![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a. What are the 2 parts of the Digestive sytem? b. Name 4 Structures in each |
a. Alimentary Canal and Associated Organs b. Alimentary: mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine Organs: teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver, pancreas |
|
|
What are the 6 digestive processes? + describe |
1. Ingestion taking food into digestive tract via the mouth 2. Propulsion movement along the digestive tract (swallowing/peristalsis) 3. Mechanical Digestion chewing, mixing with Saliva, churning in stomach, segmentation 4. Chemical Digestion Enzymatic, beginning in mouth + ending in small intestine 5. Absorption mainly in small intestine 6. Defecation elimination of indigestible substances |
|
|
Name the 4 muscles involved in Mastification |
1. Temporalis 2. Masseter 3. Medial Pterygoid 4. Lateral Pterygoid |
|

|
a. Temporalis b. Masseter c. Lateral Pterygoid d. Medial Pterygoid |
|
|
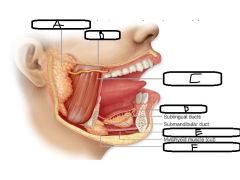
a. Name the 3 extrinsic salivary glands b. Name the intrinsic salivary gland c. Where is the intrinsic salivary gland found? |
a. - Parotid gland - Submandibular gland - Sublingual gland b. Buccal gland c. Scattered throughout oral cavity Mucosa |
|
|
a. Parotid gland b. Parotid duct c. Masseter d. Mucosa e. Sublingual gland f. Submandibular gland |
|
|
a. What is the pH range for Vinegar, Cola, Wine and Citrus Juice? b. What happens in the mouth if anything under a pH of 4 is consumed? |
a. 2-3 pH b. - Demineralisation - Anything under pH 4 dissolves the Calcium Phosphate in tooth Enamel |
|
|
a. Which chemical does Saliva contain that helps heal damage to the mouth quickly? b. Why can a cold not be passed on by drinking from the same glass as a person who is suffering from a cold? |
a. Histamine b. Because Saliva is an Antiviral |
|
|
a. What is another name for swallowing? b. What are the 2 phases of swallowing? c. Which phase is involuntary? |
a. Deglutition b. - Buccal phase - Pharyngeal-Oesophageal phase c. Pharyngeal-Oesophageal phase |
|
|
Swallowing: a. describe what happens in the Buccal phase b. describe what happens in the Pharyngeal-Oesophageal phase |
a. Tongue passes bolus into Pharynx b. - Tongue blocks mouth - Ulva blocks Nasopharynx |
|
|
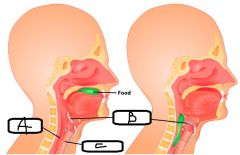
a. Which specific structure blocks food from entering the respiratory system? b. What happens when we swallow? c. What happens when anything other than air enters the Larynx? |
a. Epiglottis b. - During swallowing, the Larynx is pulled superiorly - This tips the free edge of the Epiglottis inferiorly to cover the Laryngeal outlet c. Cough reflex is triggered |
|
|
a. Oesophagus b. Epiglottis c. Larynx |
|
|
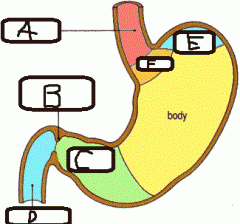
- The Oesophagus is a __(a)__ tube which is __(b)__cm long - It is __(c)__ when food is not in propulsion - It joins the Stomach at __(d)__ |
a. Muscular b. 25 (cm) c. Collapsed d. Cardiac Orifice |
|
|
a. Oesophagus b. Pyloric Sphincter c. Pyloric Canal d. Duodenum e. Fundus f. Cardiac Orifice |
|
|
a. Where is the Stomach located? b. What occurs in the Stomach? c. How long does food generally stay in the Stomach? |
a. Upper left quadrant of the Abdominopelvic cavity b. - Chemical breakdown of Proteins begin - Food is turned into Chyme (juice) c. 4-6 hours |
|
|
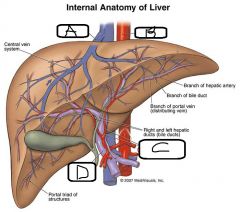
- Liver: a. Location b. Functions |
a. Left and Right upper quadrents of abdominopelvic cavity (mainly right) b. - Metabolism (Carbs, Fats, Proteins) - Vitamin/mineral storage - Excretes Bile for export to Duodenum |
|
|
a. Hepatic Vein b. Aorta c. Right + Left Hepatic Arteries d. Portal Vein |
|
|
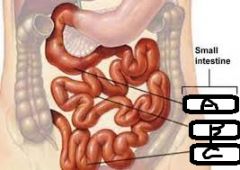
a. Name the 3 parts of the small intestine b. What are the 2 ends of the small intestine? c. What are the associated organs of the small intestine? |
a. - Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum b. - Pyloric Sphincter (Stomach) - Ileocecal Valve c. - Gallbladder - Pancreas |
|
|
What is the percentage of the total length of the small intestin of the following + describe: a. Duodenum b. Jejunum c. Ileum d. Where does the Ileum end? |
a. 5% ... Short segment which recieves digestive enzymes from: Pancreas, Gallbladder + Liver b. 40% ... Less vascularised than Ileum c. 60% ... Longest, most distal section d. At the Ileocecal valve |
|
|
a. Duodenum b. Jejunum c. Ileum |
|
|
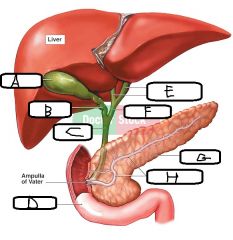
a. Gall Bladder b. Cystic Duct c. Common Bile Duct d. Duodenum e. left/right Hepatic Ducts f. Common Hepatic Duct g. Pancreas h. Pancreatic Duct |
|
|
Give 3 functions of the Gall Bladder |
- Storage of Bile from the Liver, until digestion - Concentration of Bile (up to x10), removing water and ions - Expels Bile to Cystic Duct>Bile Duct>Duodenum (Where bile is used to digest fats) |
|
|
a. What does the Pancreas do? b. Describe how Pancreatic Juice gets from Pancreas to Small Intestine |
a. Produces enzymes (Pancreatic Juice) b. PJ collects drains via Main Pancreatic Duct, which fuses with Bile Duct as it enters the Duodenum |
|
|
a. Which structures are at the ends of the Large Intestine (colon)? b. What are the 5 components of the Large Intestine? c. Very little digestion occurs in the Colon, what kind of digestion occurs? d. Primary function of Colon? |
a. - Ileocecal valve - Anus b. - Cecum - Appendix - Colon - Rectum - Anal Canal c. Digestion by Enteric Bacteria d. Elimination of faecal matter |
|

|
a. Transverse Colon b. Descending Colon c. Sigmoid Colon d. Anal Canal e. Rectum f. Appendix g. Cecum h. Ascending Colon |

