![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleosides and Nucleotides |
Former is just ribose/deoxyribose and nitrogenous base, the other adds phosphates. |
|
|
Adenine |
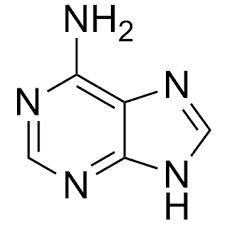
Purine |
|
|
Guanine |
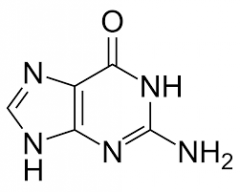
Purine |
|
|
Cytosine |
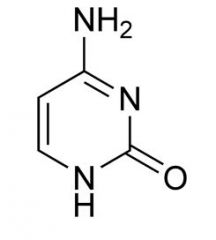
Pyrimidine |
|
|
Uracil |
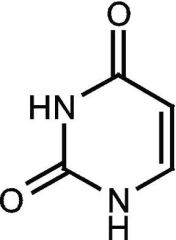
Pyrimidine |
|
|
Thymine |
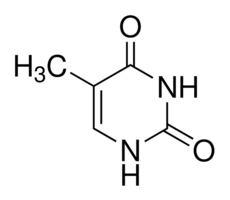
Pyrimidine |
|
|
Z-DNA |
Left-handed helix that has a zigzag appearance. Has one turn every 4.6 nm and 12 bases per turn. Can be created with high GC content, but very unstable and difficult to research. |
|
|
Histones |
A nucleoprotein (protein that associates with DNA) around which DNA is wound. Five histone proteins form histone core and contain 200 base pairs to form a nucleosome. H1 protein seals off the DNA as it enteres and leaves the nucleosome. |
|
|
Heterochromatin |
Compacted sections of chromatin. |
|
|
Euchromatin |
Dispersed sections of chromatin. |
|
|
Centromeres |
Region of DNA found in center of chromosomes. Sites of constriction, composed of heterochromatin. |
|
|
DNA Proofreading |
Where DNA molecules pass through DNA polymerase. Detects instability of hydrogen bonds between two incorrectly paired bases. Excises and replaces. Looks at methylation to determine which is parent strand. |
|
|
DNA Mismatch Repair |
Machinery in G2 phase of cell cycle, which detect and remove errors introduced in replication missed during S phase. |
|
|
Nucleotide Excision Repair |
Detects thymine dimers produced by UV light, creating a bulge or lesion recognized by excision endonuclease. Nicks phosphodiester backbone on both sides and removes oligonucleotide. DNA polymerase fills gap in 5' to 3', sealing with ligase. |
|
|
Base Excision Repair |
Detects errors such as cytosine deamination to uracil, and other small, non-helix distorting mutations. Affected base is removed, leaving behind an apurinic/aprimidinic/abasic (AP) site. AP endonuclease recognizes AP site, nicks and removes, then lets polymerase and DNA ligase fill the gap. |

