![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
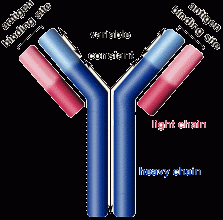
Antibody : Any of a large variety of proteins normally present in the body or produced in response to an antigen which it neutralizes, thus producing an immune response |
|
|
|
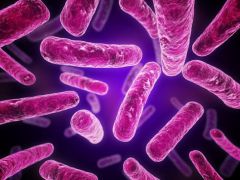
Bacteria : Microscopic, single celled organisms |
|
|
|
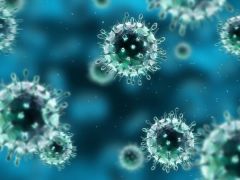
Disease : Anything that causes our body to stop working properly |
|
|
|
Pathogen : An organism that causes disease |

|
|
|
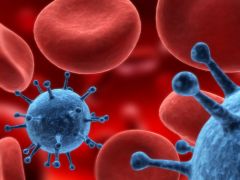
Virus : A pathogen about one hundred times smaller than a bacterium |
|
|
|
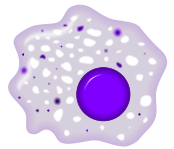
Macrophage : A white blood cell that consumes pathogens and is found in the lymph nodes |
|
|
|
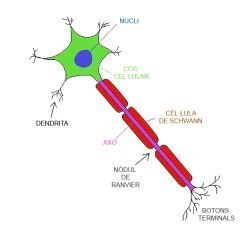
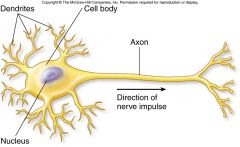
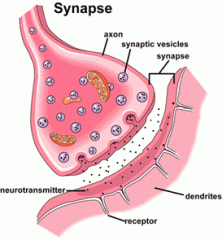
Axon : A nerve fibre that sends nerve impulses away from the cell body
|
|
|
|
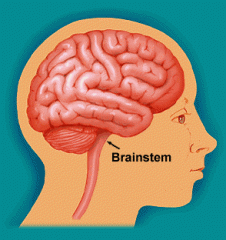
Brain stem : Part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull; it controls the body's vital functions, such as breathing, blood pressure and heart rate |
|
|
|
Cell body : The part of the neurone that contains the nucleus |
|
|
|
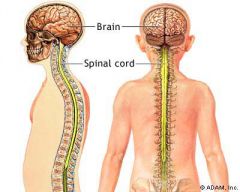
Central nervous system : The brain and the spinal cord |
|
|
|
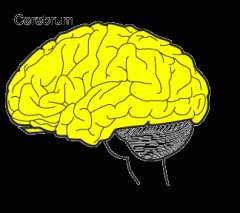
Cerebrum : Part of the brain that controls conscious thoughts, controls the movement of every body part, and receives sensory messages from each body part |
|
|
|
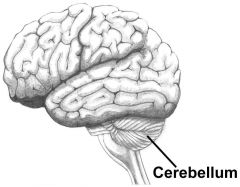
Cerebellum : Part of the brain that is responsible for coordination and balance |
|
|
|
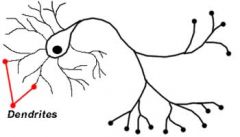
Dendrites : Branches from the cell body that receive messages from other neurones |
|
|
|
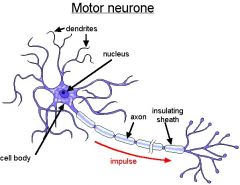
Motor neurones : Nerve cells that carry messages from the CNS |
|
|
|
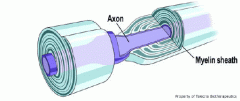
Myelin sheath : The insulating layer that covers a neurone |
|
|
|
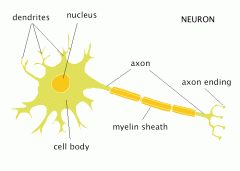
Neurone : A nerve cell |
|
|
|
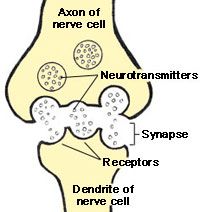
Neurotransmitter : A chemical message released at the end of an axon to be received by the next neurone's dendrites |
|
|
|
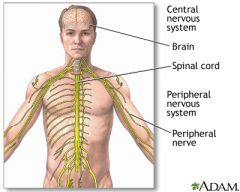
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) : The nerves that carry message to and from the central nervous system and other parts of the body
|
|
|
|
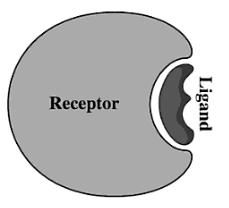
Receptor : Special cells that detect stimuli |
|
|
|
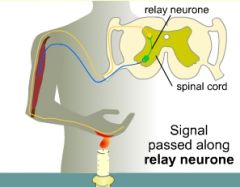
Reflex actions : Quick, automatic actions that protect the body from danger; they are also known as reflexes |
|
|
|
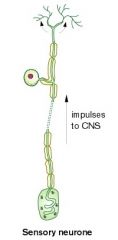
Sensory neurones : Nerve cells that carry messages from cells in the sense organs to the CNS |
|
|
|
Synapse : The space between two neurones |
|
|
|
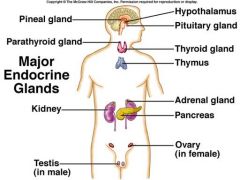
Endocrine glands : Glands that produce hormones |
|
|
|
Insulin : Hormone produced in the pancreas that causes the liver and muscles to extract glucose from the bloodstream and store it in the liver and muscles |
|
|
|
Target cell : The cells on which a hormone acts |
|
|
|
Hormone : Chemical substances that act as messengers in the body |

|
|
|
Vaccine : A chemical that causes your body to react as if it had encountered a pathogen |
|

