![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is axonal neuropathies? |
A direct injury to axons ord neuronal body, which causes degeneration of nerve tissue distal to injury |
|
|
|
What is demyelinating neuropathies? |
Damage to Schwann cells or myelin |
|
|
|
What causes mononeuropathy? |
Direct trauma or entrapment |
|
|
|
How many spinal nerves do we have |
31 pair |
|
|
|
Give the exiting position of spinal nerves in cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal. |
C1-C7 exit above, C8 exit between C7-Th1, Th1-L5 exit below, S1-S4 exit through sacral foramina and S5 and coccygeal spinal nerve exit through sacral hiatus. |
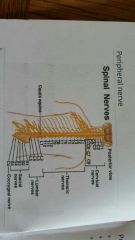
|
|
|
Cells that myelin periferal nerves? |
Schwann cells |
|
|
|
Explain endoneurium |
Covering individual axons |
|
|
|
Explain perineurium |
Covering a bundle of axons |
Fascicle |
|
|
Explain epineurium |
Outermost covering of the entire nerve |
|
|
|
Function of meningeal branch? |
Supplies vertebrae, vertebral ligaments, blood vessels of the cord and meninges |
|
|
|
Function of posterior ramus? |
Innervation of posterior trunk muscles and skin |
|
|
|
Function of anterior ramus? |
Innervation of muscles and structures of upper and lower limb and muscles and skin of lateral and anterior trunk. |
|
|
|
Give 3 causes of GBS |
Can develop spontaneously, after systemic infection, other stress |
|
|
|
What is Guillian-Barré syndrome? |
Autoimmune attack on periferal nerves and roots. It has a demyalinisation of motor axons. |
|
|
|
Give symptoms of GBS |
Relative symmetric weaknesses beginning in legs, progressing to arms. Deep tendon reflexes lost. Prominent motor axon weakness, less sensory. |
|
|
|
Vaccine or infection can cause GBS. Which ones? |
Swine flu vaccine, campylobacter jejuni, mycoplasma pneumonia, Epstein-Barr virus or HIV. |
|
|
|
What is the incidens of GBS in Sweden? |
90 cases per year |
|
|
|
How do you treat GBS? |
Plasmapherisis - removal of blood with separation and replacement of plasma. Remove antibodies from bloodstream. Supress immune system. |
|
|
|
What is chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy? |
Autoimmune inflammation of axonal myelin sheath |
|
|
|
What is CIDP characterised by? |
Symmetric weakness of proximal and distal muscles. Affecting both motor and sensory neurons. |
|
|
|
How can GBS and CIDP differentiate from each other? |
GBS worsens during 1-2 weeks. CIDP gradual onset during 1-2 months. |
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of CIDP? |
Fatigue, symmetric weakness in legs and arms, pain and parasthesia, loss of deep tendon reflexes and difficulty with coordination. |
|
|
|
How is CIDP treated? |
With corticosteroids or sometimes with plasmapherisis or immune globulin. |
|
|
|
This is the most common complication of diabetes. |
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy |
Affecting 50% of all diabetic patients |
|
|
Give 5 causes of peripheral neuropathy besides diabetes. |
Drugs, alcohol, vasculitis, thyroid disease and vitamin B1, B3, B6 or B12 deficiency. |
|
|
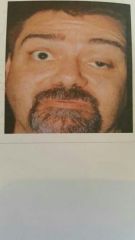
Name the disorder. |
Myasthenia Gravis MG |
|
|
|
What kind of disorde is MG? |
Neuromuscular junction disorder. |
|
|
|
What causes MG? |
Autoantibodies block the function of postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors at motor end plates. |
|
|
|
What are the common symptoms of MG? |
Ptosis of eyelids, diplopia and muscle weakness after use of the affected muscle. |
|
|
|
How can MG be treated? |
Plasmapherisis, corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs or removal of thymus |
|
|
|
What is the incidens in MG? |
3 in 100000 |
|
|
|
Name most common affected sexes and age in MG? |
More common in females, age 20-40, males may present after 60. |
|
|
|
What is the similar syndrome to myasthenia Gravis? |
Lambert-Eaton syndrome |
|
|
|
What is tetanus? |
It is acute poisoning from a neurotoxin produced by clostridium tetani |
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of tetanus? |
Tonic spasm of voluntary muscles. |
|
|
|
Give examples of muscles that can be affected. |
Facial muscles spasm, spasm of abdominal, neck and back muscles. Sphincter spasm, diphragm, chest muscles. |
|
|
|
Where can tetanus bacilli be found? |
In soil and animal feces |
|
|

Which disease? |
Tetanus |
|
|
|
What is botulism? |
Neuromuscular poisoning due to clostridium botulinum toxin. |
|
|
|
How do botulism affect people? |
Symmetric cranial nerve pals is accompanied by a symmetric descending weakness and flaccid paralysis without sensory deficits. |
|
|
|
What are the sources of infection from botulism? |
Cured or smoked fish, meat or vegetables. Home-canned foods. Can be found in honey. Sausage poisoning. |
|
|
|
Botulism occurs in 3 forms. Which ones? |
Food-borne, wound, infant |
|
|
|
What is polyneuropathy? |
Diffuse peripheral nerve disorder that is bilaterally symmetrical and thus not confined to the distribution of a single nerve or a single limb. |
|
|
|
What is mononeuropathy? |
Sensory disturbances and weaknesses in the distribution of the affected nerve. |
|
|
|
Name 2 peripheral nerve disorders that has impaired acetylcholine release from presynaptic nerve terminals. |
Eaton-Lambert syndrome and Botulism |
|
|
|
What is stocking-and-glove distribution? |
Loss of sensation and parasthesias starts in toes and spread upwards to fingers and hands. Polyneuropathies |
|

