![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
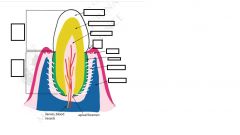
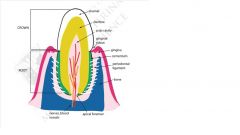
enamel
|
Crown only
Synthesized by AMELOBLASTS- found on surface but lost after eruption Hardest biological material Mineralized extracellular matrix proteins specific to enamel |
|
|
Dentine
|
Majority of hard material in tooth
Yellowish in color COONTINUOUS slow production by ODONTOBLAST Secondary dentine is darker and slightly reddish Innervations Fine nerve processes from dental pulp into dentine Mineralized extracellular matrix similar to bone NO CELLS EMBEDDED IN DENTINE |
|
|
cementum
|
Surrounds dentine of root
SOME CELLS (CEMENTOBLASTS) EMBEDDED IN CEMENTUM Not as readily degraded s cone Mineralized extracellular matrix similar to bone Dental pulp C0nnective tissue with a lot of blood vessels Nerves ( some sensory others regular blood vessel diameter) Superior and inferior alveolar arteries, veins and nerves though jaws |
|
|
Superior alveolar nerves from
|
MAXILLIARY BRANCH OF TRIGEMINAL NERVE
|
|
|
Inferior alveolar nerves from
|
MANIBULAR BRANCH OF TRIGEMNIAL NERVE
|
|
|
The trigeminal nerve is
|
the cranial nerve that supplies sensory innervations to most structures of the head
|
|
|
alveolus
|
Socket in bone (alveolar bone)
Follows shape of root (often branched) Periodontal ligament Continue ligament structure Ligament suspends tooth in alveolus Fibers run from bone to Cementum, direct towards apex of tooth Fibers insert in alveolar bone and Cementum |
|
|
gingiva
|
Adherent to tooth at root/drown interface forming GINGIVAL SULCUS (groove between gingival and tooth)
Very important to prevent periodontal disease Compromised of epithelium and connective tissue |

