![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
374 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Neural crest |
Melanocytes, aorticopulmonary septim, ganglia(autonomic, dorsal root, enteric), iris stroma, chromaffin cells, cranial nerves, odontoblasts/ossicles, parafollicular(C) cells, sclerae |
|
|
Neural tube |
CNS(neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells), pineal gland, posterior pituitary, retina |
|
|
Teratogenic drugs |
ACEI/ARB(renal failure, oligohydramnios), aminoglycosides (ototoxicity), fluoroquinolones (cartilage damage), carbamazepine/valproic acid(neural tube defects), Lithium (Ebstein anomaly), statins, warfarin |
|
|
Holoprosencephaly |
Fetal alcohol syndrome, sonic hedgehog gene mutations, patau syndrome |
|
|
Embryonic genes |
HOX: skeletal layout, SHH: cranial-caudal axis, Wnt-7: Dorsal-ventral axis |
|
|
Most common cause of neural tube defects |
Folate deficiency |
|
|
Most common preventable cause of congenital malformations in the U.S |
Alcohol use in pregnancy |
|
|
Nuclear localization signals |
4-8 amino acids, rich in proline, arginine, lysine(positive changed) |
|
|
CDK and cyclin to enter S phase |
CDK4/ cyclin D; CDK2/ cyclin E |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Add mannose-6- phosphate to lysosomal enzyme, defective-> I-cell disease |
|
|
Proteolysis |
Proteasomal degradation, lysosomal degradation, Ca-dependent enzymes |
|
|
Peroxisome |
Beta-oxidation (long-chain and branched FAs), synthesis of plasmalogen (in myelin), metabolizing ethanol |
|
|
Cytokeratin |
Epithelial cells(desmo-hemidesmosomes), found in carcinoma |
|
|
Desmin |
Muscle cells, found in rhabdomyosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
Glial fibrillary acid proteins(GFAP) |
Astrocytes, Schwann cells, other neuroglias; found in Glioblastoma |
|
|
Neurofilaments |
Axons within neurons; found in neuroblastoma |
|
|
Nuclear lamins |
Nuclear envelope |
|
|
Vimentin |
Connective tissue (support cellular membranes, fixed organelles), fibroblasts, leukocytes, endothelium; found in sarcomas |
|
|
Drugs acting on microtubules |
Inhibits growing (vincristine, vinblastine); inhibits breakdown (paclitaxel, docetaxal); Benzimidazoles (Menbendazole,albendazole,thiabendazole); Griseofulvin; colchicine |
|
|
Transport protein |
Dynein(-, alpha-tubulin); kinesin(+, beta-tubulin) |
|
|
Cilia |
Respiratory tract (trachea, bronchioles), paranasal sinuses, fallopian tubes |
|
|
Primary ciliary dyskinesia |
Immotile cilia due to dynein arm defect, infertility, bronchiectasis, chronic sinusitis, situs inversus(50%) |
|
|
Kartagener syndrome |
Bronchiectasis, chronic sinusitis, situs inversus, infertility |
|
|
Enzyme terminology |
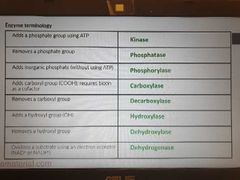
|
|
|
Digixin mechanism |
Block Na-K ATPase pump |
|
|
LDL receptor defect |
Abnormal clathrin coated pit binding site |
|
|
Arachidonic acid products |
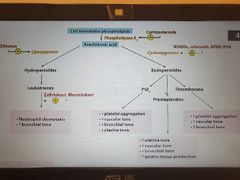
|
|
|
Nuclear damage |
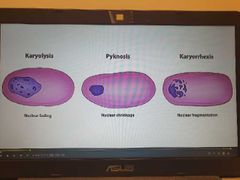
|
|
|
Apoptosis pathways |
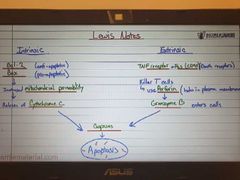
|
|
|
Coagulative necrosis |
Heart, liver, kidney; low oxygen content |
|
|
Caseous necrosis |
TB, systemic fungal infections |
|
|
Gangrenous necrosis |
Wet: bacterial infections, extremities; dry: ischemia, toes and feet |
|
|
Markers for tissue injury |
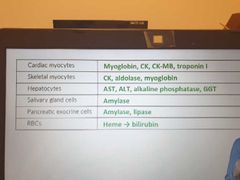
|
|
|
Red infarct |
Liver, lungs, intestine; reperfusion |
|
|
Pale(white) infarcts |
Heart, kidney, spleen |
|
|
Free radical degradation |
Catalase(H2O2-> O2 and H2O); superoxide dismutase(O2->H2O2); Glutathione peroxidase |
|
|
Acute inflammation |
Inflammatory mediators (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-alpha); vascular permeability (histamine, serotonin, bradykinin); fibrosis(collagen, reqiures Vit.C); remodeling by metalloproteinases (zinc) |
|
|
Neutrophilic chemotactic factors |
C5a, IL-8, LTB4, Kallikrein |
|
|
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency |
Abnormal LFA-1(integrin), delayed separation of umbilicus, recurrent bacterial infections |
|
|
Neutrophil extravasation |
Rolling(selectins), tight binding (integrins), diapedesis(PECAM-1), migration (C5a, IL-8, LTB4, Kallikrein) |
|
|
Fibrinogen, CRP producton |
Hepatocytes |
|
|
Type1 collagen (strong) |
Bone, skin, dentin, scar tissue |
|
|
Type 2 collagen (slippery) |
Cartilage, vitreous body, nucleus pulposus |
|
|
Type 3 collagen(stretchy) |
Granulation tissue, blood vessels, skin, uterus, fetal tissue, reticular fibers |
|
|
Type 4 collagen |
Basement membrane |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
Type1: AD, normal but deficient type1 collagen, blue sclerae, multiple fractures, hearing loss, dental abnormalities; type2: AR, perinatal lethal |
|
|
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome |
Classical: affects type5 collagen-> type1, hyperextensible skin, joint hypermobility; Vascular: type3, aterial rupture, hemorrhage, easy bruising, intracranial aneurysms |
|
|
Alport syndrome |
Type 4 collagen defects; nephritis and kidney failure, hearing loss, eye problems(cataracts, lenticonus) |
|
|
Marfan syndrome |
Defects in fibrillin-> affects elastin, hyperelastic joints, heart(valves, aorta), very tall, long arms and legs, arachnodactyly, pectus carinatum |
|
|
Alpha1- antitrypsin deficiency |
Increased elastase activity, destruction of elastin in alveoli, panacinar emphysema, hepatitis, cirrhosis, HCC |
|
|
Wound healing |
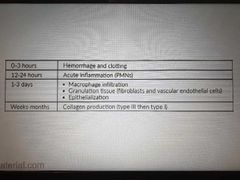
|
|
|
Vit.C in collagen synthesis |
Hydroxylation of lysine and proline |
|
|
Causes of atrophy |
Disuse, decreased hormonal signal, loss of innervation, inadequate supply of oxygen/nutrients, increased pressure |
|
|
Rapid-fire facts! |

|
|
|
Amino acids modified in the Golgi apparatus |
Serine, threonine, asparagine |
|
|
Marker for astrocytes |
Glial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP) |
|
|
Glial cell notes |

|
|
|
Substance that can cross BBB |

|
|
|
Drug most commonly used to reduce intracranial pressure |
Mannitol |
|
|
Dopamine |

|
|
|
Dopamine pathways-1 |

|
|
|
Dopamine pathways-2 |

|
|
|
Norepinephrine |

Decreased: depression, increased: anxiety, mania |
|
|
Sorotonin |

|
|
|
Acetylcholine |

|
|
|
GABA |

|
|
|
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the spinal cord |
Glycine |
|
|
Main excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS |
Glutamate |
|
|
RAS |

Lesion leads to coma |
|
|
Brain development |
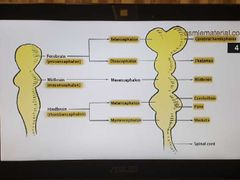
|
|
|
Alpha fetal protein |
Increased: neural tube defect, anterior abdominal wall defect; decreased: Down syndrome |
|
|
Chiari malformations |

|
|
|
Dandy-walker syndrome |

|
|
|
Pharyngeal clefts |

|
|
|
Thyroglossal duct cyst Vs. pharyngeal cleft cyst |

|
|
|
Pharyngeal pouch-1 |

|
|
|
Pharyngeal pouch-2 |

|
|
|
DiGeorge syndrome |

Thymic aplasia-> T-cell deficiency |
|
|
Pharyngeal arch-1 |

|
|
|
Pharyngeal arch-2 |

|
|
|
Frontal cortex lesion |
Disinhibition, poor judgement, primitive reflex |
|
|
Carotid sheath |
Carotid artery, jugular vein, vagus nerve |
|
|
Circle of Wills |
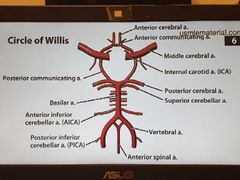
|
|
|
Conduction aphasia |
Poor repetition, arcuate fasciculus lesion |
|
|
Dysprosody |

|
|
|
Parietal cortex lesions |

|
|
|
Risks for aneurysms |
ADPKD, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, HTN, smoking, advanced age, Race(black) |
|
|
Most common cause of SAH |
Trauma; non-traumatic: aneurysm, AVM |
|
|
EDH |
MMA; Compression, then herniation of the brain; CN3 palsy (down and out); "lucid interval" |
|
|
SDH |
Bridging veins; elderly, alcoholics, trauma(whiplash, shaken baby) |
|
|
ICH(parenchymal hemorrhage) |
HTN, vascular malformations, vasculitis, amyloid angiopathy, tumors, anticoagulant |
|
|
Intraventricular hemorrhage |

|
|
|
Ischemic stroke causes |

|
|
|
Thrombolytics |
tPA, streptokinase, Urokinase |
|
|
Contraindications to thrombolytics |

|
|
|
Areas of the brain most susceptible to ischemia |
Cerebellum, neocortex, hippocampus, watershed areas |
|
|
Rpaid-fire |

|
|
|
Anterior hypothalamus |
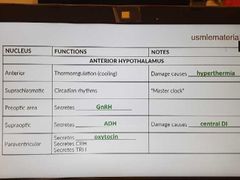
|
|
|
Tuberal hypothalamus |
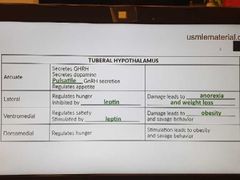
|
|
|
Posterior hypothalamus |
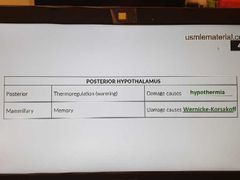
|
|
|
Lesions to amygdala |

|
|
|
Mammillary body lesions |

Due to thiamine deficiency |
|
|
Cranial nerves |
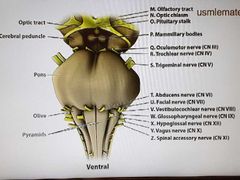
|
|
|
CN1(olfactory) |
Exits at cribriform plate |
|
|
Eye movements |
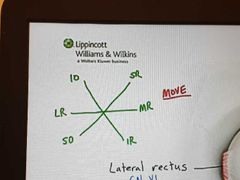
|
|
|
Pupillary light reflex |
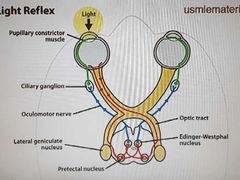
CN2: afferent; CN3: efferent |
|
|
Trigeminal nerve |
Ophthalmic (sensory, superior orbital fissure); maxillary (sensory, foramen rotundum); mandibular (sensory and motor, foramen ovale) |
|
|
Corneal reflex |
Ophthalmic branch of CN5; temporal branch of CN7 |
|
|
Jaw muscles(V-3) |
Closing: temporalis, medial pterygoid, masseter; open: lateral pterygoid |
|
|
Cavernous sinus |
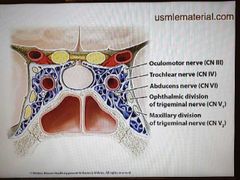
|
|
|
CN7(facial) |
Exits at internal acoustic meatus; temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical; |
|
|
Causes for facial palsy |
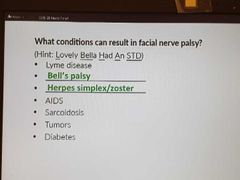
|
|
|
Facial nerve Vs. cortex lesions |
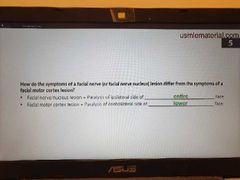
|
|
|
CN9(glossopharyngeal) |

Exits at jugular foramen(with CN10&11) |
|
|
Vagus lesions |

|
|
|
CN12(hypoglossal) lesion |
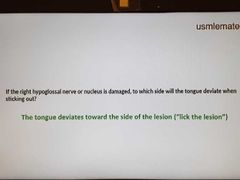
|
|
|
Gag reflex |
Tests CN9&10 |
|
|
Cavernous sinus infections |

|
|
|
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway |
Fine touch, vibration, proprioception; decussates in medulla-> medial lemniscus |
|
|
Spinothalamic tract |
Pain and temperature; ascend 1-2 levels(lissauer's tract), decussates in the anterior white commissure-> thalamus |
|
|
Corticospinal tract |
Motor, decussates in the caudal medulla->medullary pyramids |
|
|
Rostral midbrain |
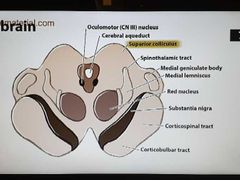
Superior colliculus lesion-> paralysis of upward gaze |
|
|
Caudal midbrain |

|
|
|
Pons blood supply |
Medial(basilar artery: median and paramedian branch); lateral(AICA) |
|
|
Medulla blood supply |
Medial: anterior spinal artery; lateral: PICA |
|
|
Vagal nuclei |

|
|
|
Horner syndrome |
Ptosis, miosis, anhydrosis |
|
|
Spinal cord anatomy |
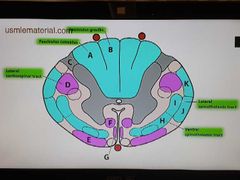
|
|
|
Romberg test |
Test of dorsal column functions, proprioception in the legs, not the cerebellum |
|
|
Parietal lobe lesions |

|
|
|
Brain stem lesion |
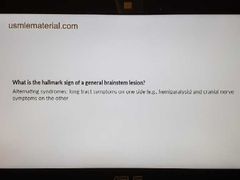
|
|
|
The rule of fours |

|
|
|
Medial/median brain stem lesions |

|
|
|
Lateral brain stem lesions |
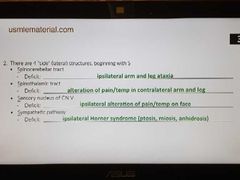
|
|
|
Wallenberg syndrome (lateral medullary syndrome) |

No motor weakness |
|
|
Intranuclear ophthalmoplegia |
Lesions medial longitudinal fasciculus, lesion eye cannot adduct, normal side abduct with nystagmus; common cause: multiple sclerosis, medial pontine stroke |
|
|
Locked-in syndrome |
Basilar artery stroke that affects bil. Pons, or central pontine myelinolysis |
|
|
Weber syndrome |
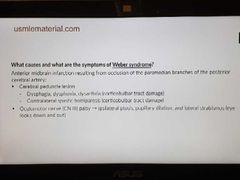
|
|
|
CSF flow |
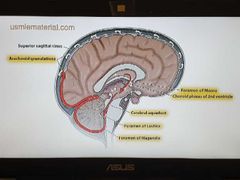
|
|
|
Normal pressure hydrocephalus |

|
|
|
Hydrocephalus |
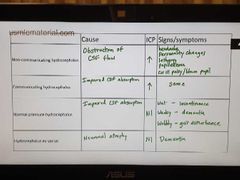
|
|
|
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension(pseudotumor cerebri) |
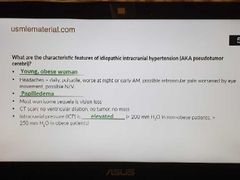
|
|
|
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Tx |
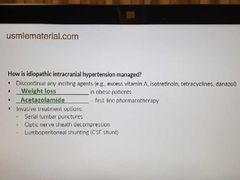
|
|
|
Lumbar puncture path |
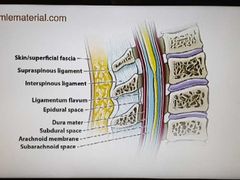
|
|
|
Tension headache |
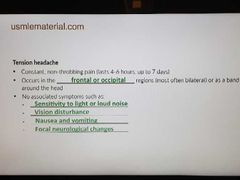
|
|
|
Migraine |

|
|
|
Cluster headache |
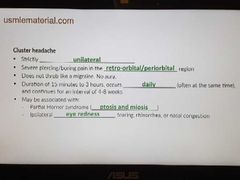
|
|
|
Tension headache and migraine Tx |

|
|
|
Contraindications of triptans |
CAD, prinzmetal angina, pregnancy |
|
|
Tx for cluster headaches |

|
|
|
Headache-1 |
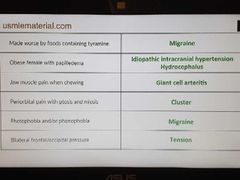
|
|
|
Headache-2 |
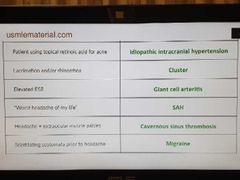
|
|
|
Headache-3 |

|
|
|
Adult brain tumors |

|
|
|
Pediatric brain tumors |

|
|
|
Herniation syndrome |
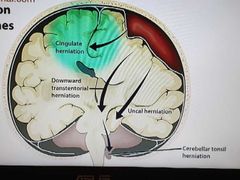
|
|
|
Schwannoma |

|
|
|
Hamangioblastoma |
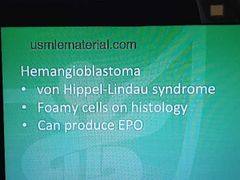
|
|
|
Pilocytic astrocytoma |
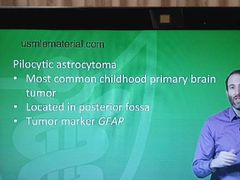
Corkscrew-like Rosenthal fibers |
|
|
Medulloblastoma & Ependymoma |

|
|
|
Medulloblastoma & Ependymoma-2 |

|
|
|
Neuronal pigmentation/inclusions |
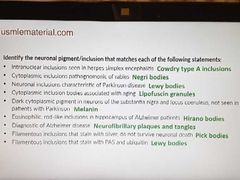
|
|
|
Alzheimer's disease |
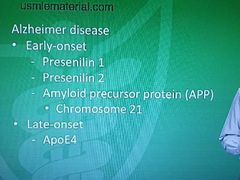
|
|
|
Alzheimer's drugs |

|
|
|
Dementia with Lewy bodies |

|
|
|
Frontotemporal dementia |

|
|
|
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease |

|
|
|
Other causes of dementia |

|
|
|
Dementia workup |

|
|
|
Causes of delirium |

|
|
|
Delirium |

|
|
|
Delirium Vs. dementia |
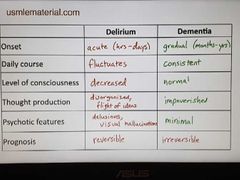
|
|
|
Rapid-fire |

|
|
|
Parietal lobe lesions |

|
|
|
Ach receptors |

|
|
|
Parasympathetic activation & cholinergic excess |
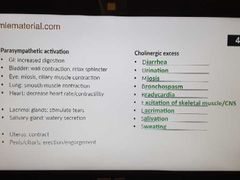
|
|
|
Organophosphate poisoning |
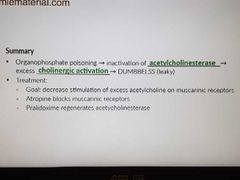
|
|
|
Myasthenia gravis |
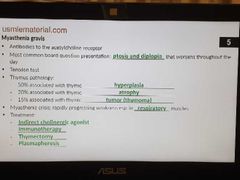
|
|
|
Ach easterase inhibitors Tx for Alzheimer's |

|
|
|
Direct cholinergics |
Bethanechol(postop ileus, urinary retention); Carbachol (glaucoma); Pilocarpine(stimulates sweat, tears, saliva); Methacholine (asthma challenge test) |
|
|
Indirect cholinergics(AchE inhibitors) |
Neostigmine (postop&neurogenic ileus); urinary retention, MG, neuromuscular blocking agent); Pyridostigmine(long time MG), Edrophonium(MG:diagnosis); Physostigmine (anticholinergic & atropine toxicity) |
|
|
Rapid-fire |
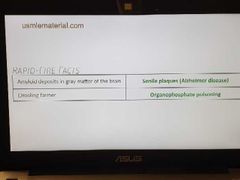
|
|
|
Parasympathetic inhibition |

|
|
|
Contraindications for anticholinergics |

|
|
|
Meds with anticholinergic effects |
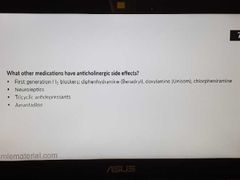
|
|
|
Meds for urinary incontinence |

|
|
|
Muscarinic antagonists |

|
|
|
Tongue innervation |
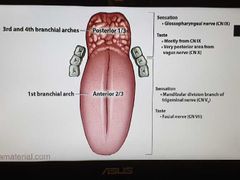
|
|
|
Alpha-1 receptors |

|
|
|
Alphal-2 receptors |
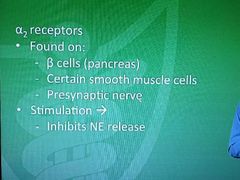
|
|
|
Beta-1 receptors |

|
|
|
Beta-2 receptors |

|
|
|
Receptor distribution |

|
|
|
Epinephrine |

|
|
|
Norepinephrine |

|
|
|
Dopamine |

|
|
|
Isoproterenol |

|
|
|
Dobutamine |

|
|
|
Phenylephrine |

|
|
|
Albuterol, levalbuterol, salmeterol |

|
|
|
Terbutaline |

|
|
|
Clonidine |
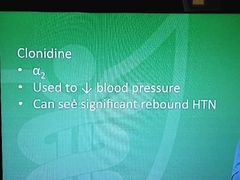
|
|
|
Amphetamine |

|
|
|
Ephedrine |

|
|
|
Cocaine |

|
|
|
Alpha-1 blockers |
Prazosin, Doxazosin, Terazosin; decreased BP, treat BPH, side effects: postural hypotension, reflex tachycardia |
|
|
Tamsulosin |
Alpha-1A,D blocker, treat BPH, less effect on BP |
|
|
Nonselective alpha blockers |
Phenoxybezamine(pheochromocytoma), phentolamine |
|
|
Nonselective beta blockers |
Propranolol, Timolol, Nadolol |
|
|
Beta-1 blockers |
Metoprplol, Atenolol, Esmolol |
|
|
Weak beta-1&2 agonists |
Acebutolol, Pindolol; act as blockers, used in patients with HTN and bradycardia |
|
|
Nebivolol |
Beta-1 blocker, also caused NO- derived vasodilation |
|
|
Aplha-1/beta-1 blockers |
Carvedilol, Labetalol |
|
|
Use of beta blockers |

|
|
|
Adverse effects of beta blockers |

|
|
|
Beta blocker notes |

|
|
|
Alpha-2 agonist |
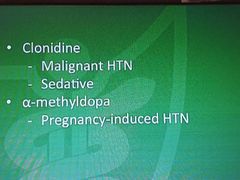
|
|
|
Cholinergic nerve |
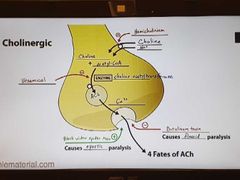
|
|
|
Noradrenergic nerve ending |
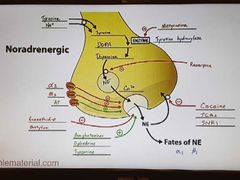
|
|
|
Metabolism of NE |

|
|
|
Metabolism of catecholamines |

|
|
|
Catecholamine synthesis |

|
|
|
Treatment for idiopathic intracranial hypertension |
Acetazolamide(pseudotumor cerebri, glaucoma, altitude sickness) |
|
|
Gq protein receptors |

|
|
|
Gi/Gs protein receptors |

|
|
|
Main pathway for tyrosine kinase receptor |
Active Ras protein-> protein kinase 1,2,3 |
|
|
G Protein notes |

|
|
|
Muscarinic receptors |
M1: enteric nevous system, M2: decrease contractility and heart rate, M3: increase bladder contraction and gut peristalsis |
|
|
Dopamine receptor |
D1: relax rebal and vascular smooth muscle; D2: found in the brain |
|
|
Histamine receptors |
H1: Nasal secretion, bronchial mucus production, pruritus, bronchoconstriction; H2: gastric acid secretion |
|
|
Vasopressin receptors |
V1: vascular smooth muscle contraction, V2: ADH receptors |
|
|
Km |
[S] at 1/2 Vmax |
|
|
Km, Vmax relationship |
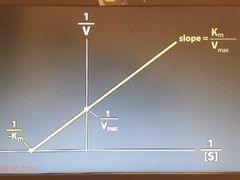
Km: enzyme's affinity for substrate (low Km-> high affinity) Vmax: affect by number of enzymes |
|
|
Inhibitors |
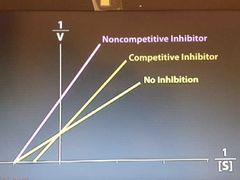
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics |

|
|
|
Half-life |
94% after 4 half-life |
|
|
Efficacy |
Maximum drug effect , dose independent |
|
|
Potency |
Same effect by different dosage of different drugs, dose dependent |
|
|
Therapeutic index |
LD50/ED50, higher the better |
|
|
Drug with low therapeutic index |
Seizure Drugs, lithium, digoxin, warfarin |
|
|
Phase 1 vs. phase 2 reactions |

|
|
|
Phase notes |

|
|
|
P450 inhibitors |

Crack Amigos |
|
|
P450 inducers |

Guiness, coronas, and PBRs induce chronic alcoholism |
|
|
Ethanol metabolism-1 |
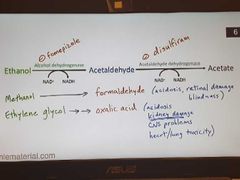
|
|
|
Ethanol metabolism-2 |
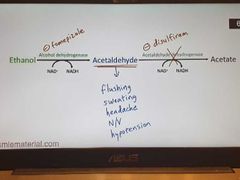
|
|
|
Disulfiram-like reactions |
Metronidazole, certain cephalosporins, procabazine, 1st- generation sulfonylureas |
|
|
Zero order elimination |

Phenytoin, ethanol, aspirin |
|
|
First order elimination |

|
|
|
Acid/base and drug elimination |

|
|
|
Drug suffix-1 |
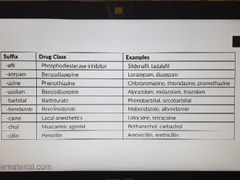
|
|
|
Drug suffix-2 |
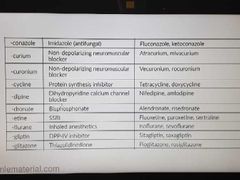
|
|
|
Drug suffix-3 |
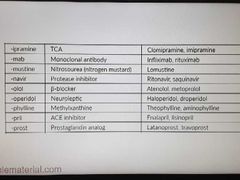
|
|
|
Drug suffix-4 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-1 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-2 |

|
|
|
Drig side effects-3 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-4 |

Treat with IV MgSO4 |
|
|
Drug side effects-5 |
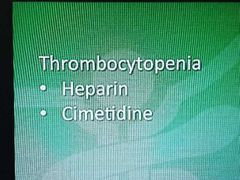
|
|
|
Drug side effects-5 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-6 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-7 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-8 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-9 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-10 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-11 |
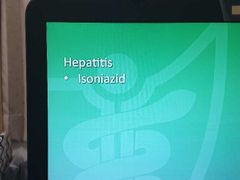
|
|
|
Drug side effects-12 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-13 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-14 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-15 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-16 |
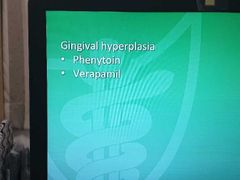
|
|
|
Drug side effects-17 |
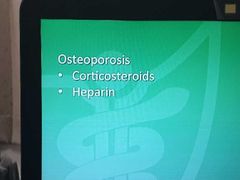
|
|
|
Drug side effects-18 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-19 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-20 |

Drug-induced lupus |
|
|
Drug side effects-21 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-22 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-23 |
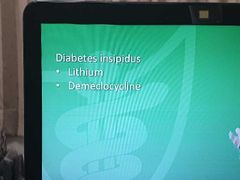
|
|
|
Drug side effects-24 |
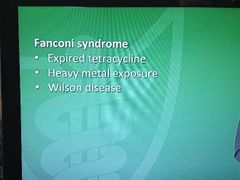
|
|
|
Drug side effects-25 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-26 |

Quindine, Quinine |
|
|
Drug side effects-27 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-28 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-29 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-30 |

|
|
|
Drug side effects-31 |

|
|
|
Antidote-1 |
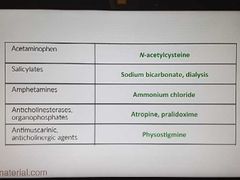
|
|
|
Antidote-2 |
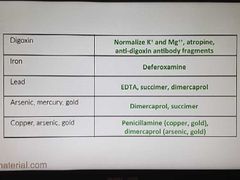
|
|
|
Antidote-3 |

|
|
|
Antidote-4 |
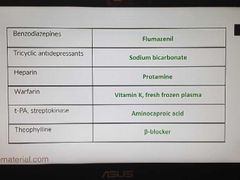
|
|
|
Spiral septum defect |

|
|
|
Heart development |
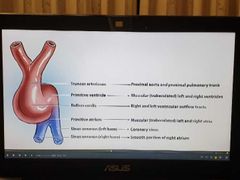
|
|
|
Fetal shunting |

|
|
|
PDA |

|
|
|
Eisenmenger syndrome |

Cyanosis, shortness of breath, clubbing |
|
|
Coarctation of aorta |

|
|
|
5 causes of cyanotic disease(right to left shunt) |
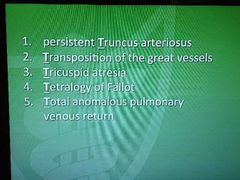
|
|
|
Ebstein anomaly |
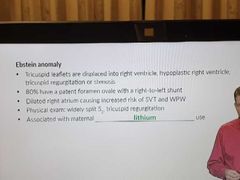
|
|
|
TOF |
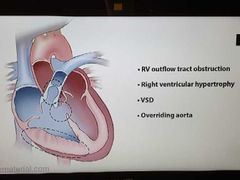
Boot-shaped heart |
|
|
Causes of congenital heart anomaly-1 |

|
|
|
Causes of congenital heart anomaly-2 |

|
|
|
Causes of congenital heart anomaly-3 |

|
|
|
Rapid-fire |
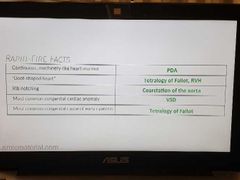
|
|
|
Cardiac output |

|
|
|
Fick principle |

|
|
|
MAP |

|
|
|
Contractility |

|
|
|
Heart failure |

|
|
|
Heart failure mechanism |
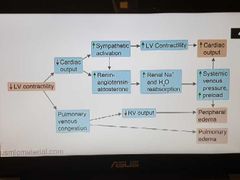
|
|
|
Renin production |

|
|
|
Left-sided heart failure |

|
|
|
Beta-blockers for heart failure |
Metoprolol, carvedilol, bisoprolol |
|
|
Vasodilators for CHF |

|
|
|
Digoxin toxicity |

|
|
|
Tx for digoxin toxicity |

|
|
|
Tx for acute CHF |

|
|
|
Capillary hydrostatic pressure |

|
|
|
Capillary permeability (Kf) |

|
|
|
Plasma oncotic pressure |

|
|
|
Interstitial oncotic pressure |

|
|
|
Tx for shock |
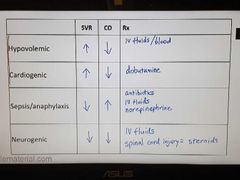
|
|
|
Cause of hypovolemic shock/cardiogenic shock |
Hypovolemic: blood loss, burn Cardiogenic: AMI, PE, CHF, arrhythmias, cardiac tamponade, Tension pneumothorax, cardiac contusion |
|
|
Femoral vessels |
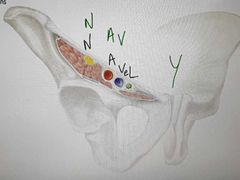
|
|
|
Central line locations |

|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics equations |

|
|
|
Pressure volume loop |
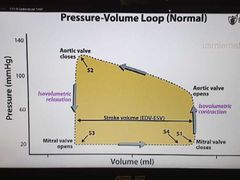
|
|
|
Pressure volume loop variations |
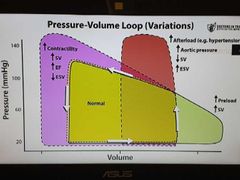
|
|
|
S3 heart sound |

|
|
|
S4 heart sound |
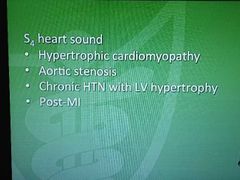
|
|
|
Wild splitting of S2 |
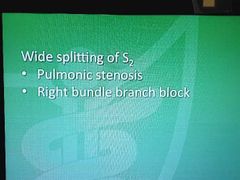
|
|
|
Paradoxical splitting of S2 |
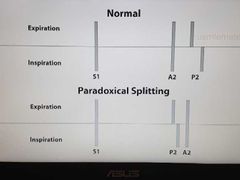
AS, LBBB |
|
|
Jugular venous waves |

|
|
|
Auscultation BN of the heart |
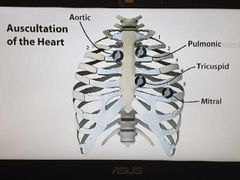
|
|
|
Benign heart sounds |

|
|
|
Breathing murmurs |

|
|
|
Hand grip |

|
|
|
Valsalva maneuver |

|
|
|
AR PE |

|
|
|
AR causes |

|
|
|
MS PE |

|
|
|
MS causes |

|
|
|
Rapid fire |
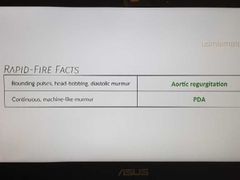
|
|
|
AS |

Pulsus parvus et tardus |
|
|
Causes of AS |

|
|
|
MR |

|
|
|
MR-2 |

|
|
|
Causes of MR |

|
|
|
TR |

|
|
|
Causes of TR |

|
|
|
Murmurs |

|
|
|
Murmurs-2 |

|
|
|
Myocytes action potential |
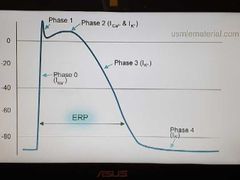
|
|
|
Pacemaker action potential |
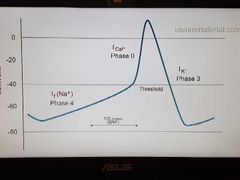
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics equations |

|
|
|
Antiarrhythmic drugs |

|
|
|
Na channel blockers |
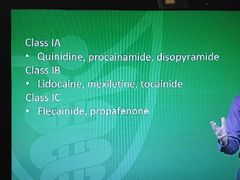
|
|
|
Procainamide |
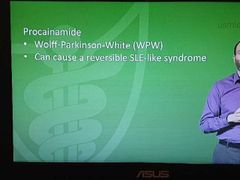
|
|
|
Drug-induced lupus |

|
|
|
Quinidine |

|
|
|
Lidocaine |

|
|
|
Flecainide and propafenone |

|
|
|
Beta-blockers |
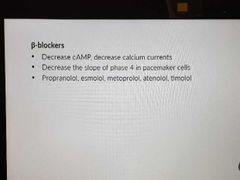
|
|
|
Beta blockers, clinical uses |

|
|
|
Beta blockers, adverse effects |

|
|
|
K channel blockers |

Toxicity: Torsades de pointes |
|
|
Amiodarone |

|
|
|
Photosensitivity |

|
|
|
Amiodarone-2 |

|
|
|
CCB |

|
|
|
CCB side effects |

|
|
|
Lewis notes |
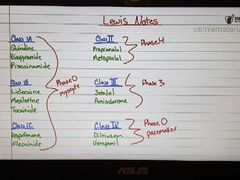
|
|
|
Adenosine |

|
|
|
Adenosine toxicity |

|
|
|
K and Mg |

|

