![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
temporary/deciduous teeth
|
Incisors
Canines Premolars |
|
|
permanent teeth only
|
molars
|
|
|
dental formula
|
Describes the number of each type of tooth in ONE SIDE of the upper and lower dental arcade of a specific species
|
|

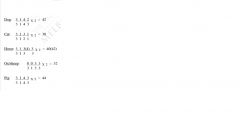
write dental formula for the following
|
|
|
|
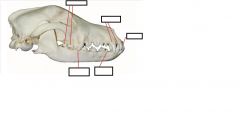
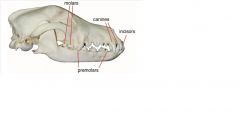
dog dentition
|
adapted for attacking pretty, tearing food, crushing bones. Food does not remain in the mouth long before it is swallowed
|
|
|
cat dentition
|
- almost no crushing teeth- fewer molars and premolars
|
|
|
carnivore incisors
|
Sharp when first erupt
Tricuspid (three bumps on occlussal surface), loss of definition with age Sharp for holding and tearing Single root |
|
|
carnivore canines
|
Weapons for attack and defense
Root much longer than crown |
|
|
carnivore premolars/molars
|
Cutting food, crushing bones
Only occlude caudually ( cannot grind) P1 upper and lower – one root Upper P2 and P3 and rest of lower cheek teeth- 2 roots Rest of upper teeth (i.e. P4, M1, M2)- 3 roots Divide crown before extraction |
|
|
Upper P4, Lower M4 in carnivores known as
|
CARNASSIAL TEETH
Rostrally sharp for cutting Causally flat for crushing Upper carnassials often infected due to crown damage |
|
|
horse canines
|
Most mares have no or not all canines erupt
Lie in diastema ( space between incisors and check teeth) No real function |
|
|
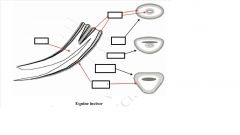
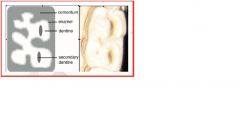
horse incisors
|
CONTINOUS GROWTH OF ROOTS, CONTINUOUS ERUPTION COMPENSATING FOR WEAR
Cement outside enamel Enamel not continuous over occlusal (grinding surface)- exposure of dentine Pulp cavity- appears and age ( filled with secondary dentine) |
|
|
INFUNDIBLUM-
|
mark, disappears with age
|
|
|
horse cheek teeth
|
Rest of M and P form continuous flat grinding surface
ERUPT CONTINUOUSLY Convoluted enamel pattern on table Abrasive enamel ridges due to different rates of wear and tear of enamel compared with dentine and Cementum No continuous covering of enamel on table Cementum around crown |
|
|
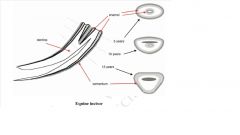
PI in horses
|
wolf tooth ( only present in some animals) and not replaced
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
ox/sheep incisors and canines
|
No upper incisors or canines- replaced by hard fibrous DENTAL PAD
Trap food and tear by head movement NO continuous eruption Lower canines identical to incisors |
|
|
ox/sheep cheek teeth
|
Increase in size from rostral to causal
Similar to horse- CONTINUOUS ERUPTION Arrangement of enamel ridges slightly different from horse, enamel stands out more. |
|
|
pig incisors
|
Lower one project forward for digging
|
|
|
pig canines
|
tusks
Erupt continuously in boars Used for tearing ( directed laterally) |
|
|
pig cheek teeth
|
For crushing and grinding, rounded cusps
NO continuous eruption |
|
|
rodent/rabbits canines
|
have none
|
|
|
rodent/rabbits incisors
|
Enamel rostrally only- sharp chisel shaped
grow continuously no pulp cavity- insensitive- can be clipped if malformation occurs due to improper occlusion |

