![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a. Define Syndrome b. Define Aneuploid |
a. a recognizable pattern of signs + symptoms that indicate a particular disease b. not an exact multiple of the haploid number |
|
|
a. Trisomy 21 = ? b. Trisomy 18 = ? c. Trisomy 13 = ? d. 45, X = ? |
a. Down Syndrome b. Edwards syndrome c. Patau syndrome d. Turner syndrome |
|
|
a. Describe 4 Facial characteristics of Down Syndrome b. Name 2 other physical characteristics of Down Syndrome |
a. - Brachycephaly - Small ears - Small nose - Open mouth with protruding tongue - Depressed nasal bridge - Epicanthic fold b. - Single palmer crease - Sandle gap - Generalized hypotonia - Inward curving short finger |
|
|
Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) - Prevalence is DS babies is __(a)__% - of these, approximately __(b)__ require surgery - leads to premature death in __(c)__% of patients |
a. 40-50% b. half c. 15-20% |
|
|
a. Ventricular septal defects is also called what? b. Describe Ventricular Septal Defects |
a. Hole in the heart b. Abnormal opening in the wall between the 2 ventricles |
|
|
Describe Atrioventricular defects |
- Defects in both atrial and ventricular septa + - Defects in atrioventricular valves |
|
|
Describe Ductus Arteriosus |
- Fetal heart: Ductus arteriosus allows blood flow between Pulmonary Artery to the Aorta - If unresolved at 3 months, surgery is recommended |
|
|
Apart from CHD, name 2 other medical complications related with Down Syndrome |
- Leukaemia - Increased risk of infection - Hypothyroidism - Hearing - Vision |
|
|
Down Syndrome: - 1 in __(a)__ live births - DS infants have developmental delays in areas like __(b)__, __(c)__ and __(d)__ - Mean IQ of __(e)__ |
a. 700 b. Sitting independently + walking c. Toilet training d. First words e. 45-50 |
|
|
DS fertility: - At least __(a)__% of T21 women are fertile - T21 men are __(b)__ fertile - Of the babies born to T21 women, __(c)__% are also T21 or have other developmental abnormalities |
a. 50% b. Rarely c. 35-50% |
|
|
DS later life: - Median age at death is __(a)__ years old - There is generally a __(b)__ decline - 2 conditions usually associated with DS individuals in later life are __(c)__ and __(d)__ |
a. 49 b. Cognitive c. Dementia d. Alzheimers |
|
|
Clinical management: - Evaluation via __(a)__ - Monitoring of __(b)__ - Prevention of __(c)__ |
a. Echocardiogram, Opthalmology (vision), hearing b. Thyroid function, Leukaemia, Dementia c. Obesity |
|
|
DS Aetiology: - 95% of cases due to __(a)__ - 4% of cases due to __(b)__ - 1% of cases due to __(c)__ |
a. Meiotic nondisjunction b. Robertsonian translocations c. Mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction) |
|
|
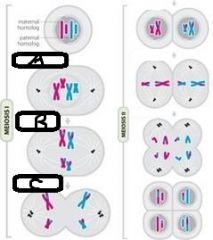
a. Prophase I b. Metaphase I c. Anaphase I |
|
|
Maternal meiotic non-disjunction: - 95% of DS results from meiotic non-disjunction, of these __(a)__% are errors in maternal meiosis - After birth, Oocytes are arrested in __(b)__ of Meiosis I - After __(c)__, the arrested oocyte is stimulated to complete meiosis I the day before ovulation, this is quickly followed by __(d)__ - The longer a woman is when she conceives, __(e)__ |
a. 85% b. Prophase I c. Puberty d. Meiosis II e. The longer the oocyte has been suspended in meiosis I |
|
|
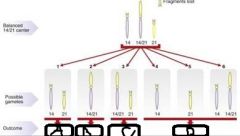
Robertsonian Translocation: - Only occurs with __(a)__ chromosomes - These include chromosomes __(b)__, __(c)__, __(d)__, __(e)__ - When RTs cause Down's, the chromosomes which are translocated are chromosomes __(f)__ and __(g)__ - The carrier of the translocation is healthy, however the progeny may develop DS if the gamete it receives from the carrier is __(h)__ |
a. Acrocentric b. 13 c. 14 d. 21 e. 22 f. 14 g. 21 h. 14/21 and 21 |
|
|
a. Normal b. Normal carrier c. Down's Syndrome d. Lethal |
|
|
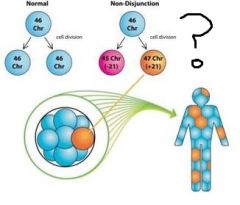
Mitotic non-disjunction: - Also known as __(?)__ |
Mosaicism |
|
|
- Mosaicism |
|
|
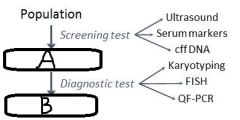
a. High risk group b. Affecteds |
|
|
a. Give 2 advantages of ultrasound b. Give 2 disadvantages of ultrasound |
a. - Non-invasive - Relatively cheap to perform - No known risk to child or mother b. - Expensive equipment - Skilled + experienced personnel required |

