![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidemiology |
Corynebacterium diphtheria Aerobic gram-positive Easily cultured Produces diphtheria toxin – can cause visceral toxicity (myocarditis, demyelination, acute tubular necrosis) Only affects affects humans – carriage can be asymptomatic (spread by respiratory droplet) Endemic in Asia and Africa Vaccine preventable |
|
|
Clinical presentation |
Typically in childhood Incubation – few days Hallmark feature – grey white pseudomembrane (adherence to underlying tissue and bleeds when pulled away) Faucial diphtheria is most common – fever/sore throat, pseudomembrane, lymphadenopathy, foul odour Can progress to tracheo-laryngeal diphtheria which can cause tracheal obstruction/stridor Malignant diphtheria is most severe – rapid progression and bulls neck appearance (rapid extension of pseudomembrane). Rapid cardiac involvement leading to heart block Cutaneous diphtheria causes skin lesions/ulcers – usually chronic but mild |
|
|
Differential diagnoses |
Strep throat Tonsillitis EBV Mumps |
|
|
Diagnosis |
Culture from mucosal lesions |
|
|
Treatment |
Penicillin or macrolides for two weeks Confirm elimination of diphtheria before treatment cessation Diphtheria antitoxin Vaccination (DTP3 in babies x3 with booster doses in childhood) Isolation of suspected cases and immunisation of close contacts Treatment may require intensive care support |
|
|
Prevention outbreak |
Prompt diagnosis Isolation Household prophylaxis Immunisation |
|
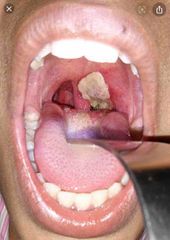
Front (Term) |
Diphtheria pseudo membrane |

