![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does DNA replication begin?
|
At the origin of replication, each bacteria only has one but eukaryotes have many
|
|
|
Which direction does DNA synthesis proceed?
|
Proceeds 5' -> 3' bidirectionally
|
|
|
What important DNA sequences are in the oriC?
|
1. AT rich regions
2. and DnaA boxes |
|
|
Why is the A-T rich region at the OriC such a good starting spot?
|
b/c there is only 2 h-bonds b/e A=T; so the strand is weaker and easier to pull apart in these areas
|
|
|
What initiates DNA replication? how does that work?
|
Binding of DnaA proteins to the DnaA box. Binding of DnaA proteins to the DnaA box causes the region to wrap around the DnaA proteins and separates the strands at the A-T region
|
|
|
What binds to the DNA sequence after DnaA protein? where does it bind?
|
DnaB protein or "helicase"; which binds to the origin
|
|
|
What does helicase do?
|
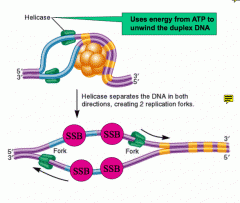
Moves along the separated DNA strands bidirectionally to separate the strands
|
|
|
What prevents the DNA strands from rejoining together after helicase separates them?
|
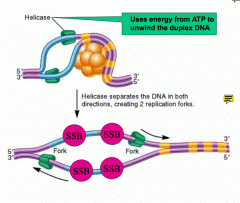
Single-stranded binding protein
|
|
|
How does Helicase separate the DNA strands?
|
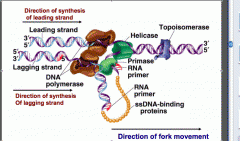
By breaking the hydrogen bonds b/e the base pairs, using ATP as an energy source
|
|
|
What do the actions of helicase generate?
|
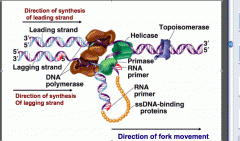
Helicase generates supercoiling ahead of it
|
|
|
What does DNA gyrase do?
|
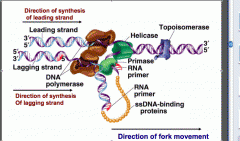
Removes supercoils from DNA
|
|
|
What does single-stranded binding protein do?
|
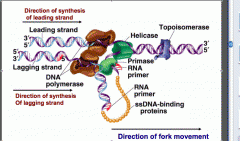
Keeps the DNA strands separated
|
|
|
What does DNA primase do?
|
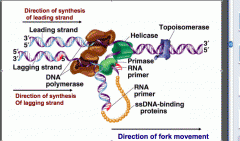
creates short RNA primers which prepares the DNA strands for synthesis
|
|
|
What molecule in DNA replication is a type II isomerase?
|
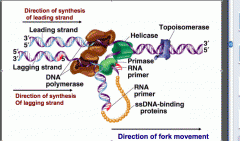
DNA gyrase
|
|
|
What molecule generates negative supercoiling? positive supercoiling?
|
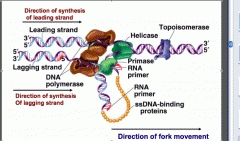
DNA gyrase generates negative supercoiling, DNA helicase generates positive supercoiling
|
|
|
How can gyrase be inhibited? what assists these antibiotics?
|
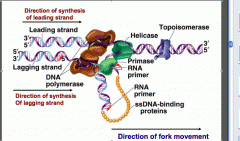
By competitive inhibition using aminocoumarins (antibiotics) by inhibiting ATPase activity at Gyrase's active site
Quinolones bind to these enzymes and prevent them from releasing from DNA |
|
|
How does DNA polymerase III work?
|
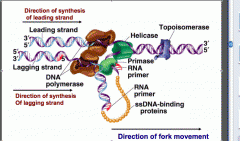
Works by using a RNA PRIMER to covalently link two nucleotides together, so for example if there was no RNA primer polymerase wouldn't be able to function
|
|
|
What DNA replication enzyme is self-correcting?
|
DNA polymerase III
|
|
|
What enzyme has separate catalytic sites that removes unpaired residues at a terminus?
|
DNA polymerase III
|
|
|
Which direction does DNA polymerase III replicate DNA? proofread DNA?
|
DNA polymerase III replicates DNA 5'->3', but it proofreads 3'->5'
|
|
|
What site does DNA polymerase III move a mismatched nucleotide to if the nucleotide is wrong?
|
The "E" or error site
|
|
|
What is the name of the discontinuous pieces of DNA copied on the lagging strand?
|
Okazaki fragments
|
|
|
What removes the RNA primers on DNA?
|
Another DNA polymerase
|
|
|
What does DNA ligase do?
|
Seals in the gaps left in the sugar-phosphate backbone by removal of the RNA primers
|
|
|
What are "nicks"? What are gaps?
|
Nicks = Single strand breaks in double stranded DNA, basically a disruption in the phosphodiester backbone of DNA
Gaps = At least one nucleotide is missing |
|
|
What strand will always have a RNA primer at the end?
|
The lagging strand
|
|
|
What does telomerase do?
|
Adds telomerase to the ends of DNA which are tandem repeats of the sequence TTGGG
|
|
|
How does telomerase work?
|
By binding to the 3' end of the parental strand and extending it using RNA-templated DNA synthesis, the extension allows DNA polymerase to complete replication of the lagging strand
|

