![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
heterotopia |
congenital; pancreatic tissue in pylorus
|
|
|
pyloric stenosis |
congenital, familial, connection to 45 XO, trisomy 18; nonbilious vomiting in 2nd-3rd week |
|
|
gastroparesis |
decr. stomach motility; early satiety, bloating; cause = autonomic neuropathy or prior vagotomy |
|
|
upper GI bleed |
melena (dark, tarry stools) - prox. to DJ junction |
|
|
erosion vs. ulcer |
limited to mucosa vs. into submucosa |
|
|
gastropathy |
loss of mucin, reactive nuclei, tortuous glands |
|
|
gastritis |
like gastropathy but inflammation is also present; acute/chronic |
|
|
causes of acute ulcers |
stress (shock, sepsis, trauma), NSAIDs, NG tubes |
|
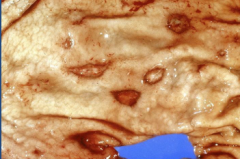
|
acute ulcer |
|
|
Gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE) |
upper GI bleed; idiopathic dilated vessels of submucosa + watermelon stomach |
|
|
Portal hypertensive gastropathy |
upper GI bleed; snakeskin pattern |
|
|
Dieulafoy lesion |
upper GI bleed; mucosal artery too large for the area -> large bleed |
|
|
acute gastritis |
non-infectious (NSAID, EtOH, smoking, drugs, uremia), severe stress (physical, ischemia & shock, trauma) |
|
|
things that protect mucosa |
mucus layer, bicarb secretion, rich blood supply |
|
|
causes of decr. bicarb in stomach |
NSAID, uremia, H. pylori |
|
|
chronic gastritis |
antral; high acid production; can spread (pangastritis); driven by H. pylori |
|
|
chronic gastritis morphology |
chronic & acute inflammation; atrophy, metaplasia, G cell hyperplasia, dysplasia |
|
|
hallmark of chronic gastritis histology |
lymphoid follicle present in the stomach |
|
|
Helicobacter pylori |
causes 90% of chronic gastritis; organism has flagella, urease (ammonia buffers gastric acid), adhesins, blood group O binding; low-grade persistent infection |
|
|
H. pylori genetic subtypes |
CagA (cytotoxin associated gene) + = more extensive infl. than CagA- => more likely to cause gastric malignancy, atrophic gastritis |
|
|
sequelae of H. pylori infection |
chronic gastritis, PUD, gastric ca, gastric lymphoma, atrophic gastritis (antrum & pylorus) |
|
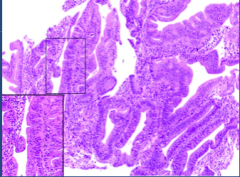
|
gastric mucosa w/ high-grade dysplasia (precursor to adenoCA) |
|
|
Peptic Ulcer Disease |
ulcer present w/ chronic gastritis; main cause = H. pylori; proximal duodenum (eating = relief), antrum (eating = worse) |
|
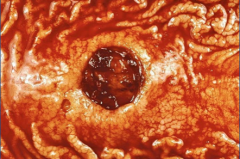
|
ulcer - note no necrotic tissue |
|
|
complications of peptic ulcer disease |
upper GI bleed, perforation (see free air under diaphragm) |
|
|
Autoimmune gastritis |
<10% chronic gastritis cases; CD4+ T-cells injure H+, K+-ATPase and gastrin R or intrinsic factor w/ autoantibodies present; affects BODY and FUNDUS |
|
|
Autoimmune gastritis - morphology & pathogenesis |
thin mucosa, lose rugal folds; lose acid production -> incr. gastrin -> G cell hyperplasia in antrum -> pernicious anemia, carcinoid tumor, achlorhydria |
|
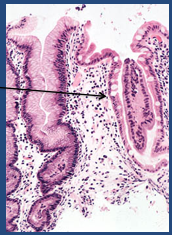
|
autoimmune gastritis - thin mucosa, atrophy, intestinal metaplasia |
|
|
Menetrier's disease |
hypertrophic/plastic gastropathy w/ low chloride and low protein; lots of mucin, little acid produced; tortuous foveolar hyperplasia w/ glandular atrophy; cause = excessive TGF-alpha |
|
|
Zollinger-ellison syndrome - definition & cause |
thickened body & fundus secondary to glandular hyperplasia; cause = excess gastrin (gastrinoma in small bowel or pancreas) |
|
|
ZE syndrome - symptoms |
therapy resistant; lots of ulcers - esp. beyond proximal duodenum; diarrhea; family hx |
|
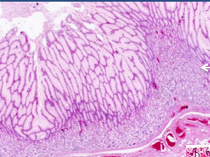
|
Menetriers (expanded foveolar cells) |
|
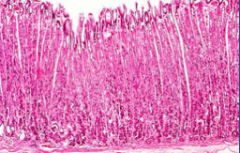
|
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (expanded glands) |
|
|
Polyps |
75% are inflammatory or hyperplasia (gastritis associated) |
|
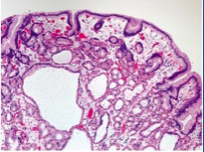
|
Fundic gland polyp - note cystic spaces; risk for dysplasia; incr. secondary to PPI use |
|
|
Adenoma |
10% of polyps, a/w FAP, gastritis & intestinal metaplasia; risk of adenoCA if >2cm |
|
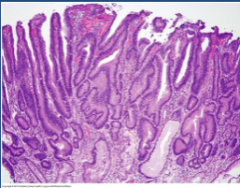
|
adenoma |
|
|
benign tumors of stomach |
leiomyoma, lipomas (rare) |
|
|
Neuroendocrine tumors |
body/fundus of atrophic gastritis or ZE syndrome (indolent); sporadic may be aggressive |
|
|
causes of adenocarcinoma in stomach |
H. pylori, environment/diet, geography, genetics |
|
|
where does adenocarcinoma MC occur? |
pylorus/antrum (60%); lesser curvature |
|
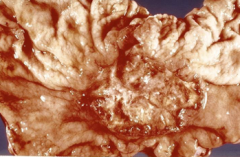
|
gastric adenocarcinoma - malignant ulcer (necrotic tissue in center, irregular edge) |
|
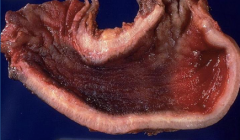
|
linitis plastica (leather bottle)- diffuse adenocarcinoma; gross |
|
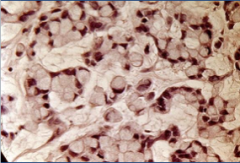
|
linitis plastica (diffuse adenocarcinoma) - see signet ring cells; NOT related to H. pylori; Krukenberg tumor (mets to ovaries) |
|
|
Acanthosis nigricans |
velvety, pigmented skin thickening a/w gastric malignancy |
|
|
overall 5ys of gastric adenoCA |
<30% in US |
|
|
Gastric lymphoma |
5% of stomach malignancies; B-cell lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT); most a/w H. pylori |
|
|
Gastri-intestinal stromal tumors (GIST) |
throughout GI tract, stomach MC; can be aggressive (malignant GIST); 80% have oncogenic mutation (tyrosine kinase C-KIT) |
|
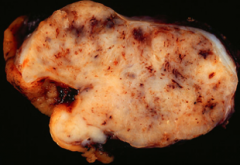
|
GIST - gross |
|
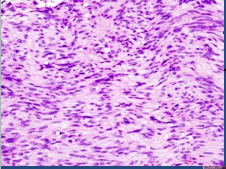
|
spindle cell GIST (MC - also epithelioid type) |
|
|
Gleevec |
Imatinib mesylate; competitive inhibitor of tyrosine kinases a/w KIT protein, ABL protein, and PLT-derived growth factor receptors - treat GISTs |

