![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When does syncope occur? |
When cardiac output falls |
|
|
What is "true" vertigo? |
Vertigo that results from a disorder of the vestibular system. |
|
|
What is the clinical sign of vertigo?
Which phase does a person see in vertigo (fast or slow)? |
Nystagmus
Slow |
|
|
What does a "right beating" nystagmus mean? |
Fast phase is to the right Slow phase is to the left |
|
|
How many degrees of freedom in 3D space?
What is roll around x-axis called? Y-axis? Z axis? |
Roll Pitch Yaw |
|
|
What is angular motion around x, y, z? What is linear motion around x, y, z? |
Rotational motion Translational motion |
|
|
What two organs detect linear motion and the effects of gravity? Which is coplanar with the vertical axis? Which is coplanar with horizontal? |
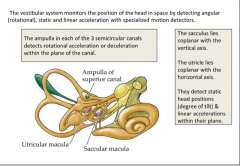
Sacculus = vertical Urticle = horizontal |
|
|
What detects angular movement?
What transduces information for each semicircular canal? |
Amupulla of the superior canal
Cupula (located inside ampulla) |
|
|
What is the purpose of the otoliths on gelatinous membrane in utricle and saccule? |
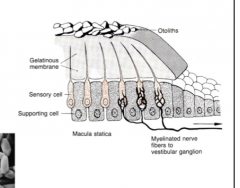
Heavy enough to distort gelatinous matrix from force caused by linear movement and by gravity. |
|
|
What is the tallest cilium? |
Kinocilium Movement => opening of K+ channels => influx of Ca2+ => Ca-dependent K channels activated that pump K+ out into perilymph
Another effect of increased Ca2+ = neurotransmitter release (aspartate or glutamate) |
|
|
Sensory nerve fibers at hair cell base: Where of cell bodies lie? Where do efferent axons project? |
Afferent half of bipolar neurons (cell bodies in Scarpa's ganglion) Efferent axons project to brainstem via vestibular nerve |
|
|
Where do the kinocilium face in the utricle?
What is the effect of tilting the head to one side? |
Midline valley called STRIOLA
Pressure will increase firing on one side and decrease it on the other. |
|
|
What are the only two types of movements that will alter the firing rate of the utricle? |
Linear force within the plane of the utricle Gravitational force when the plane is tilted |
|
|
What direction are the kinocilia oriented in the saccule? |
Away from striola Coplanar with VERTICAL axis |
|
|
What part of saccule will be activated when moving up an elevator?
What is the difference between this and the ampulla? |
Lower (IF MOVING UP) Increased forced directed toward kinocilium => open K+ channels Upper half inhibited
Ampulla hair cells point in one direction only.
|
|
|
A net increase in firing from the left vestibular apparatus causes the eyes to move which direction? |
Right |
|
|
Where is the lesion in true vertigo? |
Vestibular apparatus Ocular drift toward side of lesion |

