![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What types of DNA damage can occur |
Base damage and strand damage |
|
|
Examples of damage |
Replication errors, UV, IR, ALSO |
|
|
What can be the result of DNA damage |
Cancer, ageing, neurological dysfunction |
|
|
What are the exogenous causes of DSB? |
Radiation and chemicals |
|
|
What are the endogenous causes of DSBS |
Oxygen free radicals, DNA replication |
|
|
What are the specialised causes of DSBs? |
VDJ recombination, class switching, meiosis, topoisomerases type II |
|
|
What is the effect of DSBs |
Cancer, genome instability, apoptosis |
|
|
What happens when DNA damage is left un repair |
Translocation and fusion of chromosomes Accumulation of broken chromosomes is one of the first signs of loss of growth control, can lead to cancer |
|
|
What are the 2 repair pathways |
HR- use sister chromatid as a template to recover lost information - error free NHEJ - ligate the free ends together - error prone as loss of information |
|
|
Why do you require more than one pathway |
HR can only occurs when there is a sister chromatid to use as a template - G2/S phase of the cell cycle NHEJ can occur at any part of the cell cycle - usually G1/G0 |
|
|
Draw HR and NHEJ |
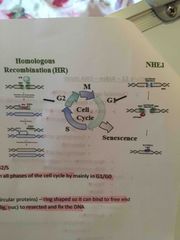
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Cbb |
Vbh |

