![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what can go wrong with the knee? |
- degenerative disease - rhematoid disease - acute monoarticular arthritis - knee sprain - degeneration or tear of a meniscus - baker's cyst - bursitis - knee effusion |
|
|
valgus stress |
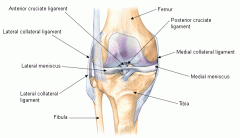
tests stability of the medial collateral ligaments
- lie the pt supine and knees slightly flexed, move thigh 30 degrees laterally to the side of the table - place one hand against the lateral knee to stabilize the femur and the other hand around the medial ankle 3. push medially against the knee and pull laterally at the ankle to open the knee joint on the medial side (valgus stress) 4. pwain or gap in the medial joint points to ligamentous laxity and a partial tear of the medial collateral ligament most injuries are on the medial side |
|
|
varus stress |
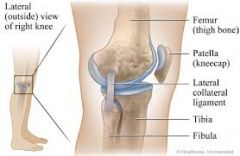
stability of lateral collateral ligaments
1. place hand against the medial surface of the knee and the other around the lateral ankle 2. push medially against the knee and pull laterally at the ankle to open the knee joint on the lateral side (varus stress) 3. pain or gap in the lateral joint line points to ligamentous laxity and a partial tear of the lateral collateral ligament |
|
|
lachman test |
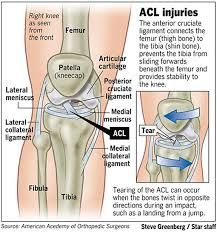
test for stability of the anterior collateral ligaments for ACL tear
1. place the knee at 15 degree flexion and externally rotated 2. grasp the distal femur on the lateral side with the hand and the proximal tibia with the other 3. simultaneously pull the tibia forward while pushing the femur back 4. estimate the degree of forward excursion of the tibia
forward excursion ACL tear |
|
|
anterior drawer test |
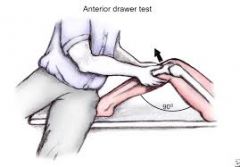
test for stability of the ACL 1. patient is supine, hips flexed to 90 degrees and feet flat on the table, cup your hands around the knee with the thumbs on the medial and lateral joint line and the fingers on the medial and lateral insertions of the hamstrings 2. draw the tibia forward and observe if it slides forward (like a drawer) from under the femur) 3. compare the degree of forward movement on the opposite side a forward jerk showing the contours of the upper tibia is a positive anterior drawer test |
|
|
posterior drawer test |
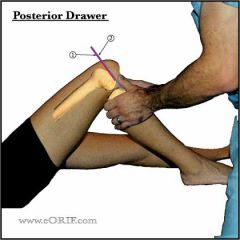
tests stability of the PCL 1. position the patient and place hands the same way as anterior drawer 2. push the tibia posteriorly and observe the degree of backward movement in the femur
isolated PCL tears are rare |
|
|
meniscal injuries |
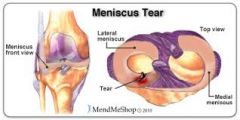
meniscus: cushioning associated with ligaments
injuries usually caused by sudden rotation in extreme flexion or or extension with crush of meniscus between condyles |
|
|
clinical assessment of meniscal injuries how do you tell the difference between a medial and lateral meniscus injury? |
pain along the joint line painful external rotation means medial meniscus injury painful internal rotation means lateral meniscus injury |
|
|
which tests are used for meniscal injuries? |
apley's test mcmurray's test |
|
|
apley's test |
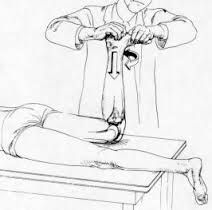
patient lies prone with knee at 90 degrees tibia and weight of foot push down then hold food and rotate knee feel the medial ligament and lateral ligament while rotating, if there's a pop and pain a meniscal tear is present
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w57I1cYXlCA |
|
|
mcmurray's test |
most specific of all tests 1. patient lies supine 2. grasp heel and flex knee 3. cup your other hand over the knee joint with fingers and thumb along the medial and lateral joint line 4. from heel, rotate the lower leg internally and externally 5. push the lateral side to apply a valgus stress on the medial side of the joint 6. at the same time, rotate the leg externally and slowly extend it
try to feel for a click/pop with associated pain at the same time then further assess for a posterior tear
|
|
|
treatment |
isolated 1st (no instability) and 2nd degree (instability) sprains >> RICE
unstable knee: brace swelling: avoid weight bearing NSAIDs topical agents rehabilitation cortisone injections
if conservative tx doesn't work then refer to orthopedic surgery |

