![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Initial workup for thyroid disease requires which:
1. H&P and TSH 2. CT-scan 3. Ultrasound of the neck 4. Nuclear medicine 5. Free T3 level |
1. H&P 2. Check TSH 3. Assess free T4 and free T3
|
|
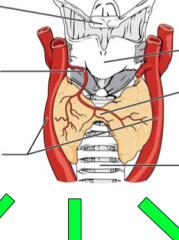
Identify the following anatomical features and the three major functions of the thyroid:
Superior thyroid artery, trachea, common carotid arteries, thyroid cartilage, hyoid bone, trachea isthmus of the thyroid |
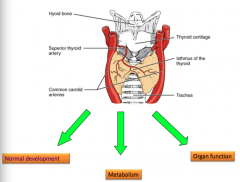
Thyroid glands takes a lot of blood |
|
|
What are the major thyroid hormone effects (think everywhere)? |

|
|
|
What are the four major aspects of thyroid hormone? (four things to think about) |

|
|
|
Which of the following is not involved in the production of thyroid hormone?
A. Pendrin B. Na-I co-transporter C. Transthyretin D. Thyroglobulin |
Transthyretin
Read about how thyroid hormone is produced |
|
|
68 yo female admitted for elective surgery. Successful. Became lethargic, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, needed intubation, developed paralytic ileum. Low heart rate, puffy face, dry skin, and edematous changes in the pretibial/foot area.
What is this condition? |
Myxedema coma = extremely swollen feet |
|
|
What are some symptoms of hypothyroidism? |

|
|
|
What are some signs of hypothyroidism? |

Rarely ever see bradycardia (myxedema coma) |
|
|
What are some causes of hypothyroidism? What is the most common cause? |

Most common cause = Low iodine intake (worldwide)
In US = radioactive iodine ablation
Also add pituitary dysfunction to the list |
|
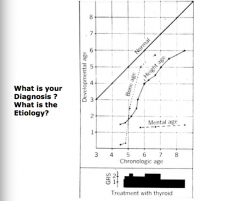
What is the diagnosis? Etiology? |
Cretinism Low thyroid hormone early in life => decreased mental age, bone and height effects
This is why we screen for thyroid hormone levels at an early age => can be prevented |
|
|
What are the three initial treatments of hypothyroidism?
Life threatening? Replacement of what? What organ do you worry about? |

Replace corticosteroids in severe hypothyroidism! => because adrenals slow down when thyroid level is low! |
|
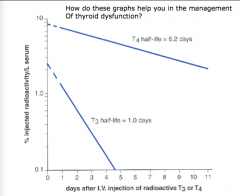
When should you check TSH again? |
Usually wait four-six half-lives (5-6 weeks) to check TSH again! |
|
|
55 yo male admitted to ICU => SOB, tachycardia, Afib, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, seizure, 50 lbs lost in last six months, has hyperthyroidism but not able to afford medication.
What is the diagnosis? |
Thyroid storm! |
|
|
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism? |

|
|
|
What are the signs of hyperthyroidism? |

|
|
|
What are some causes of elevated thyroid hormone levels? |

|
|
|
What are the initial treatments to give for thyroid storm? Drugs and how to treat life-threatening conditions. |

|
|
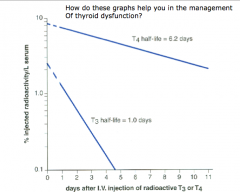
How does this graph help for hyperthyroidism? What will you measure? |
Measure T3, want to see results soon. Measure in a few days. |
|
|
49 yo admitted for chest pain, STEMI, successful cath and several stents placed, hematoma/infection at catheter site. TFTs given:
TSH = 4.9 (.5-5.0) Free T4 = 0.6 ng/dL (.7-2.0) Total T3 = 40 ng/dL (70-190)
What is going on? |
TSH goes up because T4 and T3 are on the low side. Check in a few weeks once he is out of the hospital and recovers. |
|
|
34 yo female comes to your clinic. Delivered baby 4 mo ago. Heat intolerance, palpitations and sweating. No change in bowel, PE slight tremor, moist and warm kin , HR 102, no exophthalmus, maybe a slight lid lag, slightly enlarged non-painful thyroid gland.
What is the diagnosis? |
Post-pardum thyroiditis
(Sub-acute thyroiditis)
Acute thyroiditis usually bacterial and has pain, fever, etc. |
|
|
36 yo female hyperthyroid, taking levothyroxine, asking for refill, TSH is 3.2? Says she is pregnant again. What should you do next? 1. Gratulate her 2. Ask her to come to your office for TFTs 3. Increase levothryoxine 4. Ensure your malpractice insurance is current |
3. Increase levothyroxine
DON'T WAIT FOR THYROID FUNCTION TEST! Want to make sure baby has appropriate levels. Treat two people at the same time (once baby is nine months old, most developmental things are gone) |
|
|
What are the five thyroid enlargements? |
Diffuse nontoxic simple goiter Nontixoc multinodulat goiter Toxic multinodular goiter 2 more from lecture ... |
|
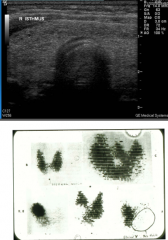
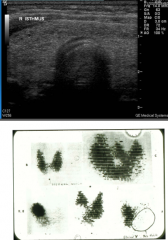
Diffusely overactive gland in bottom image. |
|
|
|
48 yo male Routine visit. Hoarse voice after cold, tender lump in throat, palpable nodule, etc... |
Thyroid cancer? What are the risk factors? Get from lecture
History of head/neck radiation Age <20 or >45 Increased nodule size >4 cm
GET CLASSIFICATION OF THYROID CANCER from slides. |

