![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
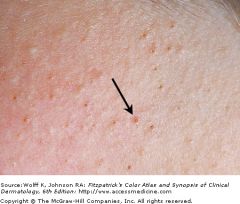
Acne vulgaris, the arrow is pointing to a comedone.
|
|
|
What is acne an inflammation of?
|
Acne is an inflammation of the pilosebaceous unit.
|
|
|
Describe the pathogenesis of acne.
|
Acne results from a change in the keratinisation pattern in the pilosebaceous unit, with the keratinous material becoming more dense and blocking secretion of sebum. These from keratin plugs, or comedones. Comedons interact with androgens and bacteria (P. acnes) to lead to inflammation. When the follicle walls break, the contents leak out onto the dermis and provoke an inflammatory response.
|
|
|
Why are androgens damaging in the pathogenesis of acne?
|
Androgens are damaging because they increase the production of serum. Androgens stimulate the pilosebaceous glands to produce more serum.
|
|
|
Why is bacteria damaging in the pathogenesis of acne?
|
Bacteria is damaging because it contains lipase, which converts lipid into fatty acids, which produce pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL1, TNF-alpha.
|
|
|
What are some contributory factors to acne? E.g. Drugs, and environmental.
|
Drugs: lithium (depression), glucocorticoids (inflammation), isoniazid (TB), oral contraceptives, androgens (e.g. testosterone).
Emotional stress can cause an outbreak, as can pressure on the skin (e.g. leaning the face on the hand). |
|
|
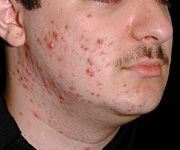
Papulopustular acne
|
|
|
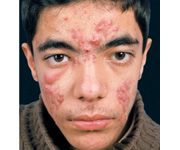
Nodulocystic acne.
Starts with comedones that turn into papulopustular lesions which enlarge and coalesce. Very painful. |
|
|
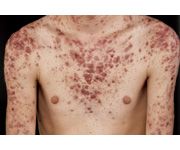
Acne conglobata. More involvement of the trunk than the face. There are coalescing nodules, cysts, abscesses and ulceration. Very painful.
|
|
|
In acne in an older woman (still pre-menopausal), what condition should be tested for? What tests would be done?
|
PCOS or hyperandrogenism.
Free testosterone, FSH, LH and DHEAS. |
|
|
When does acne flare?
|
Acne flares in the winter and with the onset of meses.
|
|
|
What is the recommended treatment for mild acne?
|
1. Topical antibiotics (e.g clindamycin), benzyl peroxide gels, and topic retionoids.
2. Oral antibiotics, e.g. doxycycline or in famels can use high doses of oral oestrogens combined with progesterone. 3. Systemic treatment with isotretinoin. |
|
|
How does isotretinion work? What does it inhibit?
|
this retinoid inhibits sebaceous gland function and keratinisation.
|
|
|
How long does it take for topical medications to work in the treatment of acne?
|
It takes about 2 months.
|
|
|
What cosmetics are best for acne sufferers?
|
The cosmetics should be oil-free and water-based.
|
|
|
What is the danger with isotretinoin?
|
It is teratogenic, so pregnancy must be prevented in girls. If used in combination with a tetracycline, it can cause benign intracranial swelling.
|
|
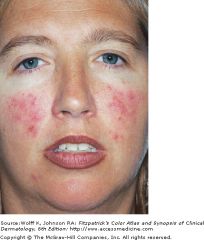
|
Rosacea.
|
|
|
What is... "A common chronic inflammatory acneiform disorder of the facial pilosebaceous units?
|
Rosacea
|
|
|
How common is rosacea? What age-group does it affect? which sex?
|
Rosacea affects approximately 10% of fair-skineed people. The age of onset is between 30 to 50 years. It is more common in females.
|
|
|
Rosacea: What is flushing?
|
Flushing is episodic reddening of the face with increases in skin temperature in response to heat stimuli, e.g. spicy food.
|
|
|
What are the common skin findings in acne rosacea?
|
Papules and pustules occur on the forehead, cheeks, nose and eyes.
Erythema and telangiectasia (engorged superficial blood vessels) are present. |
|
|
What is rhinophyma?
|
Chronic deep inflammation of the nose in acne rosacea can lead to rhinophyma.
|
|
|
What is the distribution of rosacea?
|
Symmetric localisation on the face. It is rarely on the neck, chest, back and scalp.
|
|
|
What are the ocular signs and symptoms with acne rosacea?
|
Ocular symptoms include mild conjunctivitis with soreness, grittiness and lacrimation.
Ocular signs include "red" eyes as a result of chronic blepharitis (inflammed eyelid), conjunctivitis and episcleritis. |
|
|
How is rosacea diagnosed? Are tests needed?
|
The diagnosis is usually made with clinical exam. If lesions are atypical, a bacterial culture is obtained to rule out folliculitis.
|
|
|
What are the differential diagnoses for acne rosacea?
|
Acne
Perioral dermatitis S.aureus follilculitis Lupus erythematous. |
|
|
Is rosacea acute or chronic?
|
The condition is chronic with episodes of activity followed by recurrence.
|
|
|
What factors should be avoided to prevent exacerbation of acne rosacea?
|
Hot food, hot drinks, wine, spicy foods, sunlight.
|
|
|
What is the treatment of acne rosacea?
|
1. Topical antibiotic or antiinflammatory agent. Metronidazole, sulphur.
2. Oral antibiotics, e.g. minocycline or doxycycline. 3. Tacroliumus 3. Laser treatment - reserved for bad rhinophyma or telangiectasia. |
|
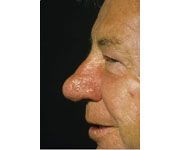
|
rhinophyma
|
|
|
What is a "distinctive scaly papular eruption around the mouth, nose and eyes that occurs almost exclusively in women?"
|
Perioral dermatitis
|
|
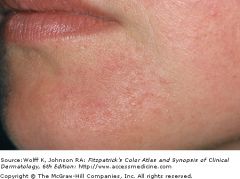
|
This is a picture of perioroal dermatitis. There is moderate involvement with early confluence of tiny papules and a few pustules in a perioral distibrution in young woman. Note typical scaring of the vermilion border (mucocutaneous junction).
|
|
|
What is the typical age of onset for perioral dermatitis?
|
The age of onset is 16 to 45 years. It can occur in children and the old.
|
|
|
What products aggravate perioral dermatitis?
|
Aggravated by topical potent fluorinated glucocorticoids, UB light, wind, heat, moisturisers with a petroleum or paraffin base.
|
|
|
What are the skin symptoms of perioral dermatitis?
|
Eruptions starts around the mouth, may involve perinasal and periocular regions.
May feel itchy, burning or tight. There are pinpoint papules and postules on a red and scaling base. There is a clear zone around the vermillion border. Pustules on the cheeks adjacent to the nostrils are common. |
|
|
Differential diagnoses of perioral dermatitis?
|
Acne
Rosacea Seborrheic dermatitis Atopic dermatitis Impetigo Demodex folliculitis (a mite infection) |
|
|
What is the course of perioral dermatitis?
|
It is usually a subacute persistent interruption that continues for months.
With oral treatment, most problems clear in four weeks. Relapse is common. |
|
|
what is the treatment for perioral dermatitis?
|
Topical - not super effective. Metronidazole cream, sulfur, erythromycine, etc. AVOID TOPICAL GLUCOCORTICOIDS as these will exacerbate or worse, induce steroid-acne.
Oral antibiotics are used if a 4 - 6 week course of topical treatment fails. Tetraccline, erythromycine, doxycycline or minocycline. Once the condition is resolved, the antibiotic is stopped over 4 -5 weeks. |
|
|
What is... "a chronic recurring disorder of the follicular unit, which produces extremely painful, deep-seated nodules, cysts, sinus tracts and scars in the apocrine gland-bearing areas of the body, including the axillae, inguingal and anogenital regions?"
|
Hidradenitis suppurativa
|
|
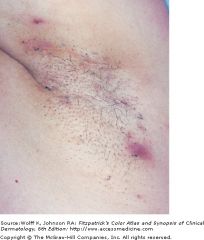
|
a disease of gland bearing skin
It presents wit extremely painful and recurrent "boils" that rupture to form sinus tracts and scars |
|
|
What is the distribution of Hidradenitis suppurativa?
|
Axillary and inguinal involvement in females.
Perianal and buttock involvement in males. |
|
|
What is the age of onset of hidradenitis suppuritava?
|
It usually does not appear until after puberty, most cases appear in the second and third generations of life.
|
|
|
What are the skin findings?
|
The skin findings of hidradenitis suppurativa is that of a double comedone , which is a blackhead with two orm ore openings the communicate under the skin.
There are also pink red nodules which are rounded without central necrosis, and extensive, deep, dermal inflmaation resulting in large painful malodorous abscesses. Sinus tracts can form. |
|
|
What tests should be done and what is the expected results?
|
A biopsy should be done, and culture. Various patholgens may colonise the lesion, e.g. s. aureus or p. aeruginosa.
|
|
|
Differential diagnoses of hidradenitis suppurativa include...?
|
Acne
Furuncle Infected bartholin's gland pilonidal cyst chron's disease |
|
|
What is the course of hidradenitis suppurativa?
|
Most patients have only mild involvement with recurrent, self-healing tender red nodules. It is often active for about 20 years, and complete remission is usual after menopause.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa?
|
Hidradenitis suppurativa is not simply an infection, and systemic antibiotics are only part of the treatment program. Combinations of (1) intralesional glucocorticoids, (2) surgery, (3) oral antibiotics, and (4) isotretinoin are used.
|

