![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Techniques of DNA Technology (6) |
Cloning Gene therapy Genetic engineering Gel electrophoresis DNA fingerprinting PCR (Polymerase reaction chain) |
|
|
Restriction Enzymes |
-AKA restriction endonucleases -enzymes that cut up dna into fragments |
|
|
palindrome |

-words spelled the same backwards and frontwards -what the framents of dna is cut up into -fragments are the same when read in opposite directions |
|
|
Transgenic organism |
is an organism that contains foreign dna within it. |
|
|
Genetic Engineering (Steps w/ insulin example) |
-the process of manually adding new DNA to an organism. 1. cut up human dna w/ restriction enzymes. 2. separate the dna fragments by gel electrophoresis. 3. find the insulin gene in the gel and insert it into a plasmid of a bacteria. 4. the bacteria will now do transcription and translation to make insulin. 5. Since the bacteria now contains human DNA it is called a transgenic organism. |
|
|
sticky ends |
unpaired nucleotides in a dna fragment |
|
|
recombinant dna |
a dna that has human and bacterial plasmid combined. |
|
|
How do restriction enzymes work? |

-dna is cut up into fragments that are palindromes -Each fragment has a sticky end, where they were broken, for attachment. -if we cut the human dna and the plasmid w/ the same restriction enzymes, the sticky ends will attach. |
|
|
gel elctrophoresis |
-used to separate proteins or DNA segments based on their size and charge. 1. place the cut up dna fragments into the wells. 2. send an electrical current through the gel. Most negative charged fragments are pulled further down to the bottom of the cell. 3. The bigger fragments are near the top because they have a less negative charge. |
|
|
In gel electrophoresis, the ________ is placed between ___________. At the top of the gel is the ___________, while the bottom is the __________. |
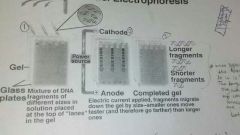
gell w/ wells
glass plates
cathode, where the wells/lanes are anode. |
|
|
DNA is ____________ b/c of ___________. |
negatively charged the phosphorous group attached in the nucleotides |
|
|
DNA fingerpinting |

a dna technology technique where the information seen in the gel electrophonesis is used to determine paternity and for forensic analysis.
the result of gel electrophonesis are the seperaed bands. No two person will have the same bands distances in cell electrophonesis. |
|
|
steps of DNA fingerprinting |
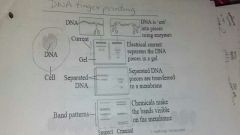
1. dna is cut into pieces in gel 2. electrical current separates the dna pieces in a gel 3. separated dna pieces are transferred to a membrane 3. chemicals make the bands visible on the membrane |
|
|
Why do we not have the same band distances in cell electrophonesis? |
b/c each person has a different sequence of nucleotides in their dna. so when electrophonesis is done, everyone will have their own unique bonding patterns and dna fragments. half from mom and half from dad. |
|
|
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) |
a dna technoloy technique used to amplify (make many copies) of a dna fragment (gene) |
|
|
nascent dna strands |
what is created/copied to add to the dna strand thats separated from pcr. |
|
|
Types of Blots
|
Northern = DNA
Southern = RNA Western = Protein |
|
|
Reasons for Blotting
|
To confirm that the correct DNA/RNA sequence was cloned To get more information about a genomic clone (ex. Regulatory gene regions or SNP variability) To subclone in order to obtain a specific region of the cloned DNA/RNA
|
|
|
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) steps |
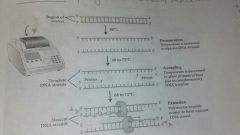
1. Denaturation- temp is increased to separate template DNA strands 2. Annealing- temp is decreased to allow for the hybridization of targeted primers (bind to complementary sites exposed during denaturation) 3. Extension (at 72⁰) to extend primers and generate the PCR product These steps are cycled through multiple times |
|
|
PCR causes a(n) ________________ amplification. |
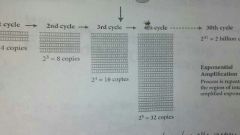
exponential |
|
|
Gene therapy (Steps and def.) |
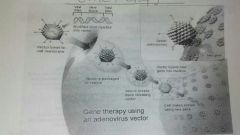
- where a virus (vector) is used to transfer a gene into a cell that does not have that gene
1. Take a gene interest and put it into a virus. 2. let the virus infect human cells (bind to cell membrane) 3. Now the human cell will have a gene it never had and can now make a protein it couldnt before. |
|
|
Cloning |
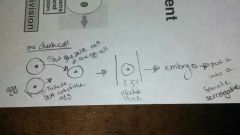
1. remove the nucleus, which contains dna, of the egg cell 2. replace with the dna from the body cell. 3. send an electic shock through the new cell as it opens the cell membrane and triggers cell division. 4. Over time, you`ll have an embryo. Place t into a female surrogate and done. |

