![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is DNA and RNA an example of? |
A nucleic acid |
|
|
Describe the structure of DNA |
DNA is double-stranded, so there are two polynucleotide strands alongside each other. The strands are antiparallel I.E.they run in opposite directions. The strands are wound round each other to form a double helix.The strands are joined together by hydrogen bonds between the bases. The bonds therefore form base pairs which are like rungs of a ladder |
|
|
State the base pairs |
Adenine (A) only binds to thymine (T) .cytosine (C) only binds to guanine (G) |
|
|
What is a Nucleotide made up of? |
A phosphate group, a simple sugar and a nitrogenous group |
|
|
Draw two nucleotides bonded together |
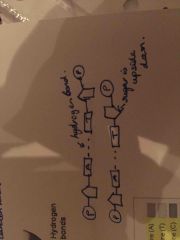
Draw to nuclear tides are bonded together |
|
|
What are three base pairs and example of? |
One specific amino acid |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A gene is a section of DNA that codes for a particular protein |
|
|
How are characteristic is controlled by genes? |
The sequence of bases in DNA determined to sequence of amino acid in polypeptides. This in turn determines the shape and function of the protein which determines the characteristics of the cell. |
|
|
What is semiconservative replication? |
It is when half of the original DNA is kept in the new DNA that has been made |
|
|
How does DNA replicate? |
Replication start at a specific sequence on the DNA molecule called the replication origin. An enzyme such as Helicase unwind and then zips DNA ,breaking the hydrogen bonds that joined the base pairs, forming two separate strands. The new DNA is built up from the four nucleotides (A, C, G and T) that are abundant in the nucleoplasm. These nucleotides attach themselves to the bases on the old strands by complimentary base pairing. The enzyme DNA polymerase joins the new nucleotides to each other by strong covalent bonds, forming the sugar phosphate backbone. A winding enzyme winds up the new strands up to form double helixes |
|
|
What is the result of a condensation reaction between two nucleotides? |
A phosphodiester bond |
|
|
What does RNA do? |
it makes sense of the code contained within the DNA molecule |
|
|
What are the differences between DNA and the RNA? |
RNA is not a double helix, it is a single polynucleotide. The deoxyribose in DNA is changed to a ribose in RNA. In RNA, the base thymine is substituted for the base uracil. RNA is a much smaller molecule than DNA |

