functions of living cells. |
Genetic Code
|
|
|
Coils of DNA that consist of genes. |
Chromosomes |
|
|
Small segments of DNA located in definite positions on particular chromosomes; functional units of heredity. |
Genes |
|
|
Complete sequence of genes in the human body; representative sample |
Human Genome |
|
|
Permanent alternations in genes of chromosomes that may produce harmful characteristics. |
Mutations |
|
|
In humans, the 22 pairs of chromosomes not related to sexual expression. |
Autosomes |
|
|
Pair of chromosomes that determines sex: XX in the normal human female, XY in the normal human male. |
Sex Chromosomes |
|
|
Father of Genetics and discovered the dominant and recessive inheritance. |
Gregor Mendel (Austrian) |
|
|
Two or more alternative forms of a gene that occupy the same position on paired chromosomes and affect the same trait. |
Alleles |
|
|
Possessing two identical alleles for a trait. |
Homozygous |
|
|
Possessing differing alleles for a trait. |
Heterozygous |
|
|
Pattern of inheritance in which a child receives different alleles, only the dominant one is expressed. |
Dominant Inheritance |
|
|
Pattern of inheritance in which a child receives identical recessive alleles, resulting in expression of a non-dominant trait |
Recessive Inheritance |
|
|
Pattern of inheritance in which multiple genes at different sites on chromosomes affect a complex trait. |
Polygenic Inheritance |
|
|
Observable characteristics of a person. |
Phenotype |
|
|
Genetic makeup of a person, containing both expressed and unexpressed characteristics |
Genotype |
|
|
The quantitative study of relative hereditary and environmental influences on behavior.
Seeks to determine the difference among people because of the differences in their environment, genes, and combination of these. |
Behavioral Genetics |
|
|
Statistical estimate of contribution of heredity to individual differences in a specific trait within a given population. |
Heritability |
|
|
If there is a strong correlation among the traits within the family, therefore it may be due to heredity. |
Family Studies |
|
|
The potential expression of a hereditary trait. |
Reaction Range |
|
|
Genetics determine the range of reaction for some traits. This term is used to define a very narrow range of reactions where only a drastic change in one's environment can change it. |
Canalization |
|
|
The effect of similar environmental conditions on genetically different individuals. |
Genotype-Environmental Interaction |
|
|
Genetic and environmental influences are in the same direction. |
Genotype-Environment Correlation |
|
|
The combination of genetic and environmental factors to produce certain complex traits. |
Multifactorial Transmission |
|
|
Mechanism that turns genes on or off and determines functions of body cells. The environment can influence when and which genes turn on and off. |
Epigenetic view |
|
|
The differential expression of certain genetic traits, depending on whether the trait has been inherited from the mother or the father.
In imprinted gene pairs, genetic information inherited from one parent is activated, but genetic information from the other parent is suppressed. |
Genome/Genetic Imprinting |
|
|
Enzyme deficiency that can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and emphysema and degenerative disease in middle age. |
Alpha, Antitrypsin Deficiency (C14) |
|
|
Severe anaemia that reduces ability of the blood to carry oxygen; nearly all affected infants and stillborn or die soon after birth. |
Alpha Thalassemia (C16) |
|
|
Severe anaemia resulting in weakness, fatigue, and frequent illness; usually fatal in adolescence or young adulthood. |
Beta Thalassemia / Cooley's anemia (C11) |
|
|
Overproduction of mucus, which collects in the lung and digestive tract; children do not grow normally and usually do not live beyond age 30; the most common inherited lethal defect among white people. |
Cystic Fibrosis (C7) |
|
|
Fatal disease usually found in males marked by muscle weakness; minor mental retardation is common; respiratory failure and death usually occur in young adulthood. |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (X) |
|
|
Excessive bleeding, usually affecting males; in its most severe form, can lead to crippling arthritis in adulthood. |
Hemophilia (X) |
|
|
Absence of brain tissues; infants are stillborn or die soon after birth. |
Anencephaly |
|
|
Incompletely closed spinal cal, muscle weakness or paralysis and loss of bladder and bowel control; often accompanied by hydrocephalus, an accumulation of spinal fluid in the brain, and mental retardation. |
Spina Bifida (C11) |
|
|
Metabolic disorder resulting in mental retardation. |
Phenylketonuria (PKU) |
|
|
Deformed red blood cells that clog blood vessels, depriving the body of oxygen; symptoms include severe pain, stunted growth, infections, leg ulcers, gallstones, pneumonia, and stroke. |
Sickle-Cell Anemia |
|
|
Degenerative disease of the brain and nerve cells, resulting in death before age 5. |
Tay-Sachs Disease |
|
|
Pattern of inheritance in which a child receives two different alleles, resulting in partial expression of a trait. |
Incomplete Dominance |
|
|
Pattern of inheritance in which certain characteristics carried on the X chromosome inherited from the mother are transmitted differently to her male and female offspring. |
Sex-Linked Inheritance |
|
|
Male; tall stature; tendency toward low IQ, especially verbal |
XYY |
|
|
Female; normal appearance, menstrual irregularities, learning disorders, mental retardation. |
XXX Triple X |
|
|
Male; sterility, underdeveloped sex characteristics, small testes, learning disorders. |
XXY Klinefelter's |
|
|
Female; short stature, webbed neck, impaired spatial abilities, no menstruation, infertility, underdeveloped sex organs. |
XO Turner's Syndrome |
|
|
Minor-to-severe mental retardation; more severe in males; delayed speech and motor development, hyperactivity; the most common inherited form of mental retardation. |
Fragile X |
|
|
Clinical service that advises prospective parents of their probably risk of having children with hereditary defects. |
Genetic Counseling |
|
|
Period of development between conception and birth |
Gestation |
|
|
Age of an unborn baby, usually dated from the first day of an expectant mother's last menstrual cycle. |
Gestational Age |
|
|
The upper parts of the body develop before the lower parts of the trunk. |
Cephalocaudal Principle |
|
|
Symptoms of Pregnancy |
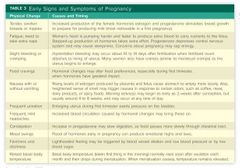
|
|
|
The parts of the body near the center develop before the extremities. |
Proximodistal Principle |
|
|
First 2 weeks of prenatal development, characterized by rapid cell division, blastocyst formation, and implantation in the wall of the uterus. |
Germinal Stage |
|
|
Germinal Stage |
Fertilization - 2 weeks
36 hrs - the zygote enters a period of rapid cell division and duplication.
72 hrs - 16 cells --> 32 cells.
6-7 days - the blastocyst attaches to uterine wall. |
|
|
The attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall, occuring at about day 6. |
Implantation |
|
|
A fluid-filled sphere; formed after the cell division on day 6. |
Blastocyst |
|
|
Part of the embryonic disk that becomes the digestive system, liver, pancreas, salivary glands, and respiratory system. |
Endoderm |
|
|
Part of the embryonic disk that becomes the outer layer of the skin, nails, teeth, hair, sensory organs, and nervous system. |
Ectoderm |
|
|
Part of the embryonic disk that becomes the middle layer of skin, muscles, skeleton, and excretory and circulatory system. |
Mesoderm |
|
|
Embryonic Stage |
2 weeks - 8 weeks
The organs and major body systems (respiratory, digestive, and nervous) develop rapidly. |
|
|
The natural expulsion from the uterus of an embryo that cannot survive outside the womb; also called miscarriage. |
Spontaneous Abortion |
|
|
Fetal Stage |
8 weeks - Birth
Characterized by increased differentiation of body parts and greatly enlarged body size. |
|
|
12 weeks after birth |
Child is able to breathe and swallow; reciprocal development in the respiratory and digestive systems.
Swallow - digestive breathe - respiratory |
|
|
14 weeks after birth |
Taste and olfactory systems start to develop |
|
|
26 weeks after birth |
Fetus is able to respond to sound and vibration |
|
|
32 weeks after birth |
Developmental plateau |
|
|
Factors that are capable of causing birth defects. |
Teratogens |
|
|
Maternal Factors of Influence on Embryonic Development |
1. Weight Gain = 16 - 40 pounds + delivered by cesarean - growth retardation; premature birth; stillborn
2. Weight before pregnancy Obesity - risk of birth defects
3. Nutrition DHA (Omega 3 Fatty Acids) + more mature sleep; advanced brain development
Folic Acid (Vitamin B) + decreases risk of anencephaly; spina bifida
Vitamin D + decreases risk of osteoporosis in baby's later life.
Dietary supplements + high chance of healthy babies |
|
|
Combination of mental, motor, and developmental abnormalities affecting the offspring of some women who drink heavily during pregnancy. |
Fetal Alchohol Syndrome |
|
|
Medical Drugs |
- Antibiotic Tetracycline - Barbiturates - Opiates - Central Nervous System Depressants (CNS) - Methotrexate - anti-cancer - Accutane - Severe Acne - Angiotensin-Converting Enzymes (ACE) inhibitors - Antipsychotic Drugs
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) - Naproxen - Ibuprofen
Hormones - Diesthylstilbestrol - Androgens |
|
|
Nicotine Effects on Pregnancy |
- Higher chance of low birth weight. - Miscarriage - Growth Retardation - Stillbirth - Small Head Circumference - Colic - Hyperkinetic Disorder - Long term respiratory, neurological, cognitive, and behavioral problems
- Second hand smoking can cause cognitive development impairment. |
|
|
Extended crying for no reason. |
Colic |
|
|
Caffeine Effects on Pregnancy |
>= 2 cups a day affects child's growth. |
|
|
Marijuana Effects on Pregnancy |
- may affect the frontal lobe functioning of the baby - problem solving skills. - minor irritability or altered sleeping patterns |
|
|
Cocaine Effects on Pregnancy |
- spontaneous abortion - delayed growth - premature labor - low birth weight - small head size - birth defects - impaired neurological development
- affects areas involved in attention and executive functioning
|
|
|
Methamphetamine Effects on Pregnancy |
- preterm delivery - low birth weight - brain damage to areas involved with learning, memory, and control - less white matter in brain = developmental delays |
|
|
AIDS Effects on Pregnancy |
Viral disease cause by HIV that undermines the effective functioning of the immune system
- perinatal transmission |
|
|
The transmission of AIDS from the mother to the child through the placenta during pregnancy, delivery, or through breastmilk after birth. |
Perinatal Transmission |
|
|
Rubella Effects on Pregnancy |
If contracted before the 11th week of pregnancy: - deafness - heart defects |
|
|
Toxoplasmosis Effects of Pregnancy |
An infection caused by parasites harbored in the bodies of cattle, sheep, pigs, and cats.
If infected during the second and third trimester: - fetal brain damage - impaired eyesight or blindness - seizures - miscarriage - stillbirth - death of the baby
If previously exposed and has antibodies to toxoplasmosis, will not affect the baby. |
|
|
Diabetes Effects on Pregnancy |
- heart and neural tube defects - high sugar levels deprive embryos of oxygen. |
|
|
Maternal DAS Effects on Pregnancy |
Moderate Anxiety + spur organization of the developing brain
Stress - active and irritable temperament in newborns - inattentiveness - negative emotionality or behavioral disorders
Chronic Stress - preterm delivery
Depression - premature delivery - developmental delays - elevated levels of violent and antisocial behaviors |
|
|
Maternal Age Effects on Pregnancy |
Age 45 + = 90% miscarriage risk
Adolescent mothers - premature or underweight babies |
|
|
Outside Environmental Hazard Effects on Pregnancy (Maternal) |
- inhalation of fine combustion particles = undersized baby - chemical related work = 2x rate of miscarriage - chemically contaminated ground water = leukemia - x-rays = mental retardation; low birth weight |
|
|
Outside Environmental Hazard Effects on Pregnancy (Paternal) |
- x-rays = low birth weight; slowed fetal growth - smoking = increased likelihood of genetic abnormality transmission - older fathers = birth defects (dwarfism, schizophrenia, autism) - teenage fathers = low birth weight; premature |

